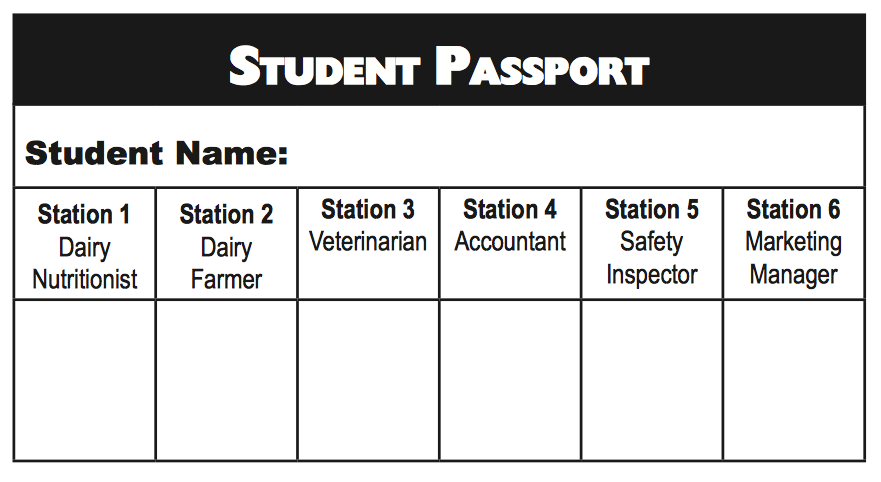
Milk Makin' Math
Students explore the numerous career opportunities involved in the dairy industry and solve real world math problems related to specific careers within the industry.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Mandi Bottoms | California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom
Acknowledgements
This lesson was funded in 2008 by the California Milk Advisory Board and the California Farm Bureau Federation. To meet the needs of California educators, Milk Matters: Discovering Dairy was created to meet the Curriculum Content Standards for California Public Schools. The unit also includes a collection of relevant resources about the dairy industry.
Executive Director: Judy Culbertson
Layout and Design: Imelda Muziom
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.4
Geography. The student understands the concepts of location, distance, and direction on maps and globes. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14.D: interpret and create visuals, including graphs, charts, tables, timelines, illustrations, and maps
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.2
Numbers and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent and compare whole numbers and understand relationships related to place value.
- Math: 3.111.5.b.2.C: represent a number on a number line as being between two consecutive multiples of 10; 100; 1,000; or 10,000 and use words to describe relative size of numbers in order to round whole numbers
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent and explain fractional units.
- Math: 5.111.7.b.3.K: add and subtract positive rational numbers fluently
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 4.111.6.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
- Math: 4.111.6.b.1.B: use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan or strategy, determining a solution, justifying the solution, and evaluating the problem-solving process and the reasonableness of the solution
- Math: 4.111.6.b.1.D: communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 4.111.6.b.4.H: solve with fluency one- and two-step problems involving multiplication and division, including interpreting remainders
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.8
Geometry and measurements. The student applies mathematical process standards to select appropriate customary and metric units, strategies, and tools to solve problems involving measurement.
- Math: 4.111.6.b.8.C: solve problems that deal with measurements of length, intervals of time, liquid volumes, mass, and money using addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division as appropriate
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 5.111.7.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
- Math: 5.111.7.b.1.B: use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan or strategy, determining a solution, justifying the solution, and evaluating the problem-solving process and the reasonableness of the solution
- Math: 5.111.7.b.1.D: communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.16
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.16.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.22
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.22.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.26
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.26.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.4.B: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.4.B: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.4.B: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others by following agreed-upon rules, norms, and protocols
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 3.111.5.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
- Math: 3.111.5.b.1.B: use a problem-solving model that incorporates analyzing given information, formulating a plan or strategy, determining a solution, justifying the solution, and evaluating the problem-solving process and the reasonableness of the solution
- Math: 3.111.5.b.1.D: communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy. The student is expected to:
- Math: 3.111.5.b.4.B: round to the nearest 10 or 100 or use compatible numbers to estimate solutions to addition and subtraction problems
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.5
Algebraic reasoning. The student applies mathematical process standards to analyze and create patterns and relationships. The student is expected to:
- Math: 3.111.5.b.5.A: represent one- and two-step problems involving addition and subtraction of whole numbers to 1,000 using pictorial models, number lines, and equations
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.2
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent, compare, and order whole numbers and decimals and understand relationships related to place value. The student is expected to:
- Math: 4.111.6.b.2.D: round whole numbers to a given place value through the hundred thousands place
- Math: 4.111.6.b.2.G: relate decimals to fractions that name tenths and hundredths
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.2
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent, compare, and order positive rational numbers and understand relationships as related to place value. The student is expected to:
- Math: 5.111.7.b.2.C: round decimals to tenths or hundredths
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for positive rational number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy. The student is expected to:
- Math: 5.111.7.b.3.A: estimate to determine solutions to mathematical and real-world problems involving addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division
- Math: 5.111.7.b.3.E: solve for products of decimals to the hundredths, including situations involving money, using strategies based on place-value understandings, properties of operations, and the relationship to the multiplication of whole numbers
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.A: decompose story problems into smaller, manageable subproblems and identify a solution to the problems
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.C: develop a plan collaboratively and document a plan that outlines specific steps taken to complete a project
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.5
Data literacy, management, and representation--collect data. The student uses digital strategies to collect and identify data. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.5.A: identify and collect numerical data such as the price of goods or temperature
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences.
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.A: decompose story problems into smaller, manageable subproblems and discuss and document various solutions to the problems
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.C: communicate design plans and solutions using a variety of options
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question.
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1.A: decompose a real-world problem into smaller, manageable subproblems using graphic organizers such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions.
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions