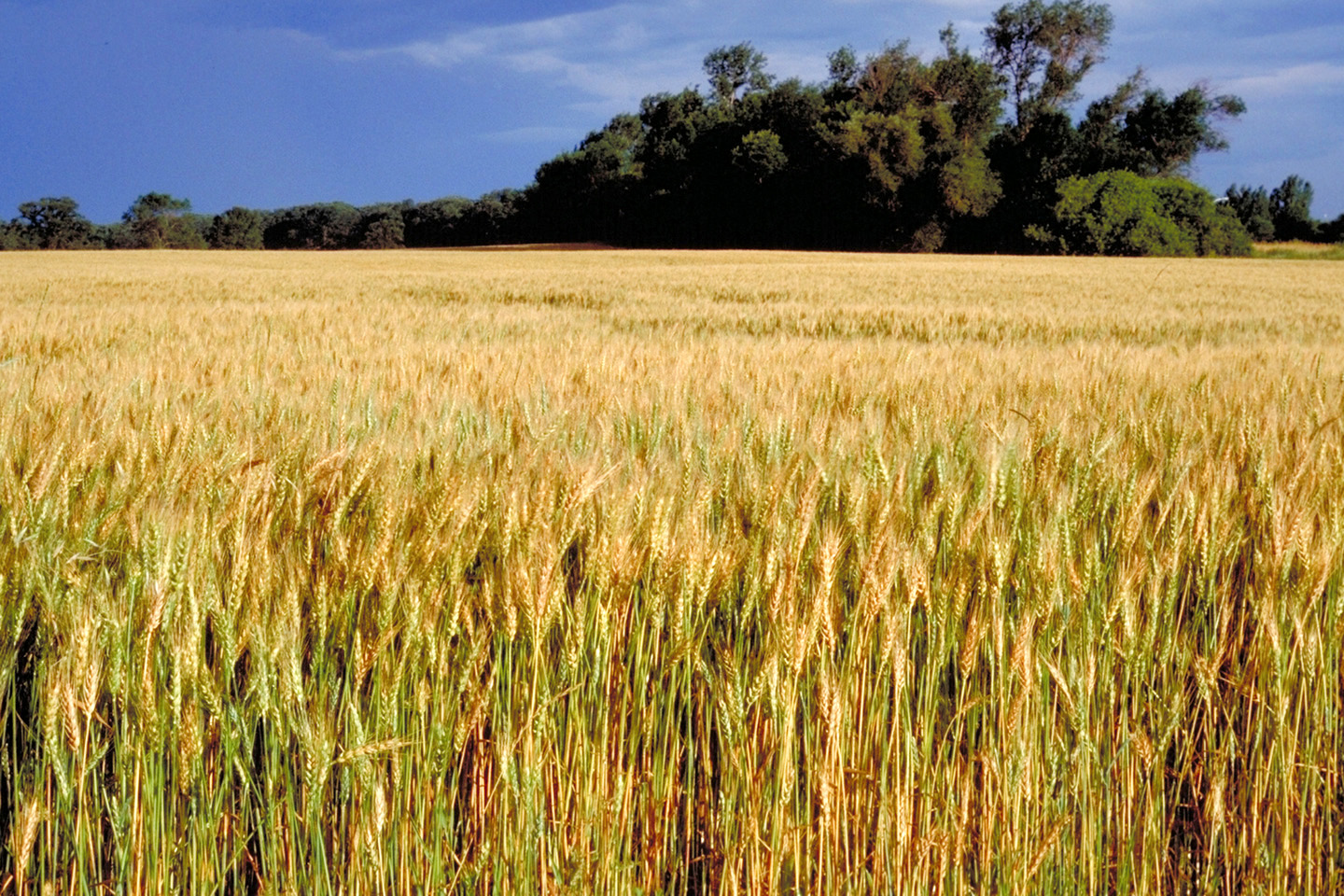
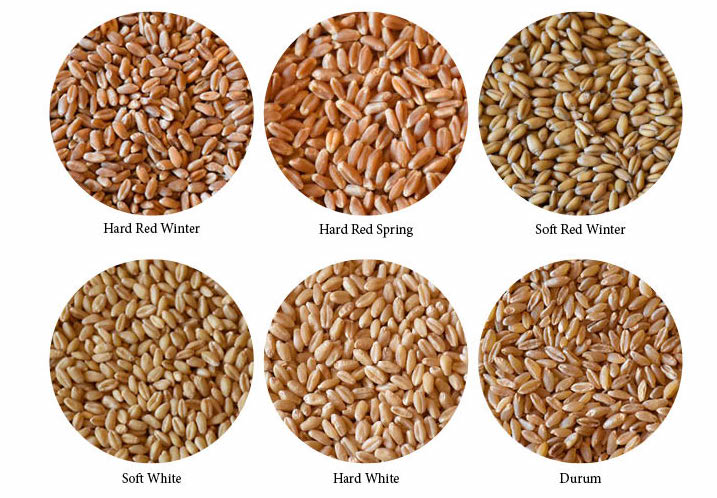
Wheat Germ DNA
Using wheat as an example, students explore how DNA determines the genetic traits of a plant and how plant breeders change the DNA of a plant to produce desired characteristics.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
St. Louis Science Center, Serita Blankenship, KS Farm Bureau; Cathy Musick, Kansas Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom; Lynn Wallin | Kansas Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Green_Revolution
- http://www.idahowheat.org/education/wheat-facts.aspx
- http://www.dimpflmeierbakery.com/five-fun-facts-wheat/
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 3.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 3.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 3.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
- ELA: 3.6.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as re-reading, using background knowledge, asking questions, and annotating when understanding break downs.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 3.7.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.1.D: The student is expected to work collaboratively with other to develop a plan of shared responsibilities.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 4.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 4.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 4.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
- ELA: 4.6.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as re-reading, using background knowledge, asking questions, and annotating when understanding break downs.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 4.7.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 5.1.D: The student is expected to work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 5.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 5.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 5.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
- ELA: 5.6.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as re-reading, using background knowledge, asking questions, and annotating when understanding break downs.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 5.7.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
-
Science: 3.112.14.b.1
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student conducts classroom and outdoor investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate practices.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.1.A: The student is expected to demonstrate safe practices as described in Texas Education Agency- approved safety standards during classroom and outdoor investigations using safety equipment as appropriate, including safety goggles or chemical splash goggles, as appropriate, and gloves.
-
Science: 3.112.14.b.4
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.4.A: The student is expected to collect, record, and analyze information using tools, including cameras, computers, hand lenses, metric rulers, Celsius thermometers, wind vanes, rain gauges, pan balances, graduated cylinders, beakers, spring scales, hot plates, meters sticks, magnets, collecting nets, notebooks, and Sun, Earth, and Moon system modes; timing devices; and materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums and aquariums.
-
Science: 4.112.15.b.1
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student conducts classroom and outdoor investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate practices.
- Science: 4.1.A: The student is expected to demonstrate safe practices as described in Texas Education Agency- approved safety standards during classroom and outdoor investigations using safety equipment, including safety goggles or chemical splash goggles, as appropriate, and gloves, as appropriate.
-
Science: 4.112.15.b.4
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry.
- Science: 4.4.A: The student is expected to collect, record, and analyze information using tools, including cameras, computers, hand lenses, metric rulers, Celsius thermometers, wind vanes, rain gauges, pan balances, graduated cylinders, beakers, spring scales, hot plates, meters sticks, magnets, collecting nets, notebooks, and Sun, Earth, and Moon system modes; timing devices; and materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums and aquariums.
-
Science: 5.112.16.b.1
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student conducts classroom and outdoor investigations following home and school safety procedures and environmentally appropriate practices.
- Science: 5.1.A: The student is expected to demonstrate safe practices as described in Texas Education Agency- approved safety standards during classroom and outdoor investigations using safety equipment, including safety goggles or chemical splash goggles, as appropriate, and gloves, as appropriate.
-
Science: 5.112.16.b.4
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student knows how to use a variety of tools and methods to conduct science inquiry.
- Science: 5.4.A: The student is expected to collect, record, and analyze information using tools, including cameras, computers, hand lenses, metric rulers, Celsius thermometers, wind vanes, rain gauges, pan balances, graduated cylinders, beakers, spring scales, hot plates, meters sticks, magnets, collecting nets, notebooks, and Sun, Earth, and Moon system modes; timing devices; and materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums and aquariums.
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.13
Science, technology, and society. The student understands how individuals have created or invented new technology and affected life in various communities, past and present. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.13.A: identify individuals who have discovered scientific breakthroughs or created or invented new technology such as Jonas Salk, Cyrus McCormick, Bill Gates, Louis Pasteur, and others
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14.C: interpret oral, visual, and print material by sequencing, categorizing, identifying the main idea, distinguishing between fact and opinion, identifying cause and effect, comparing, and contrasting
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15.D: express ideas orally based on knowledge and experiences
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.16
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.16.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19.C: analyze information by applying absolute and relative chronology through sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions;
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.22
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the impact of science and technology on society in the United States. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.22.A: identify the accomplishments of notable individuals in the fields of science and technology such as Benjamin Franklin, Eli Whitney, John Deere, Thomas Edison, Alexander Graham Bell, George Washington Carver, the Wright Brothers, and Neil Armstrong
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23.C: analyze information by applying absolute and relative chronology through sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.C: demonstrate safe practices and the use of safety equipment during classroom and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.D: use tools, including hand lenses; metric rulers; Celsius thermometers; wind vanes; rain gauges; graduated cylinders; beakers; digital scales; hot plates; meter sticks; magnets; notebooks; Sun, Earth, Moon system models; timing devices; materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums, aquariums, and collecting nets; and materials to support digital data collection such as computers, tablets, and cameras, to observe, measure, test, and analyze information
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.D: use tools, including hand lenses; metric rulers; Celsius thermometers; calculators; laser pointers; mirrors; digital scales; balances; graduated cylinders; beakers; hot plates; meter sticks; magnets; notebooks; timing devices; sieves; materials for building circuits; materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums, aquariums, and collecting nets; and materials to support digital data collection such as computers, tablets, and cameras, to observe, measure, test, and analyze information
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1C: demonstrate safe practices and the use of safety equipment during classroom and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.C: demonstrate safe practices and the use of safety equipment during classroom and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.D: use tools, including calculators, microscopes, hand lenses, metric rulers, Celsius thermometers, prisms, concave and convex lenses, laser pointers, mirrors, digital scales, balances, spring scales, graduated cylinders, beakers, hot plates, meter sticks, magnets, collecting nets, notebooks, timing devices, materials for building circuits, materials to support observations of habitats or organisms such as terrariums and aquariums, and materials to support digital data collection such as computers, tablets, and cameras to observe, measure, test, and analyze information