Nuts About Peanuts!
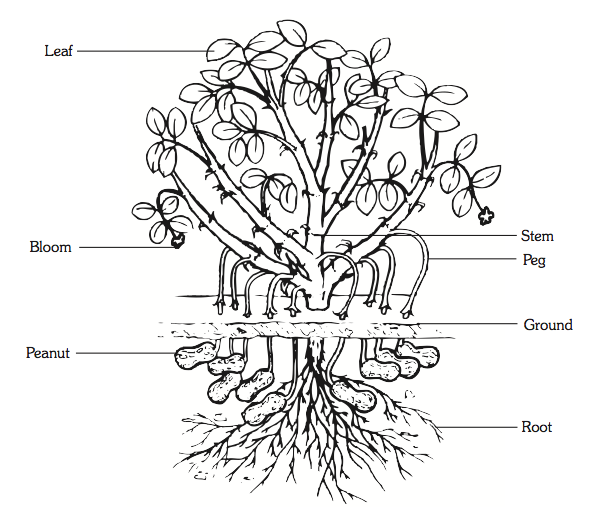
Students label the parts of a peanut plant on a diagram, follow step-by-step instructions to plant a peanut, and use a chart to record the growth of peanut plants.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Debra Spielmaker | Utah Agriculture in the Classroom
Acknowledgements
Information from American Peanut Council’s “No-Nut Peanut” a teachers kit for grades 3-5. Reprinted with permission from American Peanut Council.
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.6.E: The student is expected to make connections to personal experiences, ideas in other texts, and society.
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.8
Geography. The student understands how people adapt to and modify their environment. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.8.A: describe ways people have adapted to and modified their environment in Texas, past and present, such as timber clearing, agricultural production, wetlands drainage, energy production, and construction of dams
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 4.111.6.b.1.D: communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 5.111.7.b.1.D: communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.1
History. The student understands how individuals, events, and ideas have influenced the history of various communities. The student is expected to
- 113.14.c.1.A: describe how individuals, events, and ideas have changed communities, past and present
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.18
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the impact of science and technology on life in Texas. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.18.B: describe how scientific discoveries and innovations such as in aerospace, agriculture, energy, and technology have benefited individuals, businesses, and society in Texas
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.22
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the impact of science and technology on society in the United States. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.22.A: identify the accomplishments of notable individuals in the fields of science and technology such as Benjamin Franklin, Eli Whitney, John Deere, Thomas Edison, Alexander Graham Bell, George Washington Carver, the Wright Brothers, and Neil Armstrong
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.F: construct appropriate graphic organizers to collect data, including tables, bar graphs, line graphs, tree maps, concept maps, Venn diagrams, flow charts or sequence maps, and input-output tables that show cause and effect
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.F: construct appropriate graphic organizers to collect data, including tables, bar graphs, line graphs, tree maps, concept maps, Venn diagrams, flow charts or sequence maps, and input-output tables that show cause and effect
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.F: construct appropriate graphic organizers used to collect data, including tables, bar graphs, line graphs, tree maps, concept maps, Venn diagrams, flow charts or sequence maps, and input-output tables that show cause and effect
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.1.A: listen actively, ask relevant questions to clarify information, and make pertinent comments
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.7.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.1.A: listen actively, ask relevant questions to clarify information, and make pertinent comments
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.6.E: make connections to personal experiences, ideas in other texts, and society
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.7.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 3.111.5.b.1.D: communicate mathematical ideas, reasoning, and their implications using multiple representations, including symbols, diagrams, graphs, and language as appropriate