Edible Numbers
Students develop a working vocabulary regarding food, categorize foods by their sources, examine grocery ads, learn about food production, and apply what they learned by analyzing foods they eat at a particular meal.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Pamela Emery and Gina Hieb | California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom
Acknowledgements
The development of this lesson was funded by the California Beef Council and the California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom. To meet the needs of California educators and students, Edible Numbers was revised to support the curriculum Content Standards for California Public Schools and updated to include current statistics. Funding from the California Farm Bureau Federation and private donations made this revision possible.
Illustrators: Jack Armstrong, Joanne Borovoy, Karen Holtman, Pat Houk, and Ann Rogers
Layout and Design: Nina Danner
Sources
- http://www.agfoundation.org/resources/food-and-farm-facts-2017
- http://www.wisoybean.org/news/soybean_facts.php
- https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/dairy-data/
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Health Education: 3.115.5.b.1
Health behaviors. The student explains ways to enhance and maintain health throughout the life span.
- Health Education: 3.1.C: The student is expected to identify types of nutrients.
-
Health Education: 4.115.6.b.1
Health information. The student recognizes ways to enhance and maintain health throughout the life span.
- Health Education: 4.1.B: The student is expected to identify information on menus and food labels.
-
Health Education: 5.115.7.b.1
Health information. The student knows ways to enhance and maintain personal health throughout the life span.
- Health Education: 5.1.A: The student is expected to examine and analyze food labels and menus for nutritional content.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.11
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts- writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and uses appropriate conventions.
- ELA: 3.11.D.i: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: The student is expected to complete simple and compound sentences with subject-verb agreement.
- ELA: 3.11.D.ii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: past, present, and future verb tense.
- ELA: 3.11.D.iii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: singular, plural, common, and proper nouns.
- ELA: 3.11.D.iv: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: adjectives, including their comparative and superlative forms.
- ELA: 3.11.D.ix: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: capitalization of official titles of people, hoidays, and geographical names and places.
- ELA: 3.11.D.v: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: adverbs that convey time and adverbs that convey manner.
- ELA: 3.11.D.vi: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: prepositions and prepositional phrases.
- ELA: 3.11.D.vii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: pronouns, including subjective, objective, and possessive cases.
- ELA: 3.11.D.vii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: coordinating conjunctions to form compound subject, predicates, and sentences.
- ELA: 3.11.D.x: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: punctuation marks, including apostrophes in contractions and possessives and commas in compound sentences and items in a series.
- ELA: 3.11.D.xi: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions, including: correct spelling of words with grade appropriate orthographic patterns and rules and high frequency words.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.1.D: The student is expected to work collaboratively with other to develop a plan of shared responsibilities.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.11
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts- writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and uses appropriate conventions.
- ELA: 4.11.D: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions
- ELA: 4.11.D.i: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: complete simple and compound sentences with subject-verb agreement and avoidance of splices, run-ons, and fragments.
- ELA: 4.11.D.ii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: past tense or irregular verbs.
- ELA: 4.11.D.iii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: singular, plural, common, and proper nouns.
- ELA: 4.11.D.iv: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: adjective, including their comparative and superlative forms.
- ELA: 4.11.D.ix: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: capitalization of historical periods, events, and documents; titles of books; stories and essays; and languages, races, and nationalities.
- ELA: 4.11.D.v: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: adverbs that convey frequency and adverbs that convey degree.
- ELA: 4.11.D.vi: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: prepositions and prepositional phrases.
- ELA: 4.11.D.vii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: pronouns, including reflexive.
- ELA: 4.11.D.viii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: coordinating conjunctions to form compound subjects, predicates, and sentences.
- ELA: 4.11.D.x: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: punctuation marks, including apostrophes in possessives, commas in compound sentences, and quotation marks in dialogue.
- ELA: 4.11.D.xi: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: correct spelling of words with grade-appropriate orthographic patterns and rules and high-frequency words.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.12
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts- genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful.
- ELA: 4.12.B: The student is expected to compose information texts, including brief compositions that convey information about a topic, using a clear central idea and genre characteristics and craft.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 5.1.C: The student is expected to give an organized presentation employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, natural gestures, and conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively.
- ELA: 5.1.D: The student is expected to work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.11
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts- writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and uses appropriate conventions.
- ELA: 5.11.D: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions.
- ELA: 5.11.D.i: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: complete simple and compound sentences with subject-verb agreement and avoidance of splices, run-ons, and fragments.
- ELA: 5.11.D.ii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: past tense of irregular verbs.
- ELA: 5.11.D.iii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: collective nouns.
- ELA: 5.11.D.iv: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: adjectives, including their comparative and superlative forms.
- ELA: 5.11.D.ix: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: capitalization of abbreviations, initials, acronyms, and organizations.
- ELA: 5.11.D.v: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: conjunctive adverbs.
- ELA: 5.11.D.vi: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: prepositions and prepositional phrases and their influence on subject-verb agreement.
- ELA: 5.11.D.vii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: pronouns, including indefinite.
- ELA: 5.11.D.viii: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: subordinating conjunctions to form complex sentences.
- ELA: 5.11.D.x: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: italics and underlining for titles and emphasis and punctuation marks, including quotation marks in dialogue and commas in compound and complex sentences.
- ELA: 5.11.D.xi: The student is expected to edit drafts using standard English conventions including: correct selling of words with grade-appropriate orthographic patterns and rules and high frequency words.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.12
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts -- genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful.
- ELA: 5.12.B: The student is expected to compse information texts, including brief compositions that convey information about a topic, using a clear central idea and genre characteristics and craft.
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.4
Geography. The student understands the concepts of location, distance, and direction on maps and globes. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14.D: interpret and create visuals, including graphs, charts, tables, timelines, illustrations, and maps
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 3.1.C: The students is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems.
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 3.4.A: The student is expected to solve with fluency one-step and two-step problems involving addition and subtraction within 1,000 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
- Math: 3.4.G: The student is expected to use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, the multiply a two-digit number by a one-digit number. Strategies may include mental mathm partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties.
- Math: 3.4.K: The student is expected to solve one-step and two-step problems involving multiplication and division within 100 using strategies based on objects: pictorial models, including arrays, area models, and equal groups: properties of operation; or recall of facts.
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.8
Data analysis. The student applies mathematical process standards to solve problems by collecting, organizing, displaying, and interpreting data.
- Math: 3.8.A: The student is expected to summarize a data set with multiple categories using a frequency table, dot plot, pictograph, or bar graph with scaled intervals.
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 4.1.C: The students is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems.
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.2
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent, compare, and order whole numbers and decimals and understand relationships related to place value.
- Math: 4.2.B: The student is expected to represent the value of the digit in whole numbers through 1,000,000,000 and decimals to the hundredths using expanded notation and numerals.
- Math: 4.2.E: The student is expected to represent decimals, including tenths and hundredths, using concrete and visual models and money.
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 4.4.A: The student is expected to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals to the hundredths place using the standard algorithm.
- Math: 4.4.D: The student is expected to use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, the multiply up to a four-digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number. Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties.
- Math: 4.4.E: The student is expected to represent the quotient of up to a four-digit whole number divided by a one-digit whole number using arrays, area models, or equations.
- Math: 4.4.F: The student is expected to use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, to divide up to a four-digit dividend by a one-digit divisor.
- Math: 4.4.H: The student is expected to solve with fluency one-and two-step problems involving multiplication and division, including interpreting remainders.
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 5.1.C: The students is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems.
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.2
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent, compare, and order positive rational numbers and understand relationships as related to place value.
- Math: 5.2.A: The student is expected to represent the value of the digit in decimals through the thousandths using expanded notation and numerals.
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 5.3.B: The student is expected to multiply with fluency a three-digit number by a two-digit number using the standard algorithm.
- Math: 5.3.C: The student is expected to solve with proficiency for quotients of up to a four-digit dividend by a two-digit divisor using strategies and the standard algorithm.
- Math: 5.3.D: The student is expected to represent multiplication of decimals with products to the hundredths using objects and pictorial models, including area models.
- Math: 5.3.E: The student is expected to solve for products of decimals to the hundredths, including situations involving money, using strategies based on place-value understandings, properties of operations, and the relationship to the multiplication of whole numbers.
- Math: 5.3.I: The student is expected to represent and solve multiplication of a whole number and a fraction that refers to the same whole using objects and pictorial models, including area models.
- Math: 5.3.K: The student is expected to add and subtract positive rational numbers fluently.
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14.C: interpret oral, visual, and print material by sequencing, categorizing, identifying the main idea, distinguishing between fact and opinion, identifying cause and effect, comparing, and contrasting
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15.D: express ideas orally based on knowledge and experiences
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15.F: apply foundational language skills to engage in civil discourse about social studies topics, including those with multiple perspectives
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.D: create written and visual material such as journal entries, reports, graphic organizers, outlines, and bibliographies
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.E: apply foundational language skills to engage in civil discourse about social studies topics, including those with multiple perspectives
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.D: create written and visual material such as journal entries, reports, graphic organizers, outlines, and bibliographies
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.E: apply foundational language skills to engage in civil discourse about social studies topics, including those with multiple perspectives
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences.
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question.
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1.A: decompose a real-world problem into smaller, manageable subproblems using graphic organizers such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions.
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions
 Food origins, nutrition, and grade-level appropriate mathematics (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, graphing, problem solving, and statistics) are taught in this lesson. The interdisciplinary approach in Edible Numbers makes it suitable for self-contained classrooms, core, and home school settings. Grocery advertisement scavenger hunts are the highlight of this unit. Use them as they are written, or incorporate single lessons from the unit into an already established curriculum.
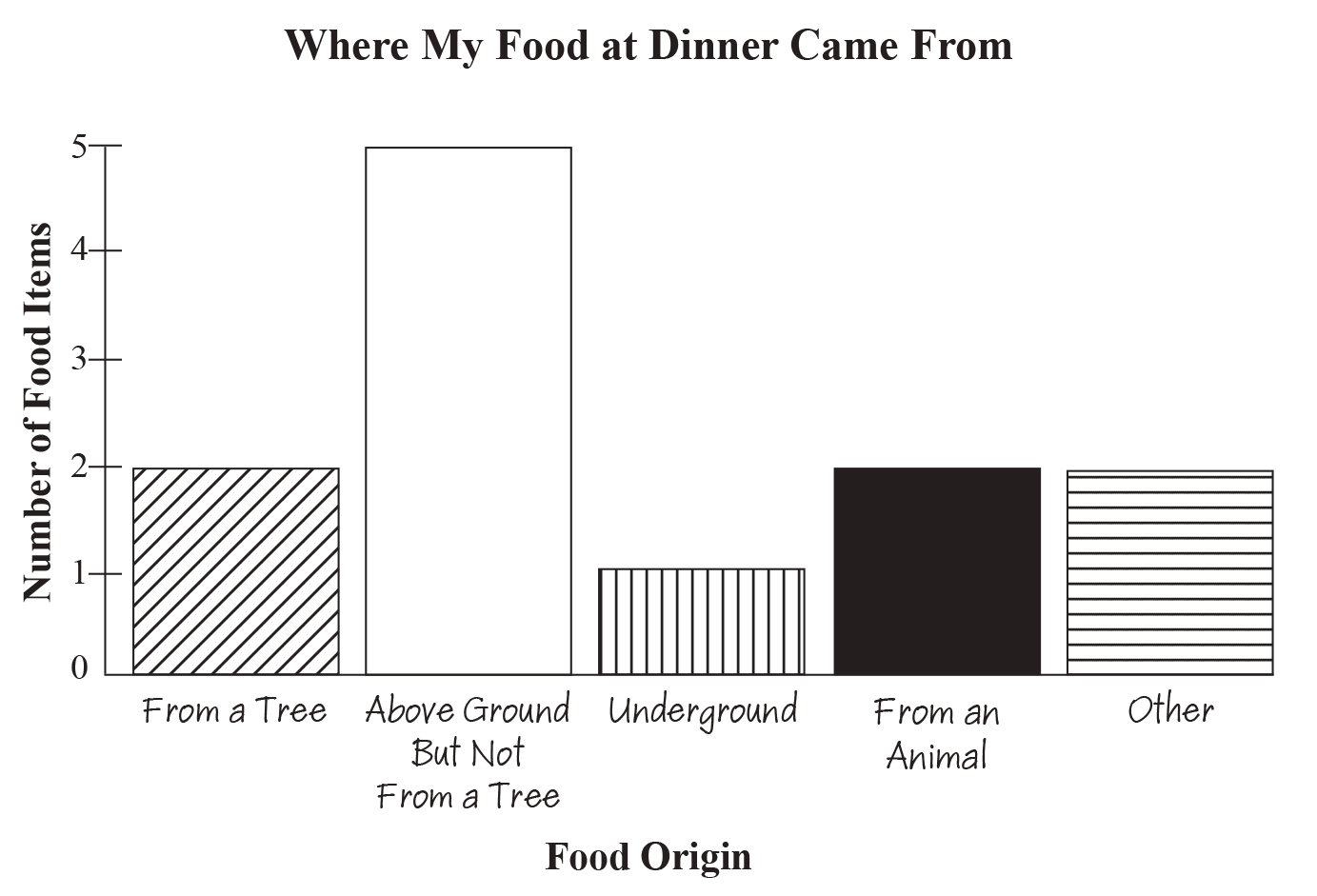
Food origins, nutrition, and grade-level appropriate mathematics (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, graphing, problem solving, and statistics) are taught in this lesson. The interdisciplinary approach in Edible Numbers makes it suitable for self-contained classrooms, core, and home school settings. Grocery advertisement scavenger hunts are the highlight of this unit. Use them as they are written, or incorporate single lessons from the unit into an already established curriculum.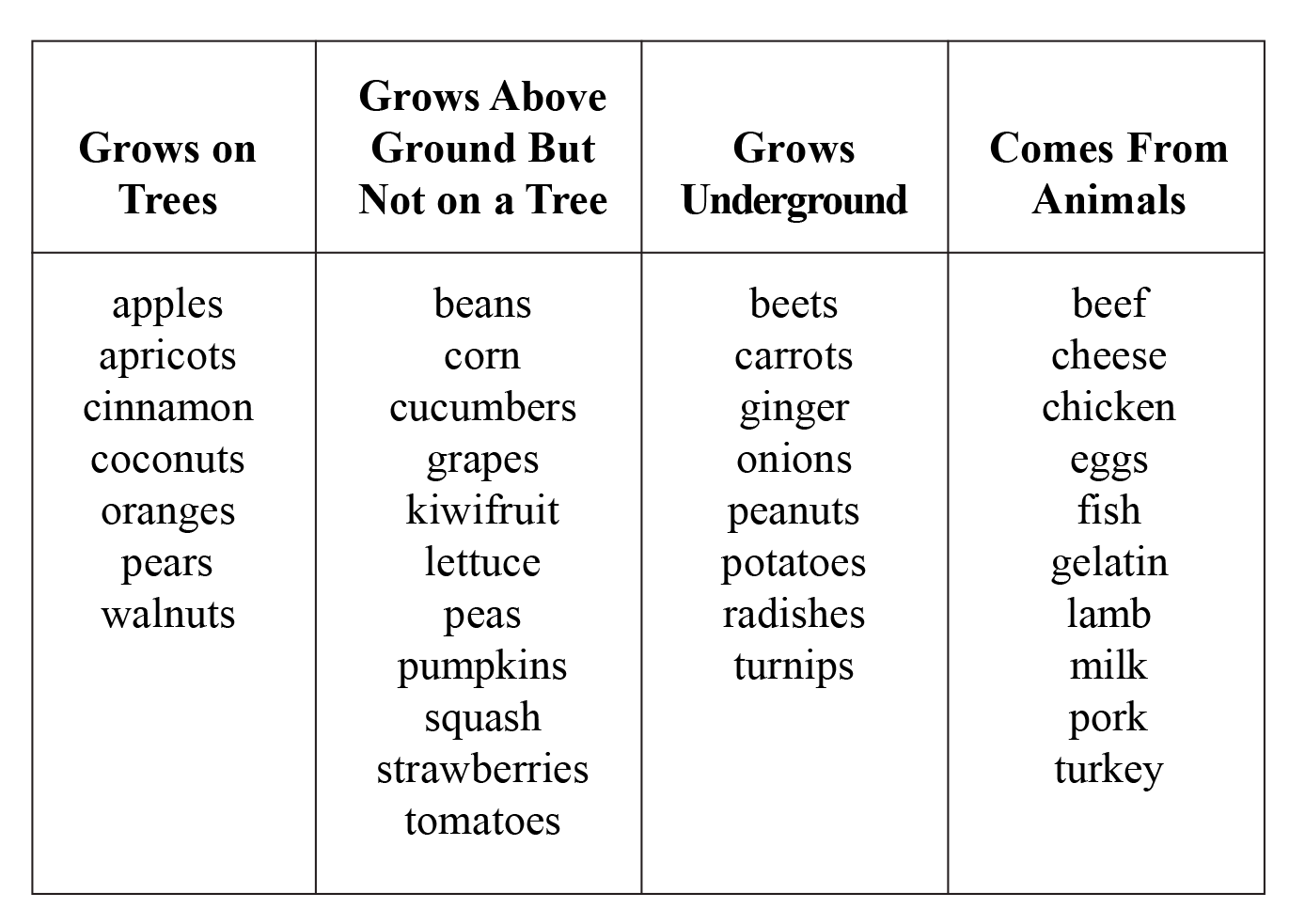 Nutrition fact labels provide information that can be useful when determining the nutritional value of a product. They contain the recommended daily allowance, known as the RDA which is the estimated amount of calories per day, determined by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Research Council and the National Academy of Sciences, necessary for good health. The ingredients are listed in order of quantity. For example, the main ingredient in a cherry breakfast bar is wheat flour, which is produced by a grain that is a cultivated cereal crop used as food. The second ingredient is sugar, and the third ingredient is cherries. If this were a food your students were to record on a chart, they would check three or more boxes—Grows Above Ground But Not On a Tree for the wheat, Grows Underground for the sugar, Grows on a Tree for the cherries, etc.
Nutrition fact labels provide information that can be useful when determining the nutritional value of a product. They contain the recommended daily allowance, known as the RDA which is the estimated amount of calories per day, determined by the Food and Nutrition Board of the National Research Council and the National Academy of Sciences, necessary for good health. The ingredients are listed in order of quantity. For example, the main ingredient in a cherry breakfast bar is wheat flour, which is produced by a grain that is a cultivated cereal crop used as food. The second ingredient is sugar, and the third ingredient is cherries. If this were a food your students were to record on a chart, they would check three or more boxes—Grows Above Ground But Not On a Tree for the wheat, Grows Underground for the sugar, Grows on a Tree for the cherries, etc.

 Review mathematics vocabulary with your students. The terms they should understand include sum, difference, total price, product, place value in decimals, etc. Students will search through grocery advertisements to find a part of an advertisement that satisfies a particular problem on the scavenger hunt.
Review mathematics vocabulary with your students. The terms they should understand include sum, difference, total price, product, place value in decimals, etc. Students will search through grocery advertisements to find a part of an advertisement that satisfies a particular problem on the scavenger hunt.