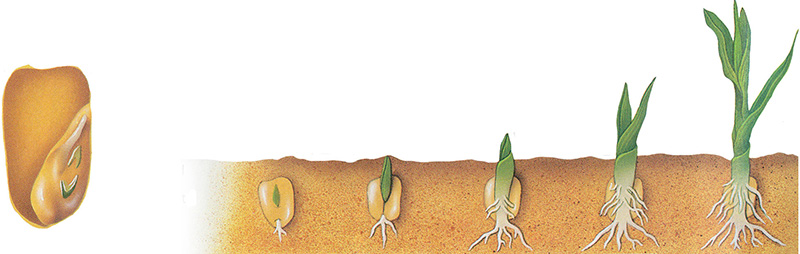
Inherited Traits in the Living Corn Necklace (Grades 6-8)
Students will observe the growth of Indian corn and popcorn seeds, observe similarities and differences between the two varieties, and discuss heredity.
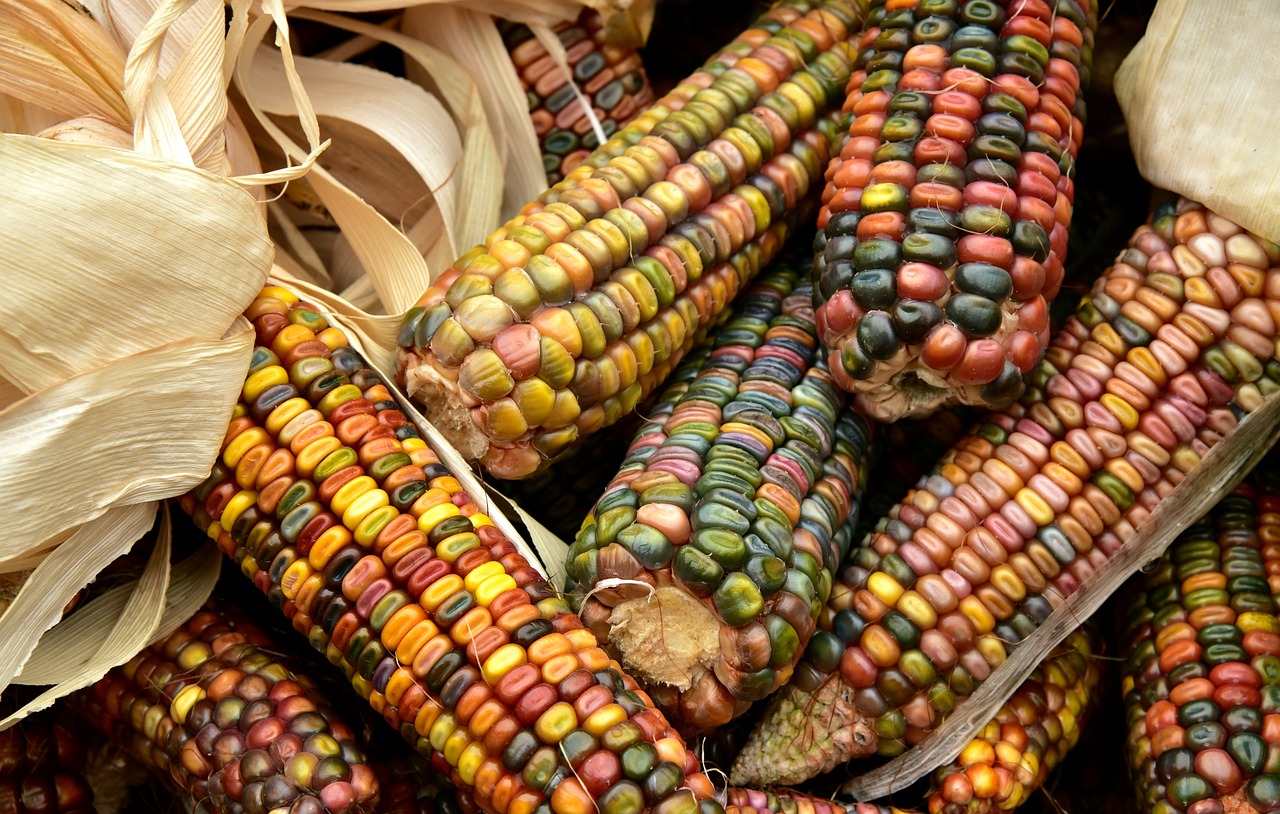

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Debra Spielmaker | Utah Agriculture in the Classroom
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.C: evaluate significant historical and current agriculture, food, and natural resources developments.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7
The student applies appropriate research methods to agriculture, food, and natural resources topics. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7.B: use a variety of resources for research and development.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7.C: describe scientific methods of research.
- Principles of Agricultures, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7.A: discuss major research and developments in the fields of agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to plant systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.A: describe the structure and functions of plant parts.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.B: discuss and apply plant germination, growth, and development.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.C: describe plant reproduction, genetics, and breeding.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.D: identify plants of importance to agriculture, food, and natural resources
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 6.1.D: The student is expected to participate in student-led discussions by eliciting and considering suggestions from other group members, taking notes, and identifying points of agreement and disagreement.
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.1.D: participate in student-led discussions by eliciting and considering suggestions from other group members, taking notes, and identifying points of agreement and disagreement.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.11
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful.
- ELA: 6.11.B: The student is expected to compose informational texts, including multi- paragraph essays that convey information about a topic, using a clear controlling idea or thesis statement and genre characteristics and craft.
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.11.B: compose informational texts, including multi-paragraph essays that convey information about a topic, using a clear controlling idea or thesis statement and genre characteristics and craft
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 7.1.D: The student is expected to engage in meaningful discourse and provide and accept constructive feedback from others.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.1.D: engage in meaningful discourse and provide and accept constructive feedback from others
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.11
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful.
- ELA: 7.11.B: The student is expected to compose informational texts, including multi- paragraph essays that convey information about a topic, using a clear controlling idea or thesis statement and genre characteristics and craft.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.11.B: compose informational texts, including multi-paragraph essays that convey information about a topic, using a clear controlling idea or thesis statement and genre characteristics and craft
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 8.1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively in discussions, plant agendas with clear goals and deadlines, set time limits for speakers, take notes, and vote on key issues.
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.1.D: participate collaboratively in discussions, plan agendas with clear goals and deadlines, set time limits for speakers, take notes, and vote on key issues
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.11
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful.
- ELA: 8.11.B: The student is expected to compose informational texts, including multi- paragraph essays that convey information about a topic, using a clear controlling idea or thesis statement and genre characteristics and craft.
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.11.B: compose informational texts, including multi-paragraph essays that convey information about a topic, using a clear controlling idea or thesis statement and genre characteristics and craft
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands that ecosystems are dependent upon the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.A: diagram the flow of energy within trophic levels and describe how the available energy decreases in successive trophic levels in energy pyramids; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.B: describe how ecosystems are sustained by the continuous flow of energy and the recycling of matter and nutrients within the biosphere.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows how systems are organized and function to support the health of an organism and how traits are inherited. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.13.D: describe and give examples of how natural and artificial selection change the occurrence of traits in a population over generations.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands stability and change in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.12.A: explain how disruptions such as population changes, natural disasters, and human intervention impact the transfer of energy in food webs in ecosystems;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows how cell functions support the health of an organism and how adaptation and variation relate to survival. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.13.A: identify the function of the cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, ribosomes, cytoplasm, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and vacuoles in plant or animal cells;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.13.C: describe how variations of traits within a population lead to structural, behavioral, and physiological adaptations that influence the likelihood of survival and reproductive success of a species over generations.