Robots in High-Tech Farming (Grades 3-5)
Students discover the four main components of robots, explore how robots are used in agriculture, and program and operate a robot to address a farming challenge.
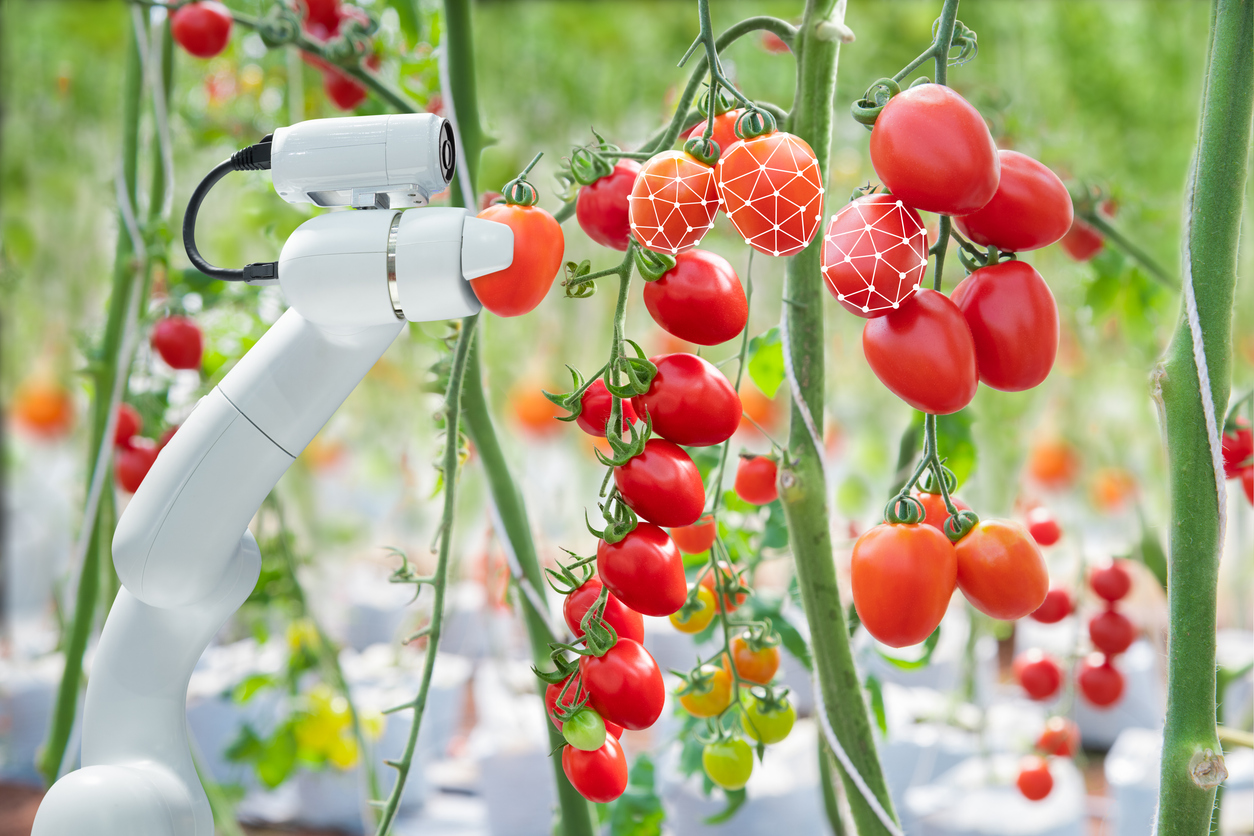

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Lynn Wallin | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- https://www.theautomationengineer.com/markets-sectors/automated-agriculture-robots-future-farming/
- https://nifa.usda.gov/topic/agriculture-technology
- http://www.handsfreehectare.com/
- https://www.sciencefriday.com/segments/the-origin-of-the-word-robot/
- https://nifa.usda.gov/announcement/usdas-national-institute-food-and-agriculture-announces-support-collaborative-robotics
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.1.C: express an opinion supported by accurate information, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, and the conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.12
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts -- genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful.
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.12.B: compose informational texts, including brief compositions that convey information about a topic, using a clear central idea and genre characteristics and craft
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.13
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.13.E: demonstrate understanding of information gathered
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.13.H: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 6.1.C: The student is expected to give an organized presentation with a specific stance and position, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, natural gestures, and conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively.
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.16
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.16.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.22
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.22.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.4.A: explain how scientific discoveries and innovative solutions to problems impact science and society
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.1.C: speak coherently about the topic under discussion, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, and the conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others by following agreed-upon rules, norms, and protocols
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.12
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.12.B: compose informational texts, including brief compositions that convey information about a topic, using a clear central idea and genre characteristics and craft
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.13
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.13.E: demonstrate understanding of information gathered
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.13.H: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.12
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--genres. The student uses genre characteristics and craft to compose multiple texts that are meaningful. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.12.B: compose informational texts, including brief compositions that convey information about a topic, using a clear central idea and genre characteristics and craft
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.13
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.13.E: demonstrate understanding of information gathered
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.13.H: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.A: decompose story problems into smaller, manageable subproblems and identify a solution to the problems
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.C: develop a plan collaboratively and document a plan that outlines specific steps taken to complete a project
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences.
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.A: decompose story problems into smaller, manageable subproblems and discuss and document various solutions to the problems
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.C: communicate design plans and solutions using a variety of options
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question.
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1.A: decompose a real-world problem into smaller, manageable subproblems using graphic organizers such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions.
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions
 to the class or show the
to the class or show the