Plant Propagation
Students will learn about two types of plant propagation – seed planting (sexual) and stem cuttings (asexual) and recognize the genetic differences in these processes, as well as the advantages and disadvantages of each method.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Sue Knott | Minnesota Agriculture in the Classroom
Acknowledgements
- The Living Necklace (seed necklace) activity in Session 1, step 5 was created by Utah Agriculture in the Classroom. A kit with the supplies can be purchased from agclassroomstore.com.
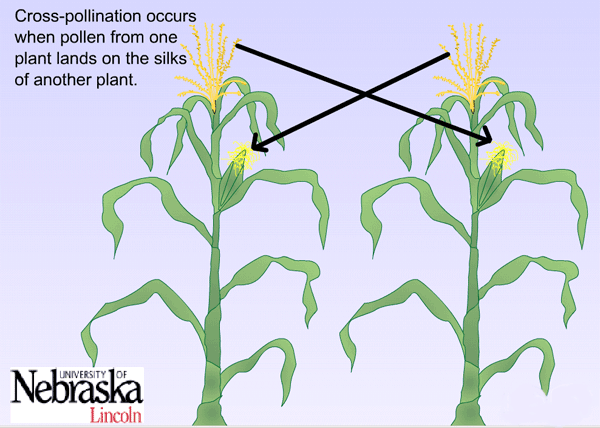
- Cross Pollination Image from http://passel.unl.edu/Image/siteImages/CrossPollinationLG.gif
- Information for Seed to Seed 101 from Seeds! The Promise of Life Published by the National Gardening Association with support from the National Garden Bureau Spring 2002.
- Images for Seed to Seed 101 from http://urbanext.illinois.edu/gpe/case4/c4facts1a.html
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to plant systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.A: describe the structure and functions of plant parts.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.B: discuss and apply plant germination, growth, and development.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.C: describe plant reproduction, genetics, and breeding.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.D: identify plants of importance to agriculture, food, and natural resources
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.E: use tools, equipment, and personal protective equipment common to plant systems.
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.C: use appropriate safety equipment and practices during laboratory, classroom, and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.H: distinguish between scientific hypotheses, theories, and laws.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows that organisms have an organizational structure and variations can influence survival of populations. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.13.C: describe how variations within a population can be an advantage or disadvantage to the survival of a population as environments change
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.C: use appropriate safety equipment and practices during laboratory, classroom, and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.H: distinguish between scientific hypotheses, theories, and laws.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands that ecosystems are dependent upon the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.B: describe how ecosystems are sustained by the continuous flow of energy and the recycling of matter and nutrients within the biosphere.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows how systems are organized and function to support the health of an organism and how traits are inherited. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.13.C: compare the results of asexual and sexual reproduction of plants and animals in relation to the diversity of offspring and the changes in the population over time; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.13.D: describe and give examples of how natural and artificial selection change the occurrence of traits in a population over generations.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.14
Organisms and environments. The student knows how the taxonomic system is used to describe relationships between organisms. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.14.A: describe the taxonomic system that categorizes organisms based on similarities and differences shared among groups; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.14.B: describe the characteristics of the recognized kingdoms and their importance in ecosystems such as bacteria aiding digestion or fungi decomposing organic matter.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.C: use appropriate safety equipment and practices during laboratory, classroom, and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.H: distinguish between scientific hypotheses, theories, and laws.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows how cell functions support the health of an organism and how adaptation and variation relate to survival. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.13.B: describe the function of genes within chromosomes in determining inherited traits of offspring; and
- Science: 8.112.28.b.13.C: describe how variations of traits within a population lead to structural, behavioral, and physiological adaptations that influence the likelihood of survival and reproductive success of a species over generations.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.D: paraphrase and summarize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.D: paraphrase and summarize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.D: paraphrase and summarize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate