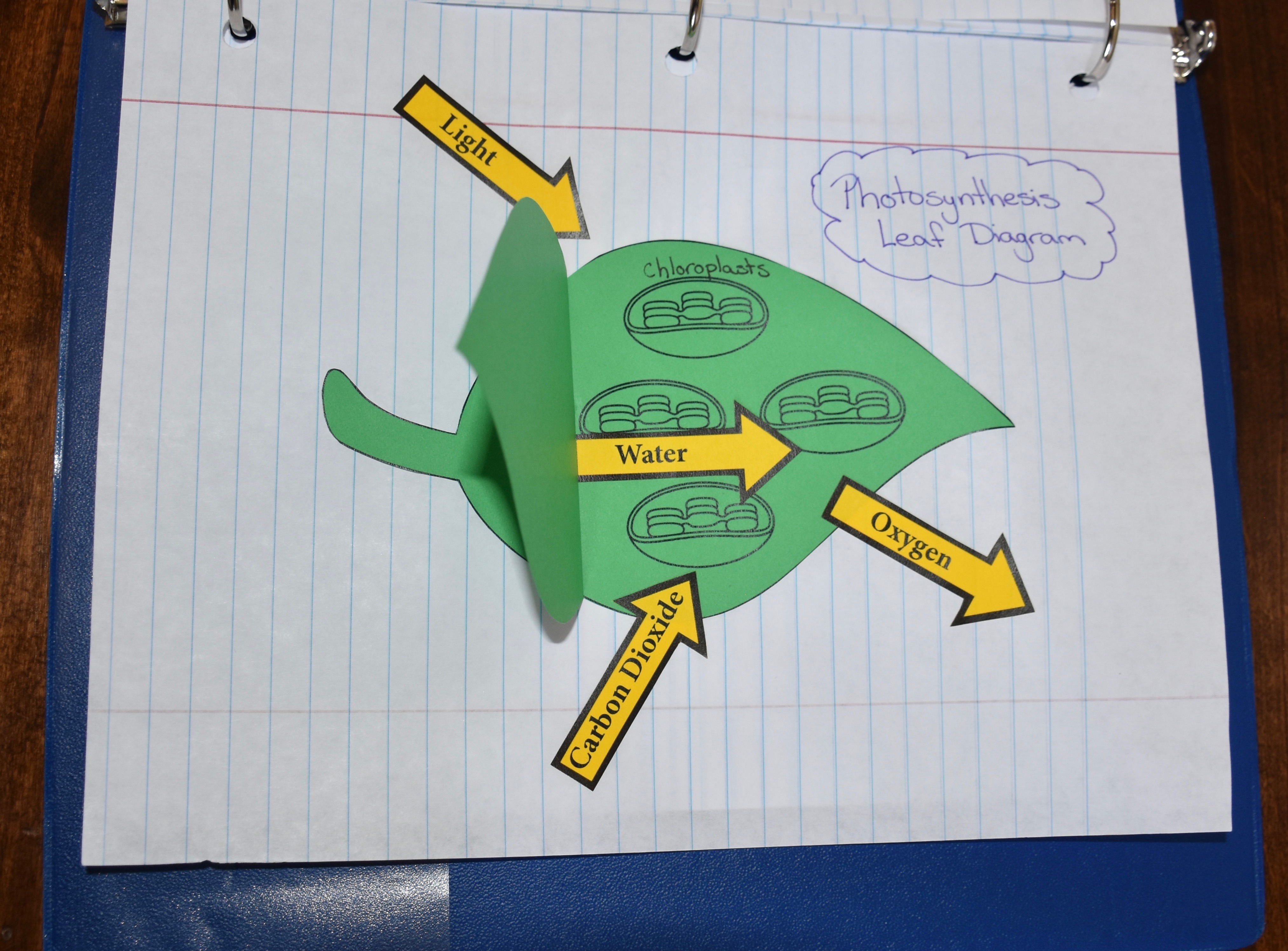
Photosynthesis: Energy's Journey From Farm to You
Explore photosynthesis to discover how plants obtain energy from the sun and then continue following energy's path to see how energy can flow through ecosystems to ultimately provide food for humans.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Rashel Clark and Lynn Wallin | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL) and Dairy West
Acknowledgements
Activity 1 was originally written by Lynn Wallin in the elementary lesson plan, Desktop Greenhouses.
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to plant systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.A: describe the structure and functions of plant parts.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.6
Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is made of atoms, can be classified according to its properties, and can undergo changes. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.6.E: identify the formation of a new substance by using the evidence of a possible chemical change, including production of a gas, change in thermal energy, production of a precipitate, and color change.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.B: explain how conservation, increased efficiency, and technology can help manage air, water, soil, and energy resources.
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands that ecosystems are dependent upon the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.A: diagram the flow of energy within trophic levels and describe how the available energy decreases in successive trophic levels in energy pyramids; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.B: describe how ecosystems are sustained by the continuous flow of energy and the recycling of matter and nutrients within the biosphere.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.14
Organisms and environments. The student knows how the taxonomic system is used to describe relationships between organisms. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.14.B: describe the characteristics of the recognized kingdoms and their importance in ecosystems such as bacteria aiding digestion or fungi decomposing organic matter.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.6
Matter and energy. The student understands that matter can be classified according to its properties and matter is conserved in chemical changes that occur within closed systems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.6.E: investigate how mass is conserved in chemical reactions and relate conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms using chemical equations, including photosynthesis
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands stability and change in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.12.A: explain how disruptions such as population changes, natural disasters, and human intervention impact the transfer of energy in food webs in ecosystems;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how human activity can impact the hydrosphere. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.11.A: analyze the beneficial and harmful influences of human activity on groundwater and surface water in a watershed; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.11.B: describe human dependence and influence on ocean systems and explain how human activities impact these systems.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate