Nutrient Deficiencies of Plants
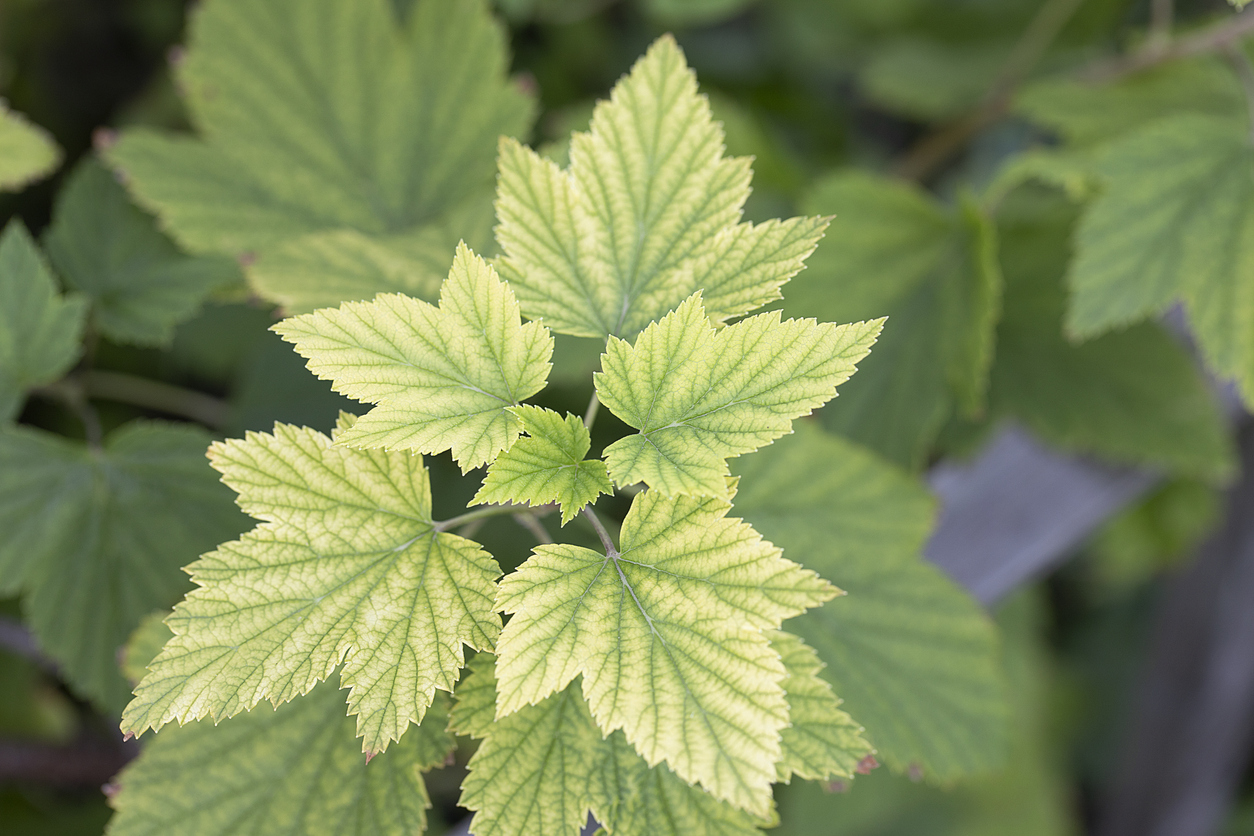
People and plants are very different types of organisms. For example, people have blood, while plants have sap. People are consumers, while plants are producers. Despite their many differences, both people and plants are made up of cells. In order for cells to be healthy, they must have certain nutrients. If a person is lacking a needed vitamin, mineral, or essential element, then a deficiency is the result. We are familiar with the results of some nutrient deficiencies. For example, if a person lacks iron, he or she becomes anemic or if a person lacks calcium, their bones become brittle. As discussed in section 2.0 Plants and Their Essential Elements, plants require a variety of elements to be present in different amounts in order to support healthy growth. A nutrient deficiency results if a particular nutrient is not available in sufficient quantity to meet the needs of the growing plant. Nutrient toxicity occurs when a nutrient is present in such an excess that it harms the plant. Table 9 lists most of the essential plant nutrients and describes what happens when plants have too little or too much of them.
As discussed above, when a plant is out of nutrient balance, it displays symptoms that are characteristic for that particular nutrient. A farmer concerned for the health of their crops must use scientific tools to prevent deficiencies and, if necessary, to examine these symptoms and diagnose problems, much like a physician does when encountering a patient with a dietary deficiency. Soil and plant tissue tests are used to detect nutrient imbalances. Once the problem has been identified, steps are taken to correct the imbalance. Farmers prescribe fertilizers for their crops in a manner similar to doctors prescribing vitamins for their patients.
Nourishing Crops with Fertilizers
As discussed above, plants grown in soil depleted of nutrients can display a wide variety of symptoms and greatly limit the quantity and quality of harvested crops. Fertilizer is essentially plant food. It is added to replenish nutrients that people indirectly extract from the soil by harvesting plants. In non-agricultural ecosystems, the nutrients removed by plants are returned to the soil after the plants die and decompose. On farms, some of these nutrients are removed in the form of harvested crops, so it is often necessary to replace them with fertilizers. The essential components of most fertilizers are the macronutrients nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. All three of these elements play essential roles in allowing plants to access the free energy of the sun through photosynthesis and must be present in adequate amounts to ensure healthy crop growth.
Humans have been raising crops for nearly 10,000 years. Even ancient farmers fertilized their crops. The use of human and animal waste to increase soil fertility was recorded in China over 2,000 years ago. During the “golden age” of Greece from 800 to 200 BC, historians discussed methods for using sewage and classifying manures according to their value for crop production. Although these ancient cultures lacked our understanding of chemistry, they were observant and learned through trial and error how to help their crops grow. Mineral fertilizer in the form of saltpeter or potassium nitrate is mentioned by early Greek and Roman writers and in the Bible. Ancient Greeks also used salt brines to fertilize palm trees. 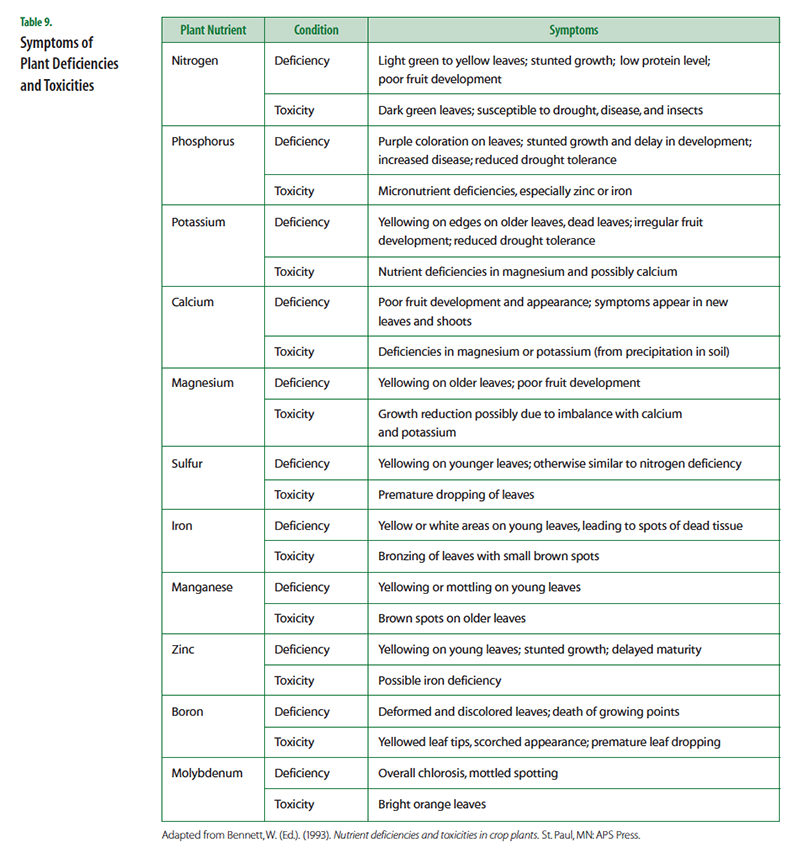
Justus von Liebig (1803–1873) is known as the founder of the modern fertilizer industry. Using the contributions of other scientists as well as his own discoveries, Liebig formulated the “mineral theory,” which held that crops “grow or diminish in exact proportion” to the amount of nutrient applied. Leibig stressed the value of replacing nutrients to maintain soil fertility. He also developed the “law of the minimum,” which states that if one essential element is deficient, then plant growth will be lacking even when all other essential elements are abundant. If the deficient element is supplied, then growth will increase up to the point where the supply is no longer the limiting factor. 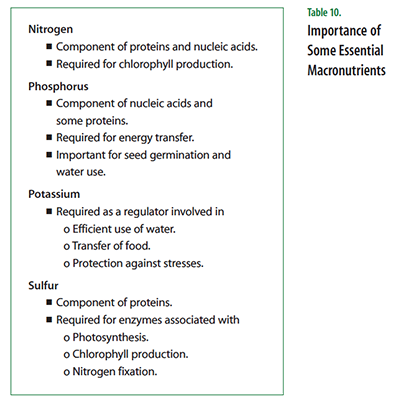 The concept of the law of the minimum has been modified through the years as scientists have achieved a better understanding of the variables affecting plant growth. Moisture, temperature, insect control, weed control, light, plant population, and genetic capabilities of plant varieties are now part of this rule.
The concept of the law of the minimum has been modified through the years as scientists have achieved a better understanding of the variables affecting plant growth. Moisture, temperature, insect control, weed control, light, plant population, and genetic capabilities of plant varieties are now part of this rule.

Today, commercial fertilizers are obtained from a variety of natural sources. The world’s first commercial fertilizer was sodium nitrate mined from natural deposits in Chile and imported into Europe and the United States starting around1830. Around the same time, ammonium sulfate, a by-product of the manufacture of coal gas used for illumination, was sold as a commercial fertilizer.
Nitrogen (the builder)
 Nitrogen (N) is a primary building block for all organisms. It is a component of every amino acid and therefore essential to making proteins. As part of the chlorophyll molecule, nitrogen helps keep plants green. Nitrogen, along with magnesium, is the only element in the chlorophyll molecule that the plant obtains from the soil.
Nitrogen (N) is a primary building block for all organisms. It is a component of every amino acid and therefore essential to making proteins. As part of the chlorophyll molecule, nitrogen helps keep plants green. Nitrogen, along with magnesium, is the only element in the chlorophyll molecule that the plant obtains from the soil.
Vigorous plant growth is associated with adequate nitrogen nutrition, in part because nitrogen plays a key role in cell division. If cell division is slowed or stopped, so is leaf growth, which affects the surface area of the leaf exposed to the sun. A smaller surface area reduces the plant’s ability to produce biomass (yield). In addition to increasing yield, nitrogen also improves crop quality by increasing its protein content. Crop plants generally require more nitrogen to grow at their full potential than non-crop plants.
In 1918, scientists Fritz Haber (1868–1934) and Carl Bosch (1874–1940) were awarded the Nobel Prize for developing nitrogen fertilizer by synthesizing ammonia from nitrogen gas and hydrogen. While this process has been modified several times, today the Haber-Bosch process remains the method by which nitrogen fertilizer is commercially produced. Some academics have even suggested that this process has been of greater fundamental importance to the modern world than the invention of the airplane, nuclear energy, space flight, or television.20 The Haber-Bosch process has increased the amount of plant-available nitrogen produced on land by 60-70 percent compared to the natural processes of biological nitrogen fixation and lightning.23 Ammonia can be used in a wide variety of field conditions and is a major source of nitrogen applied to crops in the United States. Ammonia contains 82 percent nitrogen and is an important component for most nitrogen-based fertilizers. Another nitrogen source is urea, which is made by reacting ammonia with carbon dioxide and is 45 percent nitrogen.
Organic sources of nitrogen have long been used as fertilizers. Between the years 1850 and1900, the major natural organics were human excrement, cottonseed meals, fish scrap, and slaughterhouse wastes. In 1910, approximately 90 percent of the nitrogen used in the United States came from organic sources. As competition from commercial fertilizers grew, the contributions from organics decreased to 34 percent in 1920 and to 3.4 percent in 1950.
A new form of fertilizer was developed in the 1950s called activated sewage sludge. This material is made by passing wastewater through filters and centrifuging it to remove debris, oil, grease, and grit. The wastewater is then oxygenated to help microorganisms break down the biomass. Excess water is removed, and the final product is a thick, fibrous cake that is dried in kilns at high temperature to kill any remaining microorganisms or pathogens.
Phosphorus (the Energy Supplier)
Phosphorus (P) is found in every living cell. In plants, it serves as both a structural  element and as a catalyst for biochemical reactions. Phosphorus is a component of DNA and ATP. It also plays vital roles in capturing light during photosynthesis, helping with seed germination, and helping plants use water efficiently. Plants also use phosphorus to help fight external stress and prevent disease.
element and as a catalyst for biochemical reactions. Phosphorus is a component of DNA and ATP. It also plays vital roles in capturing light during photosynthesis, helping with seed germination, and helping plants use water efficiently. Plants also use phosphorus to help fight external stress and prevent disease.
Animal and human bones contain insoluble calcium phosphate. As early as 2,000 years ago, Chinese farmers treated bones with lime and spread them on their fields. The lime treatment was necessary to convert the calcium phosphate into a more soluble form that plant roots could absorb. In the 1800s, fertilizer manufacturers wanted to produce phosphorus fertilizers that were more effective and plentiful than bones. They turned to natural deposits of phosphate rock in the fossilized remains of ancient marine life found in rock deposits around the world. The phosphate in these deposits exists in various forms of a very stable compound called apatite. To make the fertilizer called superphosphate, the phosphate rock is treated with acid or heat to render the phosphorus more soluble. Superphosphate production began in the United States in South Carolina in 1849.
Potassium (the Regulator)
Potassium (K) is essential to the workings of every living cell. Although potassium is  not a part of any important plant structure, it plays critical roles in several physiological processes. Potassium activates enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions involved with growth. It plays an important role in water balance by regulating the opening and closing of stomates (the pores in leaves through which gases are exchanged). Potassium also helps regulate the rate of photosynthesis through its role in the production of ATP. Other aspects of plant health influenced by potassium include the growth of strong stalks, protection from extreme temperatures, and the ability to fight stress and pests such as weeds and insects.
not a part of any important plant structure, it plays critical roles in several physiological processes. Potassium activates enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions involved with growth. It plays an important role in water balance by regulating the opening and closing of stomates (the pores in leaves through which gases are exchanged). Potassium also helps regulate the rate of photosynthesis through its role in the production of ATP. Other aspects of plant health influenced by potassium include the growth of strong stalks, protection from extreme temperatures, and the ability to fight stress and pests such as weeds and insects.
Potassium used in the manufacture of fertilizers comes from sedimentary salt beds left behind following the evaporation of ancient seas and lakes. Nearly all potassium fertilizer is in the form of potassium chloride. The potassium fertilizer industry started in western Europe, where there are significant deposits of such ores. North America has the world’s largest reserves of potassium deposits. Other parts of the world containing potassium deposits include Brazil, China, Israel, Jordan, and Russia.
Sulfur (the Synthesizer)
Sulfur (S) is one of the most abundant elements in the soil and is one of the first elements scientists described. Like nitrogen, it is an essential component in the life of a cell. Sulfur is a component of the amino acids methionine and cysteine, which are used in the synthesis of proteins in all living things. Sulfur also is needed by enzymes associated with photosynthesis and chlorophyll synthesis. Sulfur is extracted from deep, naturally occurring underground deposits, from natural gas and crude oil, from the smelting of certain metal ores, and from gases produced by burning coal.
Micronutrients
Among the micronutrients, the following four types of deficiencies are commonly addressed through the use of fertilizers:
- Boron (B) is an essential nutrient in the growth and development of new cells. In plants, boron helps regulate flowering, pollination, seed development, and sugar transport.
- Copper (Cu) is a critical regulator of several plant enzyme systems and is necessary for protein synthesis and nitrogen metabolism.
- Manganese (Mn) is a part of several plant enzyme systems and plays a role in photosynthesis by regulating chlorophyll synthesis.
- Zinc (Zn) is an essential enzyme regulator involved with the synthesis of protein, starch, and growth hormones.

Organic and Commercial Fertilizers
During the past 20 years or so, the United States has witnessed a large growth in what is called organic farming. Although organic farming can be complicated to define, generally it relies on methods that use products that have been designated as “natural.” Today, the organic foods industry has annual sales of approximately $14 billion, with organic products representing 2.5 percent of all U.S. grocery spending.
Farmers who fertilize their crops have the choice of using either organic or commercial fertilizers, or a combination of the two types. As the name suggests, organic fertilizers come from once-living material such as plants or animal manure. Commercial fertilizers consist of natural ingredients that have been subjected to a chemical process to make a fertilizer with increased and uniform nutrient content. Commercial fertilizers come from either natural mineral deposits or, in the case of nitrogen, from Earth’s atmosphere. Chemically, there is no difference between a nitrogen atom that comes from fertilizer, animal manure, a compost pile, or the atmosphere; provided they are in the same form (e.g. ammonium, nitrate or urea) they are the same as far as the plants are concerned. However, there are differences in the rate at which the nitrogen from these sources is made available to plants and the ratio of nitrogen to other elements such as phosphorus.
A major distinction between organic fertilizers and commercial ones is the quantities of nutrients they contain and the farmers’ knowledge about those quantities. Unlike commercial fertilizers, organic nutrient sources typically do not come with a guarantee of nutrient content. Organic material may supply high levels of one nutrient but low levels of another, creating an imbalance for crop plants. In contrast, commercial fertilizers contain known and often higher quantities of nutrients, which make it convenient for farmers to apply them at rates that ensure that growing plants’ needs are met and nutrient losses to the environment are minimized.
An advantage of plant-based organic fertilizers (e.g. compost) is that the nutrients are released slowly, so they are less likely to be supplied faster than plants can use them. For this reason they are often considered less damaging to the environment than mineral fertilizers. However, manure-based organic sources are typically more volatile—or subject to movement—in the environment than commercial fertilizers. If any nutrient—commercial or organic—is applied at a rate higher than plants can use it, the excess may run off the fields or disperse into the air and contribute to nutrient pollution (see section 8.1Nutrient Pollution ). Most organic fertilizers used on farms are manure based.
Meeting Crop’s Nutrient Needs
Fertilizers can be applied as liquids or solids or, as in the case of anhydrous ammonia, as a pressurized gas that is injected into the soil. Bagged fertilizers are sold in a wide variety of mixtures. It is easy to read their contents from the fertilizer label. The percentage by weight of the three macronutrients—nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium—is listed as the fertilizer’s NPK ratio. For example, a label with an NPK ratio of 24-6-6 means that the fertilizer contains 24 percent nitrogen, 6 percent phosphate, and 6 percent potassium. Some fertilizers also contain micronutrients, which are nutrients needed in smaller amounts for plant health and growth. Fertilizer labels also indicate the amounts of micronutrients as well as any inert ingredients such as sand that are included to provide bulk and make the fertilizer easier to apply.
Farmers use scientific methods to determine the appropriate nutrient balance for their crops. Because every farm field is different, farmers need to be able to select best-management practices (BMPs) that are suited to their growing conditions. Factors that may influence BMP selection include soil, climate, topography, and crop nutrient requirements. Often, farmers work with a certified crop adviser, a trained nutrient management professional, to assess growing and environmental conditions and develop a nutrient management plan.
The soil composition of farm fields varies greatly—often even on the same farm. Ensuring that crops get the precise amount of nutrients needed while minimizing nutrient losses to the environment involves consideration of a number of variables including the existing nutrient content of the soil and the crop nutrient needs. Soils can contain rich reserves of nutrients. Before fertilizing, farmers must measure the existing amounts of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium already in the soil. Then they can select a fertilizer that meets the needs of their crops. Sometimes, fertilizers are custom-blended to meet the farmer’s needs. After the right product has been selected, the nutrient management plan must also take into account the criteria described in Table 11.
Organic or Commercial: Which Is Better?
A quick answer to the question of which fertilizer is better is that neither organic nor commercial nutrient sources are better for plants. Both have their places and should be used where appropriate and each has its advantages and disadvantages. Farmers need to examine the relative merits and decide when and where each type of fertilizer should be used. Because most organic fertilizers used on farms are from livestock, we focus here on manure-based organic fertilizers.
Manure-based organic materials encourage the use of local natural resources. They use little or no synthetic additives. Manure fertilizers may be viewed as economic and agronomic nutrient supplements along with mineral fertilizers in the production of crops. They contain varying amounts of plant nutrients and provide organic carbon, which is part of any productive agricultural soil. They improve the biological, chemical, and physical properties of soils.
There are, however, some concerns associated with certain forms of manure-based organic fertilizer. First, when animal manures are produced in confined areas, excessive amounts of nutrients can accumulate in crop fields if the manure is over-applied near the site where it was produced. This can pose a threat of nitrate leaching to groundwater and phosphorus moving into surface waters through runoff and erosion. Second, the relatively fixed nutrient ratios of organic fertilizers can result in too much phosphorus being present in heavily manured soils, because crops usually require much less phosphorus than nitrogen. In addition, significant amounts of ammonia gas (NH3) can also be lost to the atmosphere.
By comparison, plant-based organic fertilizers are usually low in nutrient content. They contain some soluble nutrients, but most is released slowly as microbes in the soil break down the organic material into water-soluble forms that the plant roots can absorb. This feature may be an advantage when fertilizer is applied infrequently because it is less likely to overwhelm the system with soluble nutrients, which can result in nutrient loss to the environment. However, it also makes it difficult to time the release of nutrients to match the needs of the growing crop.
Commercial fertilizers contain precise, guaranteed levels of nutrients, in forms that are readily available for plant uptake and use. It is possible to time their application to meet crop requirements, assuring efficient nutrient use and minimizing any potential impact on the environment. Because of their high nutrient content, commercial fertilizers are easy and economical to ship great distances from their point of production.
However, the high nutrient content of commercial fertilizers also means that the potential for overuse is greater. Farmers need to apply commercial fertilizers as specified by a nutrient management plan that is designed for the specific conditions of their fields. Nutrient management plans use data from soil and plant tissue testing to help farmers use the proper amounts of nutrients at the optimal times. Nutrient management plans also keep farmers from wasting money by using too much fertilizer and from contributing unwanted nutrients to the air, ground-water, and local waterways. For example, although agriculture practices such as plowing can increase soil erosion, well-managed agricultural soils have less erosion than soils without an appropriate balance of nutrients. This is important because soil erosion in areas such as the Gulf of Mexico is an important contributor of nutrient pollution.


 The concept of the law of the minimum has been modified through the years as scientists have achieved a better understanding of the variables affecting plant growth. Moisture, temperature, insect control, weed control, light, plant population, and genetic capabilities of plant varieties are now part of this rule.
The concept of the law of the minimum has been modified through the years as scientists have achieved a better understanding of the variables affecting plant growth. Moisture, temperature, insect control, weed control, light, plant population, and genetic capabilities of plant varieties are now part of this rule.
 Nitrogen (N) is a primary building block for all organisms. It is a component of every amino acid and therefore essential to making proteins. As part of the chlorophyll molecule, nitrogen helps keep plants green. Nitrogen, along with magnesium, is the only element in the chlorophyll molecule that the plant obtains from the soil.
Nitrogen (N) is a primary building block for all organisms. It is a component of every amino acid and therefore essential to making proteins. As part of the chlorophyll molecule, nitrogen helps keep plants green. Nitrogen, along with magnesium, is the only element in the chlorophyll molecule that the plant obtains from the soil. element and as a catalyst for biochemical reactions. Phosphorus is a component of DNA and ATP. It also plays vital roles in capturing light during photosynthesis, helping with seed germination, and helping plants use water efficiently. Plants also use phosphorus to help fight external stress and prevent disease.
element and as a catalyst for biochemical reactions. Phosphorus is a component of DNA and ATP. It also plays vital roles in capturing light during photosynthesis, helping with seed germination, and helping plants use water efficiently. Plants also use phosphorus to help fight external stress and prevent disease. not a part of any important plant structure, it plays critical roles in several physiological processes. Potassium activates enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions involved with growth. It plays an important role in water balance by regulating the opening and closing of stomates (the pores in leaves through which gases are exchanged). Potassium also helps regulate the rate of photosynthesis through its role in the production of ATP. Other aspects of plant health influenced by potassium include the growth of strong stalks, protection from extreme temperatures, and the ability to fight stress and pests such as weeds and insects.
not a part of any important plant structure, it plays critical roles in several physiological processes. Potassium activates enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions involved with growth. It plays an important role in water balance by regulating the opening and closing of stomates (the pores in leaves through which gases are exchanged). Potassium also helps regulate the rate of photosynthesis through its role in the production of ATP. Other aspects of plant health influenced by potassium include the growth of strong stalks, protection from extreme temperatures, and the ability to fight stress and pests such as weeds and insects.