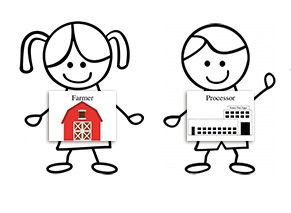
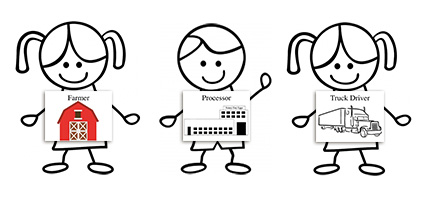
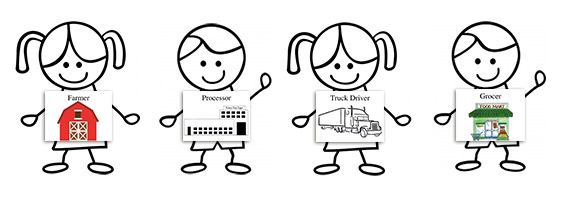
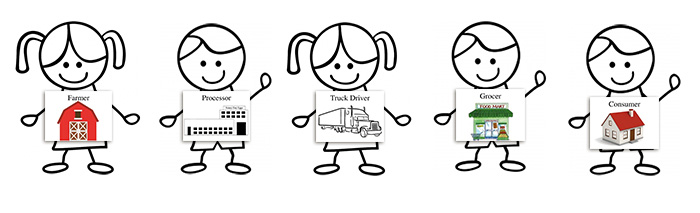
Eggs: From Hen to Home (Grades K-2)
Students trace the production path of eggs, beginning on the farm and ending in their home and identify the culinary uses and nutritional benefits of eggs.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner | National Agriculture in the Classroom Organization (NAITCO)
Acknowledgements
A "MAZE" ing Egg activity sheet provided by Utah Agriculture in the Classroom.
Sources
- https://www.dietaryguidelines.gov/sites/default/files/2020-07/ScientificReport_of_the_2020DietaryGuidelinesAdvisoryCommittee_first-print.pdf
- https://www.incredibleegg.org/articles/eggs-and-heart-health
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: K.110.2.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking - - oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: K.1.C: The student is expected to share information and ideas by speaking audibly and clearly using the conventions of language.
-
ELA: K.110.2.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: K.6.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as illustrating or writing.
-
ELA: 1.110.3.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking - - oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 1.1.C: The student is expected to share information and ideas about the topic under discussion, speaking clearly at an appropriate pace and using the conventions of language.
-
ELA: 1.110.3.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking -- fluency. The student reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 1.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking -- fluency. The student reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 1.110.3.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 1.7.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as illustrating or writing.
-
ELA: 2.110.4.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking -- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 2.1.C: The student is expected to share information and ideas that focus on the topic under discussion, speaking clearly at an appropriate pace and using the conventions of language.
-
ELA: 2.110.4.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking -- fluency. The student reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 2.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking -- fluency. The student reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 2.110.4.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 2.7.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as illustrating or writing.
-
Social Studies: K.113.11.c.13
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: K.113.11.c.13.D: sequence and categorize information
-
Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.16
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.16.D: sequence and categorize information
-
Social Studies: 2.113.13.c.15
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 2.113.13.c.15.D: interpret oral, visual, and print material by sequencing, categorizing, identifying the main idea, predicting, comparing, and contrasting
-
Science: 2.112.4.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that living organisms have basic needs that must be met through interactions within their environment. The student is expected to:
- Science: 2.112.4.b.12.A: describe how the physical characteristics of environments, including the amount of rainfall, support plants and animals within an ecosystem