Freshest Fruits
Students determine where fruits grow and their nutritional value by completing an activity to observe the size, shape, texture, and seeds of various fruits.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Shaney Emerson and Michelle Risso | California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom
Acknowledgements
This lesson update was funded by a grant from the Network for a Healthy California.
Executive Director: Judy Culbertson
Illustrator: Erik Davison
Layout & Design: Nina Danner
Copy Editor: Leah Rosasco
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: K.110.2.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking - - oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: K.110.2.b.1.C: share information and ideas by speaking audibly and clearly using the conventions of language
- ELA: K.110.2.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others by following agreed-upon rules for discussion, including taking turns;
-
ELA: 1.110.3.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking - - oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 1.110.3.b.1.C: share information and ideas about the topic under discussion, speaking clearly at an appropriate pace and using the conventions of language
- ELA: 1.110.3.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others by following agreed-upon rules for discussion, including listening to others, speaking when recognized, and making appropriate contributions
-
ELA: 2.110.4.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking -- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 2.110.4.b.1.C: share information and ideas that focus on the topic under discussion, speaking clearly at an appropriate pace and using the conventions of language
- ELA: 2.110.4.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others by following agreed-upon rules for discussion, including listening to others, speaking when recognized, making appropriate contributions, and building on the ideas of others
-
Math: K.111.2.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop an understanding of addition and subtraction situations in order to solve problems.
- Math: K.111.2.b.3.B: solve word problems using objects and drawings to find sums up to 10 and differences within 10
-
Math: K.111.2.b.8
Data analysis. The student applies mathematical process standards to collect and organize data to make it useful for interpreting information.
- Math: K.111.2.b.8.B: use data to create real-object and picture graphs
- Math: K.111.2.b.8.C: draw conclusions from real-object and picture graphs
-
Math: 1.111.3.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies for whole number addition and subtraction computations in order to solve problems.
- Math: 1.111.3.b.3.D: apply basic fact strategies to add and subtract within 20, including making 10 and decomposing a number leading to a 10
-
Math: 1.111.3.b.8
Data analysis. The student applies mathematical process standards to organize data to make it useful for interpreting information and solving problems.
- Math: 1.111.3.b.8.B: use data to create picture and bar-type graphs
- Math: 1.111.3.b.8.C: draw conclusions and generate and answer questions using information from picture and bar-type graphs
-
Math: 2.111.4.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve addition and subtraction problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 2.111.4.b.4.A: recall basic facts to add and subtract within 20 with automaticity
-
Math: 2.111.4.b.10
Data analysis. The student applies mathematical process standards to organize data to make it useful for interpreting information and solving problems.
- Math: 2.111.4.b.10.B: organize a collection of data with up to four categories using pictographs and bar graphs with intervals of one or more
- Math: 2.111.4.b.10.D: draw conclusions and make predictions from information in a graph
-
Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.9
Economics. The student understands the value of work. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.9.B: describe how various jobs contribute to the production of goods and services
-
Social Studies: 2.113.13.c.16
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 2.113.13.c.16.E: communicate information visually, orally, or in writing based on knowledge and experiences in social studies
-
Social Studies: K.113.11.c.14
Social studies skills. The student communicates in oral and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: K.113.11.c.14.C: communicate information visually, orally, or in writing based on knowledge and experiences in social studies
- Social Studies: K.113.11.c.14.D: create and interpret visuals, including pictures and maps
-
Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.17
Social studies skills. The student communicates in oral, visual, and written forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.17.C: communicate information visually, orally, or in writing based on knowledge and experiences in social studies
- Social Studies: 1.113.12.c.17.D: create and interpret visual and written material
-
Science: 2.112.4.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 2.112.4.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 2.112.4.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 2.112.4.b.1.F: record and organize data using pictures, numbers, words, symbols, and simple graphs
-
Science: K.112.2.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: K.112.2.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations.
- Science: K.112.2.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence.
- Science: K.112.2.b.1.F: record and organize data using pictures, numbers, words, symbols, and simple graphs.
-
Science: K.112.2.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: K.112.2.b.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models.
- Science: K.112.2.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats.
-
Science: K.112.2.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: K.112.2.b.4.A: explain how science or an innovation can help others.
-
Science: K.112.2.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student uses recurring themes and concepts to make connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: K.112.2.b.5.A: identify and use patterns to describe phenomena or design solutions.
- Science: K.112.2.b.5.F: describe the relationship between the structure and function of objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: K.112.2.b.6
Matter and its properties. The student knows that objects have physical properties that determine how they are described and classified. The student is expected to identify and record observable physical properties of objects, including shape, color, texture, and material, and generate ways to classify objects.
- Science: K.112.2.b.6: Matter and its properties. The student knows that objects have physical properties that determine how they are described and classified. The student is expected to identify and record observable physical properties of objects, including shape, color, texture, and material, and generate ways to classify objects.
-
Science: K.112.2.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that plants and animals depend on the environment to meet their basic needs for survival. The student is expected to:
- Science: K.112.2.b.12.A: observe and identify the dependence of plants on air, sunlight, water, nutrients in the soil, and space to grow.
-
Science: K.112.2.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows that organisms resemble their parents and have structures and undergo processes that help them interact and survive within their environments. The student is expected to:
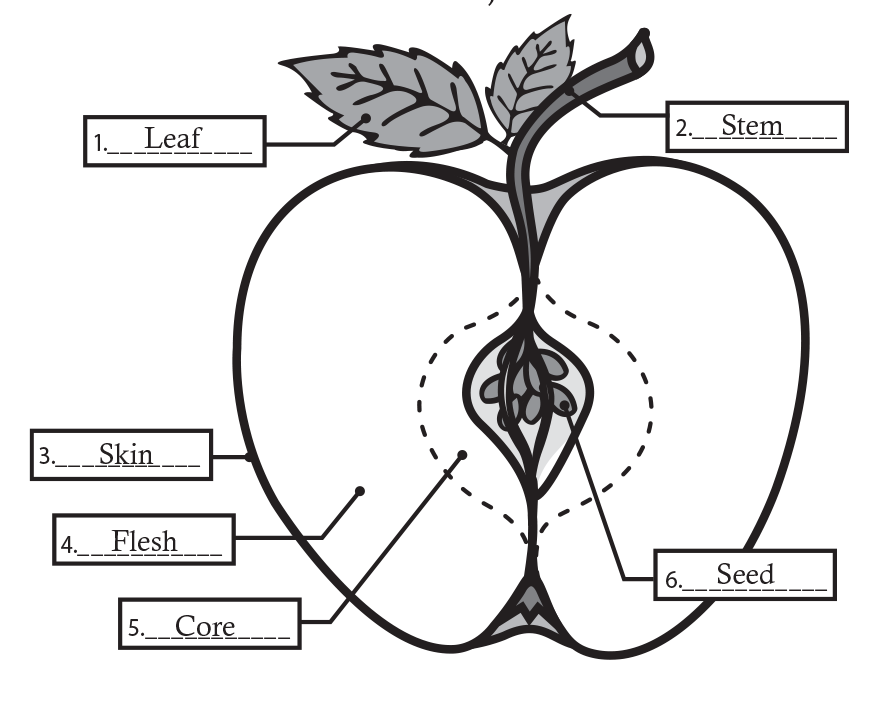
- Science: K.112.2.b.13.A: identify the structures of plants, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Science: K.112.2.b.13.C: identify and record the changes from seed, seedling, plant, flower, and fruit in a simple plant life cycle.
- Science: K.112.2.b.13.D: identify ways that young plants resemble the parent plant.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations.
- Science: 1.112.3.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence.
- Science: 1.112.3.b.1.F: record and organize data using pictures, numbers, words, symbols, and simple graphs.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models.
- Science: 1.112.3.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.4.A: explain how science or an innovation can help others.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student uses recurring themes and concepts to make connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.5.A: identify and use patterns to describe phenomena or design solutions.
- Science: 1.112.3.b.5.F: describe the relationship between the structure and function of objects, organisms, and systems.
- Science: 1.112.3.b.5.G: describe how factors or conditions can cause objects, organisms, and systems to either change or stay the same.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.6
Matter and its properties. The student knows that objects have physical properties that determine how they are described and classified. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.6.A: classify objects by observable physical properties, including shape, color, and texture, and attributes such as larger and smaller and heavier and lighter.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.11
Earth and space. The student knows that earth materials and products made from these materials are important to everyday life. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.11.A: identify and describe how plants, animals, and humans use rocks, soil, and water.
-
Science: 1.112.3.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that the environment is composed of relationships between living organisms and nonliving components. The student is expected to:
- Science: 1.112.3.b.12.A: classify living and nonliving things based upon whether they have basic needs and produce young.
- Science: 1.112.3.b.12.C: identify and illustrate how living organisms depend on each other through food chains.
-
Science: 2.112.4.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 2.112.4.b.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models
- Science: 2.112.4.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Science: 2.112.4.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 2.112.4.b.4.A: explain how science or an innovation can help others
-
Science: 2.112.4.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student uses recurring themes and concepts to make connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 2.112.4.b.5.A: identify and use patterns to describe phenomena or design solutions
- Science: 2.112.4.b.5.F: describe the relationship between the structure and function of objects, organisms, and systems
-
Science: 2.112.4.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows that organisms have structures and undergo processes that help them interact and survive within their environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 2.112.4.b.13.A: identify the roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds of plants and compare how those structures help different plants meet their basic needs for survival