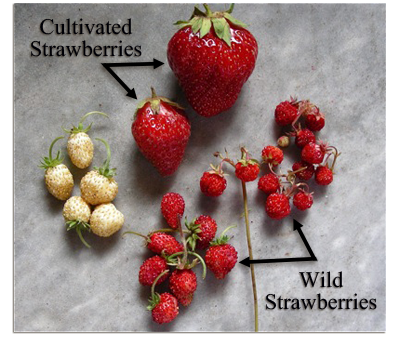
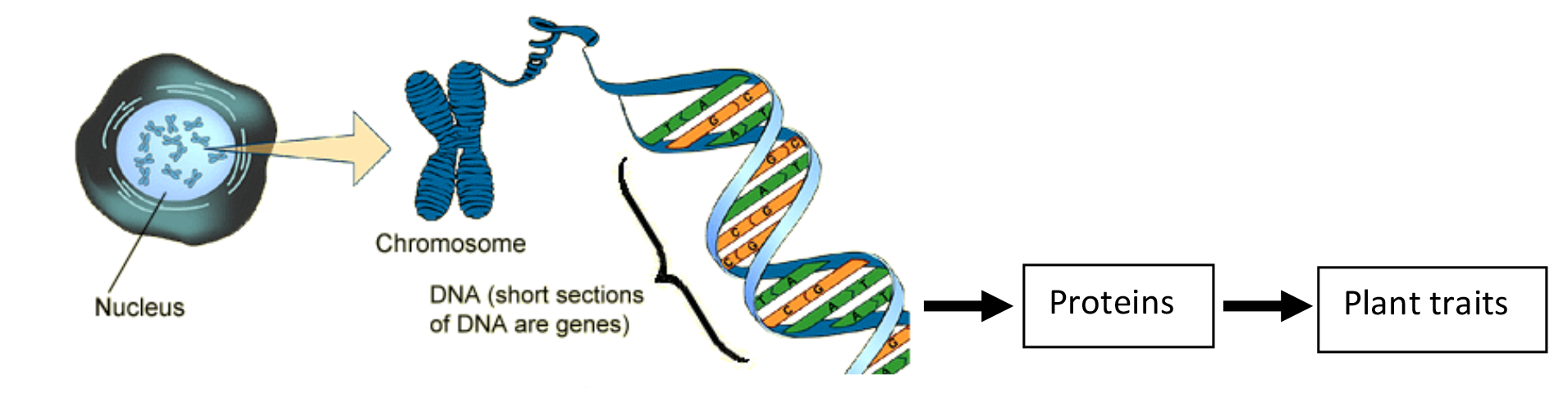
Strawberry Breeding and Genetics
Students learn about DNA by extracting it from strawberries. Students also analyze the similarities and differences of their extraction process to those on Genetic Engineering: The Journey of a Gene. Students learn how genetic testing (including DNA extraction) is useful in breeding new varieties of strawberries.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Caitlin Falcone, Erin Ingram, and Molly Brandt | University of Nebraska – Lincoln
Acknowledgements
Author Affiliations:
- Caitlin Falcone: Lourdes Central Catholic, Nebraska City, NE
- Erin Ingram: University of Nebraska-Lincoln, IANR Science Literacy Initiative, National Center for Agricultural Literacy
- Molly Brandt: University of Nebraska-Lincoln, IANR Science Literacy Initiative, National Center for Agricultural Literacy
Sources
- http://ffanewhorizons.org/farm-facts-about-strawberries/
- http://www.agmrc.org/commodities-products/fruits/strawberries/
- https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2010/12/101226131607.htm
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.A: define the scope of agriculture.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to plant systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.C: describe plant reproduction, genetics, and breeding.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.D: identify plants of importance to agriculture, food, and natural resources
-
World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.21
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.21.F: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning for an intended audience and purpose
-
Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and Its Benefits: 113.31.d.21
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and Its Benefits: 113.31.d.21.F: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning for an intended audience and purpose
-
English I: 110.36.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English I: 110.36.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, building on the ideas of others, contributing relevant information, developing a plan for consensus building, and setting ground rules for decision making
-
English I: 110.36.c.11
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- English I: 110.36.c.11.F: synthesize information from a variety of sources
-
English II: 110.37.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundation language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English II: 110.37.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, building on the ideas of others, contributing relevant information, developing a plan for consensus building, and setting ground rules for decision making
-
English III: 110.38.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English III: 110.38.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, offering ideas or judgments that are purposeful in moving the team toward goals, asking relevant and insightful questions, tolerating a range of positions and ambiguity in decision making, and evaluating the work of the group based on agreed-upon criteria
-
English II: 110.37.c.11
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- English II: 110.37.c.11.F: synthesize information from a variety of sources
-
English III: 110.38.c.11
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- English III: 110.38.c.11.F: synthesize information from a variety of sources
-
English IV: 110.39.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English IV: 110.39.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, offering ideas or judgments that are purposeful in moving the team toward goals, asking relevant and insightful questions, tolerating a range of positions and ambiguity in decision making, and evaluating the work of the group based on agreed-upon criteria
-
English IV: 110.39.c.11
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- English IV: 110.39.c.11.F: synthesize information from a variety of sources
-
Advanced Animal Science: 130.10.c.8
The student applies the principles of molecular genetics and heredity. The student is expected to:
- Advanced Animal Science: 130.10.c.8.C: identify the parts of the nucleotide and the difference between the nucleotides found in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) versus ribonucleic acid (RNA).
- Advanced Animal Science: 130.10.c.8.D: explain the functions of DNA and RNA.
- Advanced Animal Science: 130.10.c.8.E: describe how heredity is used in the selection of livestock such as knowing the difference between outbreeding and inbreeding/linebreeding.
-
World History Studies: 113.42.d.28
Social studies skills. The student understands how historians use historiography to interpret the past and applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- World History Studies: 113.42.d.28.F: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning for an intended audience and purpose
-
Advanced Plant and Soil Science: 130.25.c.15
The student evaluates components of plant science as they relate to crop production. The student is expected to:
- Advanced Plant and Soil Science: 130.25.c.15.A: analyze plant physiology, genetics, and reproduction of various crops.
-
Advanced Plant and Soil Science: 130.25.c.17
The student diagrams the structure and function of nucleic acids in the mechanism of genetics. The student is expected to:
- Advanced Plant and Soil Science: 130.25.c.17.A: describe components of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and illustrate how information for specifying the traits of an organism is carried in DNA.
- Advanced Plant and Soil Science: 130.25.c.17.B: identify and illustrate how changes in DNA cause phenotypic or genotypic changes.
- Advanced Plant and Soil Science: 130.25.c.17.C: compare and contrast genetic variations observed in plants and animals.
-
Biology: 112.42.c.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Biology: 112.42.c.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Biology: 112.42.c.1.D: use appropriate tools such as microscopes, slides, Petri dishes, laboratory glassware, metric rulers, digital balances, pipets, filter paper, micropipettes, gel electrophoresis and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) apparatuses, microcentrifuges, water baths, incubators, thermometers, hot plates, data collection probes, test tube holders, lab notebooks or journals, hand lenses, and models, diagrams, or samples of biological specimens or structures
- Biology: 112.42.c.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence
- Biology: 112.42.c.1.F: organize quantitative and qualitative data using scatter plots, line graphs, bar graphs, charts, data tables, digital tools, diagrams, scientific drawings, and student-prepared models
- Biology: 112.42.c.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems
-
Biology: 112.42.c.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Biology: 112.42.c.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models and consistent with scientific ideas, principles, and theories
-
Biology: 112.42.c.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Biology: 112.42.c.4.B: relate the impact of past and current research on scientific thought and society, including research methodology, cost-benefit analysis, and contributions of diverse scientists as related to the content
- Biology: 112.42.c.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field in order to investigate STEM careers
-
Biology: 112.42.c.7
Science concepts--mechanisms of genetics. The student knows the role of nucleic acids in gene expression. The student is expected to:
- Biology: 112.42.c.7.A: identify components of DNA, explain how the nucleotide sequence specifies some traits of an organism, and examine scientific explanations for the origin of DNA
- Biology: 112.42.c.7.B: describe the significance of gene expression and explain the process of protein synthesis using models of DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
- Biology: 112.42.c.7.C: identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes
- Biology: 112.42.c.7.D: discuss the importance of molecular technologies such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), gel electrophoresis, and genetic engineering that are applicable in current research and engineering practices