At Home on the Range (Grades 3-5)
Students investigate rangelands by growing their own grass to represent a beef or sheep ranch.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Debra Spielmaker | Utah Agriculture in the Classroom
Acknowledgements
Story-writing activity (Activity 3) contributed by Hooper Elementary (Hooper, UT) teacher Sharlie Wade.
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 3.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 3.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 3.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 3.7.F: The student is expected to respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.1.D: The student is expected to work collaboratively with other to develop a plan of shared responsibilities.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 4.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 4.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 4.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 4.7.F: The student is expected to respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 5.1.D: The student is expected to work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 5.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 5.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 5.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 5.7.F: The student is expected to respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate.
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.4
Geography. The student understands the concepts of location, distance, and direction on maps and globes. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14.D: interpret and create visuals, including graphs, charts, tables, timelines, illustrations, and maps
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.4.C: identify, create, and interpret maps of places that contain map elements, including a title, compass rose, legend, scale, and grid system
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 3.1.A: The student is expected to apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace.
- Math: 3.1.C: The students is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems.
-
Math: 3.111.5.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 3.4.A: The student is expected to solve with fluency one-step and two-step problems involving addition and subtraction within 1,000 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
- Math: 3.4.G: The student is expected to use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, the multiply a two-digit number by a one-digit number. Strategies may include mental mathm partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties.
- Math: 3.4.K: The student is expected to solve one-step and two-step problems involving multiplication and division within 100 using strategies based on objects: pictorial models, including arrays, area models, and equal groups: properties of operation; or recall of facts.
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 4.1.A: The student is expected to apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace.
- Math: 4.1.C: The students is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems.
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.2
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent, compare, and order whole numbers and decimals and understand relationships related to place value.
- Math: 4.2.D: The student is expected to round whole numbers to a given place value through the hundred thousands place.
-
Math: 4.111.6.b.4
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 4.4.A: The student is expected to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals to the hundredths place using the standard algorithm.
- Math: 4.4.D: The student is expected to use strategies and algorithms, including the standard algorithm, the multiply up to a four-digit number by a one-digit number and to multiply a two-digit number by a two-digit number. Strategies may include mental math, partial products, and the commutative, associative, and distributive properties.
- Math: 4.4.H: The student is expected to solve with fluency one-and two-step problems involving multiplication and division, including interpreting remainders.
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding.
- Math: 5.1.A: The student is expected to apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace.
- Math: 5.1.C: The students is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems.
-
Math: 5.111.7.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop and use strategies and methods for whole number computations in order to solve problems with efficiency and accuracy.
- Math: 5.3.B: The student is expected to multiply with fluency a three-digit number by a two-digit number using the standard algorithm.
- Math: 5.3.E: The student is expected to solve for products of decimals to the hundredths, including situations involving money, using strategies based on place-value understandings, properties of operations, and the relationship to the multiplication of whole numbers.
- Math: 5.3.K: The student is expected to add and subtract positive rational numbers fluently.
-
Science: 3.112.14.b.2
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses scientific practices during laboratory and outdoor investigations.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.2.A: The student is expected to plan and implement descriptive investigations, including asking and answering questions, making inferences, and selecting and using equipment or technology needed, to solve a specific problem in the natural world.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.2.B: The student is expected to collect and record data by observing and measuring using the metric system and recognize differences between observed and measured data.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.2.F: The student is expected to communicate valid conclusions supported by data in writing, by drawing pictures, and through verbal discussion.
-
Science: 3.112.14.b.9
Organisms and environments. The student knows and can describe patterns, cycles, systems, and relationships within the environments.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.9.A: The student is expected to observe and describe the physical characteristics of environments and how they support populations and communities of plants and animals within an ecosystem.
-
Science: 3.112.14.b.10
Organisms and environments. The student knows that organisms undergo similar life processes and have structures that help them survive within their environments.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.10.A: The student is expected to explore how structures and functions of plants and animals allow them to survive in a particular environment.
-
Science: 4.112.15.b.2
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses scientific practices during laboratory and outdoor investigations.
- Science: 4.2.A: The student is expected to plan and implement descriptive investigations, including asking well defined questions, making inferences, and selecting and using appropriate equipment or technology to answer his/her questions.
- Science: 4.2.B: The student is expected to collect and record data by observing and measuring, using the metric system, and using descriptive words.
- Science: 4.2.F: The student is expected to communicate valid oral and written results supported by data.
-
Science: 5.112.16.b.2
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses scientific practices during laboratory and outdoor investigations.
- Science: 5.2.A: The student is expected to describe, plan, and implement simple experimental investigations testing one variable.
- Science: 5.2.C: The student is expected to collect and record information using detailed observations and accurate measuring.
- Science: 5.2.D: The student is expected to analyze and interpret information to construct reasonable explanations from direct (observable) and indirect (inferred) evidence.
- Science: 5.2.F: The student is expected to communicate valid conclusions in both written and verbal forms.
-
Science: 5.112.16.b.9
Organisms and environments. The student know s that there are relationships, systems, and cycles within environments.
- Science: 5.9.C: The student is expected to predict the effects of changes in ecosystems caused by living organisms, including humans, such as the overpopulation of grazers or the building of highways.
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15.A: use social studies terminology correctly
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15.D: express ideas orally based on knowledge and experiences
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19.C: analyze information by applying absolute and relative chronology through sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions;
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.7
Geography. The student understands the location and patterns of settlement and the geographic factors that influence where people live. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.7.A: identify and describe the patterns of settlement such as rural, urban, and suburban
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23.C: analyze information by applying absolute and relative chronology through sequencing, categorizing, identifying cause-and-effect relationships, comparing, contrasting, finding the main idea, summarizing, making generalizations and predictions, and drawing inferences and conclusions
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant features, patterns, or sources of error
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student describes patterns, cycles, systems, and relationships within environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.12.B: predict how changes in the ecosystem affect the cycling of matter and flow of energy in a food web

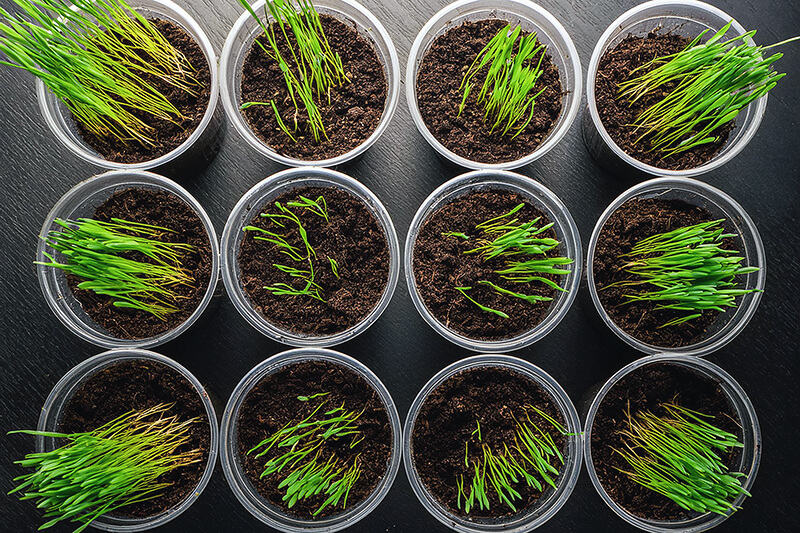
 Once the seeds germinate, keep the peat pots moist, and allow the grass to grow until it has reached 2–3 inches (5-7 cm) in height. Students will be applying two different grazing treatments and will leave some of the grass untreated.
Once the seeds germinate, keep the peat pots moist, and allow the grass to grow until it has reached 2–3 inches (5-7 cm) in height. Students will be applying two different grazing treatments and will leave some of the grass untreated.