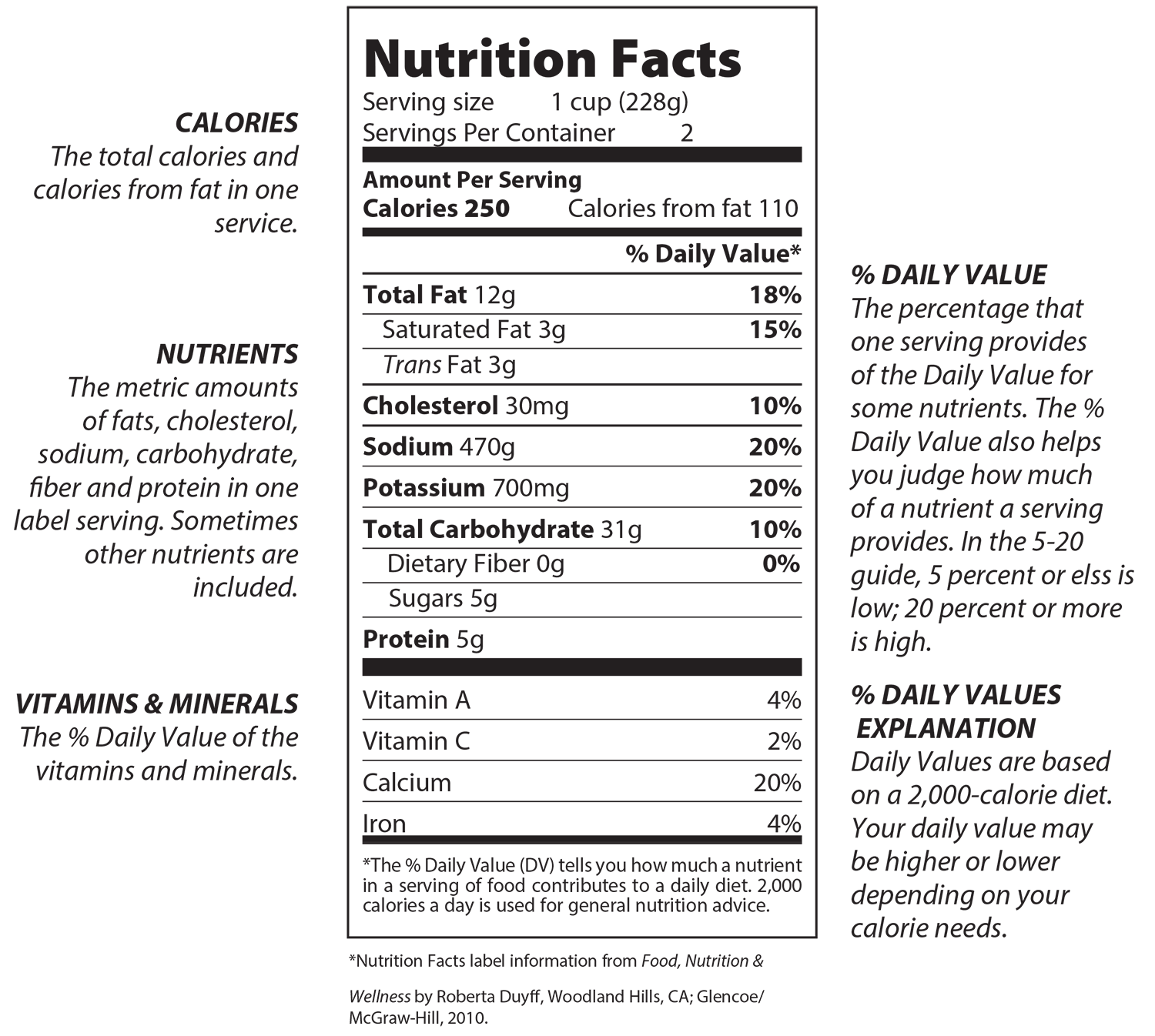
FoodMASTER Middle: Weights and Measures
Students will use common household measurement tools and scientific measurement tools and various methods of measurement to compare for accuracy. Students will also calculate percent error by comparing their measurements to actual values and apply these principles to analyze and decipher the components of a food as indicated on the Nutrition Facts label.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
FoodMASTER
Acknowledgements
This lesson was partnered with East Carolina University. The FoodMASTER program was supported by the Science Education Partnership Award (SEPA) which is funded from the National Center for Research Resources, a component of the National Institutes of Health.
- Primary Authors:
- Virginia Stage, PhD, RDN, LDN
- Mary White
- Ashley Roseno, MAEd, MS, RDN, LDN
- Melani W. Duffrin, PhD, RDN, LDN
- Graphic Design: Cara Cairns Design, LLC
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.D: use appropriate tools such as graduated cylinders, metric rulers, periodic tables, balances, scales, thermometers, temperature probes, laboratory ware, timing devices, pH indicators, hot plates, models, microscopes, slides, life science models, petri dishes, dissecting kits, magnets, spring scales or force sensors, tools that model wave behavior, satellite images, hand lenses, and lab notebooks or journals;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to assess quantitative relationships in data; and
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that interdependence occurs between living systems and the environment. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.12.A: investigate how organisms and populations in an ecosystem depend on and may compete for biotic factors such as food and abiotic factors such as availability of light and water, range of temperatures, or soil composition;
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.D: use appropriate tools such as graduated cylinders, metric rulers, periodic tables, balances, scales, thermometers, temperature probes, laboratory ware, timing devices, pH indicators, hot plates, models, microscopes, slides, life science models, petri dishes, dissecting kits, magnets, spring scales or force sensors, tools that model wave behavior, satellite images, hand lenses, and lab notebooks or journals;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to assess quantitative relationships in data; and
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands that ecosystems are dependent upon the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.A: diagram the flow of energy within trophic levels and describe how the available energy decreases in successive trophic levels in energy pyramids; and
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.D: use appropriate tools such as graduated cylinders, metric rulers, periodic tables, balances, scales, thermometers, temperature probes, laboratory ware, timing devices, pH indicators, hot plates, models, microscopes, slides, life science models, petri dishes, dissecting kits, magnets, spring scales or force sensors, tools that model wave behavior, satellite images, weather maps, hand lenses, and lab notebooks or journals;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to assess quantitative relationships in data; and
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Math: 6.111.26.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 6.111.26.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
- Math: 6.111.26.b.1.C: select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems
-
Math: 6.111.26.b.4
Proportionality. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop an understanding of proportional relationships in problem situations. The student is expected to:
- Math: 6.111.26.b.4.H: convert units within a measurement system, including the use of proportions and unit rates
-
Math: 7.111.27.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 7.111.27.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
- Math: 7.111.27.b.1.C: select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems
-
Math: 7.111.27.b.4
Proportionality. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent and solve problems involving proportional relationships. The student is expected to:
- Math: 7.111.27.b.4.E: convert between measurement systems, including the use of proportions and the use of unit rates
-
Math: 8.111.28.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 8.111.28.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
- Math: 8.111.28.b.1.C: select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems
-
Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.D: design a plan collaboratively using visual representation to document a problem, possible solutions, and an expected timeline for the development of a coded solution