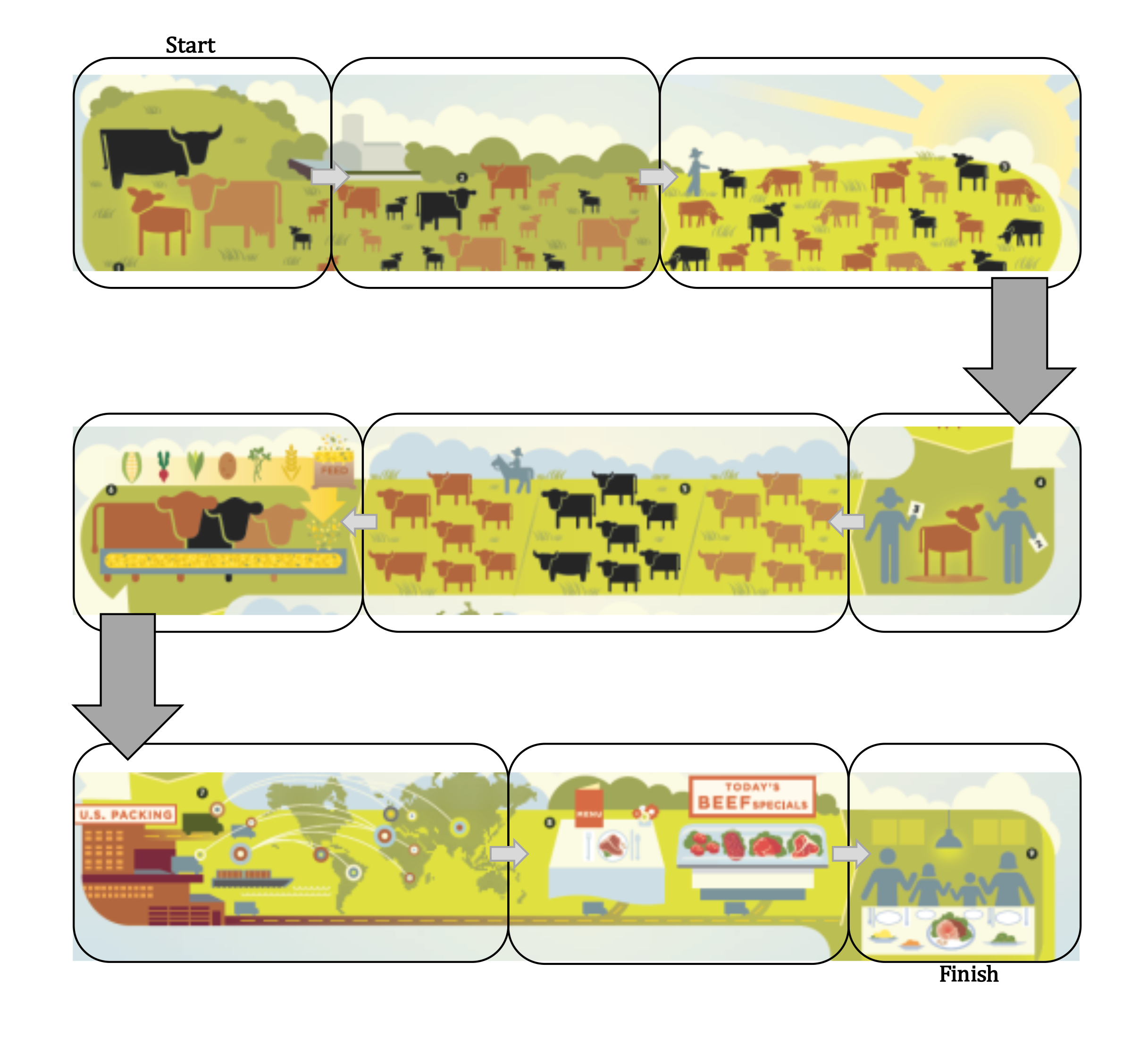
The Remarkable Ruminant
In this lesson, students will follow the farm to fork process of producing beef, learn how cattle and other ruminants convert grass into nutrient-rich foods such as milk and meat, discover ways cattle recycle food waste, and identify careers in the beef cattle industry.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Katy Wright | Arizona Beef Council
Acknowledgements
- Beef lifecycle image in Activity 1 is from the explorebeef.org website.
- Remarkable Ruminant worksheet in Activity 2 is from the Iowa Beef Council.
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.E: identify careers in agriculture, food, and natural resources with required aptitudes in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, language arts, and social studies.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to animal systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12.A: describe animal growth and development.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12.C: identify and evaluate breeds and classes of livestock.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12.D: explain animal selection, reproduction, breeding, and genetics.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.11
Economics. The student understands the factors that caused Texas to change from an agrarian to an urban society. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.11.B: explain the changes in the types of jobs and occupations that have resulted from the urbanization of Texas
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.G: evaluate details read to determine key ideas
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.1.D: participate collaboratively in discussions, plan agendas with clear goals and deadlines, set time limits for speakers, take notes, and vote on key issues
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.6
Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is made of atoms, can be classified according to its properties, and can undergo changes. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.6.B: investigate the physical properties of matter to distinguish between pure substances, homogeneous mixtures (solutions), and heterogeneous mixtures;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.6.C: identify elements on the periodic table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, and rare Earth elements based on their physical properties and importance to modern life;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.6.D: compare the density of substances relative to various fluids; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that interdependence occurs between living systems and the environment. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.12.A: investigate how organisms and populations in an ecosystem depend on and may compete for biotic factors such as food and abiotic factors such as availability of light and water, range of temperatures, or soil composition;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.6
Matter and energy. The student distinguishes between elements and compounds, classifies changes in matter, and understands the properties of solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.6.C: distinguish between physical and chemical changes in matter;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.6.D: describe aqueous solutions in terms of solute and solvent, concentration, and dilution; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.6.E: investigate and model how temperature, surface area, and agitation affect the rate of dissolution of solid solutes in aqueous solutions.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands that ecosystems are dependent upon the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.A: diagram the flow of energy within trophic levels and describe how the available energy decreases in successive trophic levels in energy pyramids; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.B: describe how ecosystems are sustained by the continuous flow of energy and the recycling of matter and nutrients within the biosphere.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows how systems are organized and function to support the health of an organism and how traits are inherited. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.13.A: identify and model the main functions of the systems of the human organism, including the circulatory, respiratory, skeletal, muscular, digestive, urinary, reproductive, integumentary, nervous, immune, and endocrine systems
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.6
Matter and energy. The student understands that matter can be classified according to its properties and matter is conserved in chemical changes that occur within closed systems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.6.A: explain by modeling how matter is classified as elements, compounds, homogeneous mixtures, or heterogeneous mixtures;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.6.E: investigate how mass is conserved in chemical reactions and relate conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms using chemical equations, including photosynthesis
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands stability and change in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.12.A: explain how disruptions such as population changes, natural disasters, and human intervention impact the transfer of energy in food webs in ecosystems;
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.1.D: participate in student-led discussions by eliciting and considering suggestions from other group members, taking notes, and identifying points of agreement and disagreement.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.G: evaluate details read to determine key ideas
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.D: paraphrase and summarize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.1.D: engage in meaningful discourse and provide and accept constructive feedback from others
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.D: paraphrase and summarize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.5.G: evaluate details read to determine key ideas
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.D: paraphrase and summarize texts in ways that maintain meaning and logical order
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.F: respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate