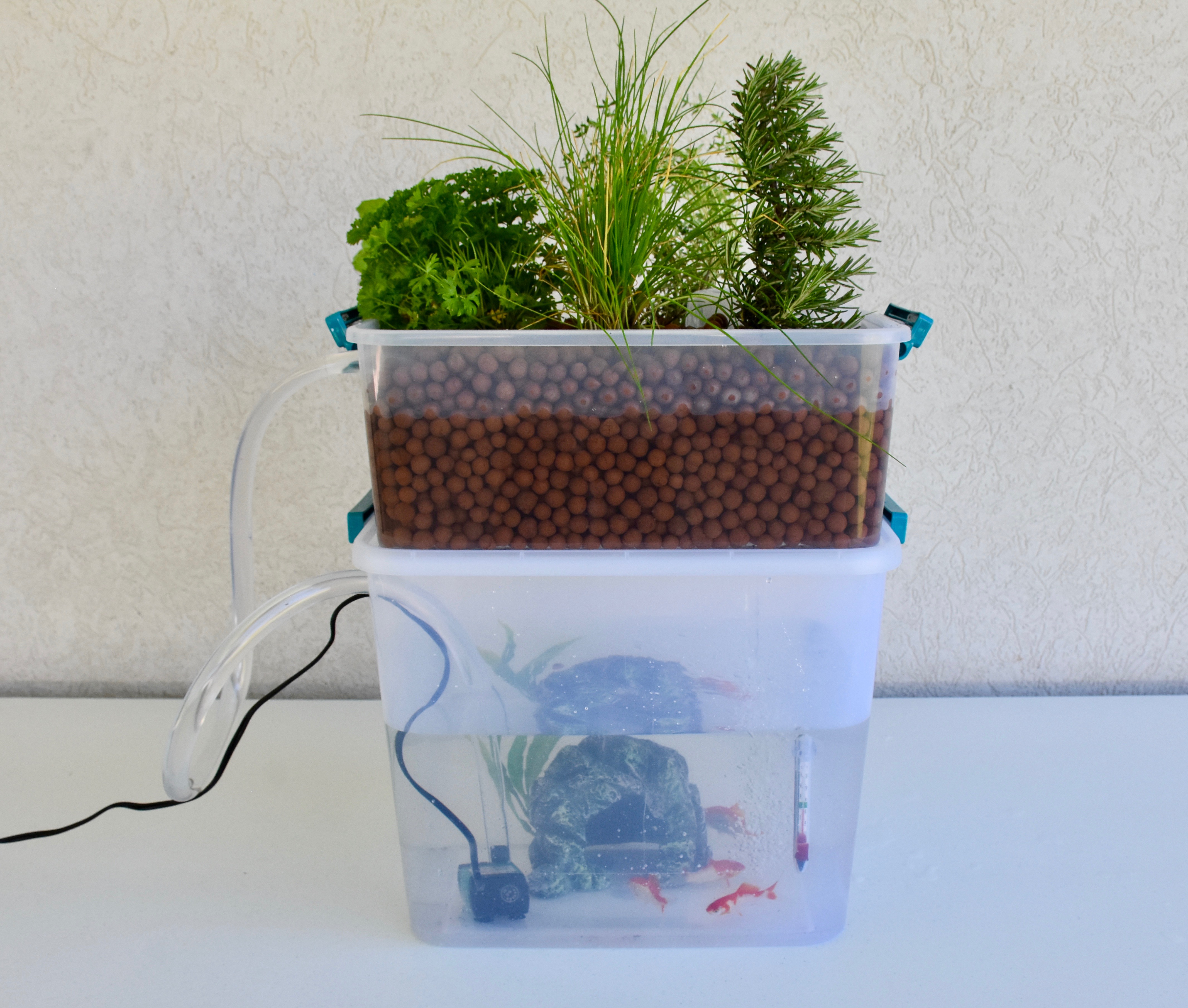
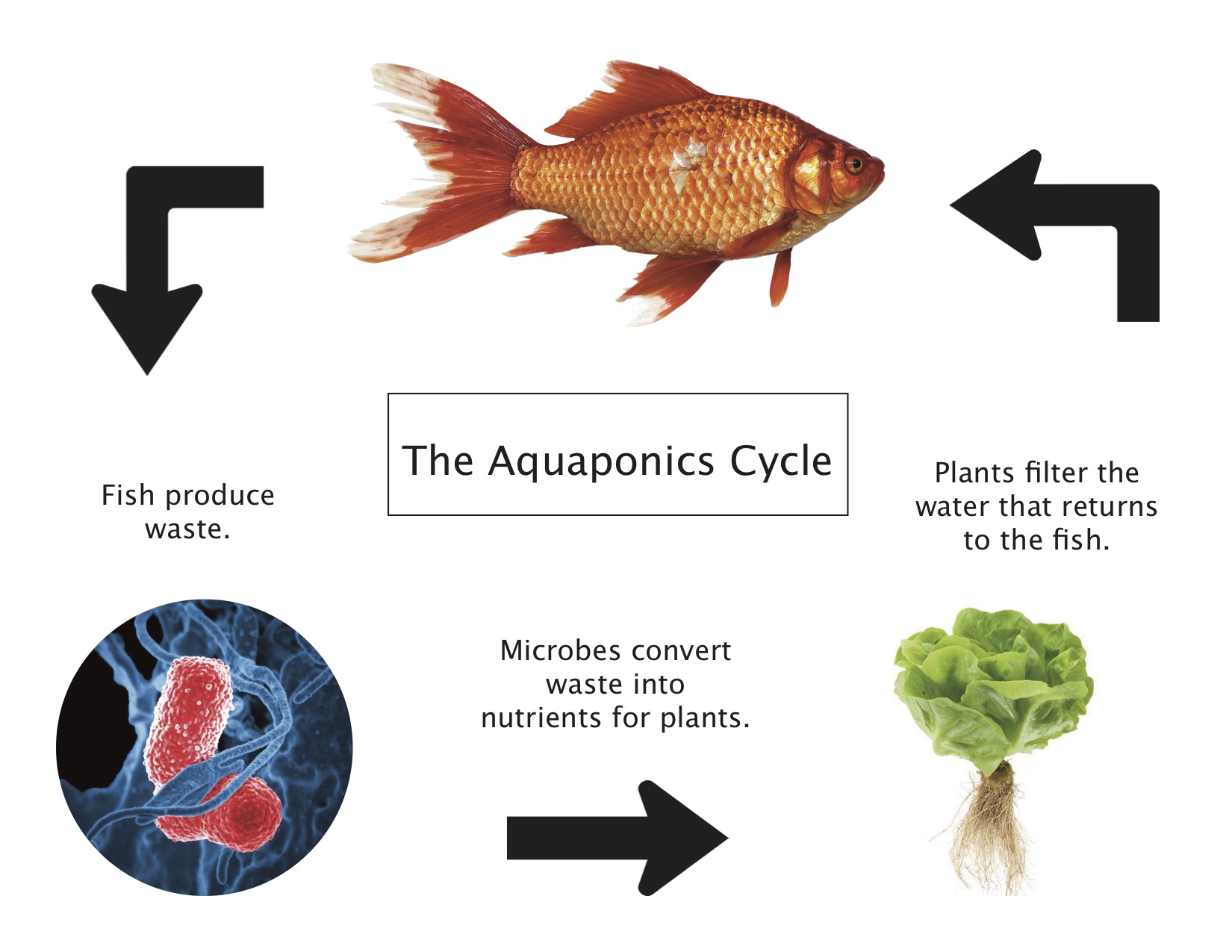
Exploring Aquaponics (Grades 3-5)
Students identify the basic needs of plants and fish and engineer, assemble, maintain, and observe a small-scale aquaponics system that meets plant and fish needs.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Lynn Wallin | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Acknowledgements
- Activity 1 was adapted from the lesson What Do Plants Need to Grow? created by the California Foundation for Agriculture in the Classroom.
- Classroom Aquaponics System Assembly and Maintenance Guide created by Joe Furse for the National Center for Agricultural Literacy.
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.1.C: express an opinion supported by accurate information, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, and the conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.4
Geography. The student understands the concepts of location, distance, and direction on maps and globes. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.14.D: interpret and create visuals, including graphs, charts, tables, timelines, illustrations, and maps
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.13
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.13.E: demonstrate understanding of information gathered
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.13.H: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.8
Geography. The student understands how people adapt to and modify their environment. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.8.B: explain reasons why people have adapted to and modified their environment in Texas, past and present, such as the use of natural resources to meet basic needs, facilitate transportation, and enhance recreational activities
-
Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 3.113.14.c.15.D: express ideas orally based on knowledge and experiences
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.19.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
- Social Studies: 4.113.15.c.21.D: create written and visual material such as journal entries, reports, graphic organizers, outlines, and bibliographies
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.23.D: organize and interpret information in outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
- Social Studies: 5.113.16.c.25.D: create written and visual material such as journal entries, reports, graphic organizers, outlines, and bibliographies
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.C: demonstrate safe practices and the use of safety equipment during classroom and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.D: use tools, including hand lenses; metric rulers; Celsius thermometers; wind vanes; rain gauges; graduated cylinders; beakers; digital scales; hot plates; meter sticks; magnets; notebooks; Sun, Earth, Moon system models; timing devices; materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums, aquariums, and collecting nets; and materials to support digital data collection such as computers, tablets, and cameras, to observe, measure, test, and analyze information
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, objects, and processes or design a prototype for a solution to a problem
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, properties, and material
- Science: 3.112.5.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant features, patterns, or sources of error
- Science: 3.112.5.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to compare patterns and relationships
- Science: 3.112.5.b.2.D: evaluate a design or object using criteria
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models
- Science: 3.112.5.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
- Science: 3.112.5.b.3.C: listen actively to others’ explanations to identify relevant evidence and engage respectfully in scientific discussion
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.4.A: explain how scientific discoveries and innovative solutions to problems impact science and society
- Science: 3.112.5.b.4.B: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.5.A: identify and use patterns to explain scientific phenomena or to design solutions
- Science: 3.112.5.b.5.C: use scale, proportion, and quantity to describe, compare, or model different systems
- Science: 3.112.5.b.5.D: examine and model the parts of a system and their interdependence in the function of the system
- Science: 3.112.5.b.5.E: investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter through systems
- Science: 3.112.5.b.5.G: explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how natural resources are important and can be managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.11.A: explore and explain how humans use natural resources such as in construction, in agriculture, in transportation, and to make products
- Science: 3.112.5.b.11.B: explain why the conservation of natural resources is important
- Science: 3.112.5.b.11.C: identify ways to conserve natural resources through reducing, reusing, or recycling
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student describes patterns, cycles, systems, and relationships within environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.12.B: identify and describe the flow of energy in a food chain and predict how changes in a food chain such as removal of frogs from a pond or bees from a field affect the ecosystem
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows that organisms undergo similar life processes and have structures that function to help them survive within their environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.13.B: explore, illustrate, and compare life cycles in organisms such as beetles, crickets, radishes, or lima beans
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.C: demonstrate safe practices and the use of safety equipment during classroom and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.D: use tools, including hand lenses; metric rulers; Celsius thermometers; calculators; laser pointers; mirrors; digital scales; balances; graduated cylinders; beakers; hot plates; meter sticks; magnets; notebooks; timing devices; sieves; materials for building circuits; materials to support observation of habitats of organisms such as terrariums, aquariums, and collecting nets; and materials to support digital data collection such as computers, tablets, and cameras, to observe, measure, test, and analyze information
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.F: construct appropriate graphic organizers to collect data, including tables, bar graphs, line graphs, tree maps, concept maps, Venn diagrams, flow charts or sequence maps, and input-output tables that show cause and effect
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, objects, and processes or design a prototype for a solution to a problem
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, properties, and material
- Science: 4.112.6.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant features, patterns, or sources of error
- Science: 4.112.6.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to compare patterns and relationships
- Science: 4.112.6.b.2.D: evaluate experimental and engineering designs
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models
- Science: 4.112.6.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
- Science: 4.112.6.b.3.C: listen actively to others’ explanations to identify relevant evidence and engage respectfully in scientific discussion
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.4.A: explain how scientific discoveries and innovative solutions to problems impact science and society
- Science: 4.112.6.b.4.B: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.5.A: identify and use patterns to explain scientific phenomena or to design solutions
- Science: 4.112.6.b.5.C: use scale, proportion, and quantity to describe, compare, or model different systems
- Science: 4.112.6.b.5.D: examine and model the parts of a system and their interdependence in the function of the system
- Science: 4.112.6.b.5.G: explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how natural resources are important and can be managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.11.A: identify and explain advantages and disadvantages of using Earth's renewable and nonrenewable natural resources such as wind, water, sunlight, plants, animals, coal, oil, and natural gas
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student describes patterns, cycles, systems, and relationships within environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.12.A: investigate and explain how most producers can make their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through the cycling of matter
- Science: 4.112.6.b.12.B: describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy through food webs, including the roles of the Sun, producers, consumers, and decomposers
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.C: demonstrate safe practices and the use of safety equipment during classroom and field investigations as outlined in Texas Education Agency-approved safety standards
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.D: use tools, including calculators, microscopes, hand lenses, metric rulers, Celsius thermometers, prisms, concave and convex lenses, laser pointers, mirrors, digital scales, balances, spring scales, graduated cylinders, beakers, hot plates, meter sticks, magnets, collecting nets, notebooks, timing devices, materials for building circuits, materials to support observations of habitats or organisms such as terrariums and aquariums, and materials to support digital data collection such as computers, tablets, and cameras to observe, measure, test, and analyze information
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.F: construct appropriate graphic organizers used to collect data, including tables, bar graphs, line graphs, tree maps, concept maps, Venn diagrams, flow charts or sequence maps, and input-output tables that show cause and effect
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, objects, and processes or design a prototype for a solution to a problem
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, properties, and materials
- Science: 5.112.7.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant features, patterns, or sources of error
- Science: 5.112.7.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to compare patterns and relationships
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.3.A: develop explanations and propose solutions supported by data and models
- Science: 5.112.7.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
- Science: 5.112.7.b.3.C: listen actively to others’ explanations to identify relevant evidence and engage respectfully in scientific discussion
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation for society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.4.A: explain how scientific discoveries and innovative solutions to problems impact science and society
- Science: 5.112.7.b.4.B: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.5.A: identify and use patterns to explain scientific phenomena or to design solutions
- Science: 5.112.7.b.5.C: use scale, proportion, and quantity to describe, compare, or model different systems
- Science: 5.112.7.b.5.D: examine and model the parts of a system and their interdependence in the function of the system
- Science: 5.112.7.b.5.G: explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how natural resources are important and can be managed. The student is expected to design and explain solutions such as conservation, recycling, or proper disposal to minimize environmental impact of the use of natural resources.
- Science: 5.112.7.b.11: Earth and space. The student understands how natural resources are important and can be managed. The student is expected to design and explain solutions such as conservation, recycling, or proper disposal to minimize environmental impact of the use of natural resources.
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student describes patterns, cycles, systems, and relationships within environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.12.A: observe and describe how a variety of organisms survive by interacting with biotic and abiotic factors in a healthy ecosystem
- Science: 5.112.7.b.12.B: predict how changes in the ecosystem affect the cycling of matter and flow of energy in a food web
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.13
Organisms and environments. The student knows that organisms undergo similar life processes and have structures and behaviors that help them survive within their environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.13.A: analyze the structures and functions of different species to identify how organisms survive in the same environment
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.1.C: speak coherently about the topic under discussion, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, and the conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others by following agreed-upon rules, norms, and protocols
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.13
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.13.E: demonstrate understanding of information gathered
- ELA: 3.110.5.b.13.H: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.13
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.13.E: demonstrate understanding of information gathered
- ELA: 4.110.6.b.13.H: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.1.D: work collaboratively with others to develop a plan of shared responsibilities
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 5.110.7.b.6.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.C: develop a plan collaboratively and document a plan that outlines specific steps taken to complete a project
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences.
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to analyze data in graphs to identify and discuss trends and inferences
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.C: communicate design plans and solutions using a variety of options
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question.
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions.
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to analyze and transform data and make inferences to answer questions