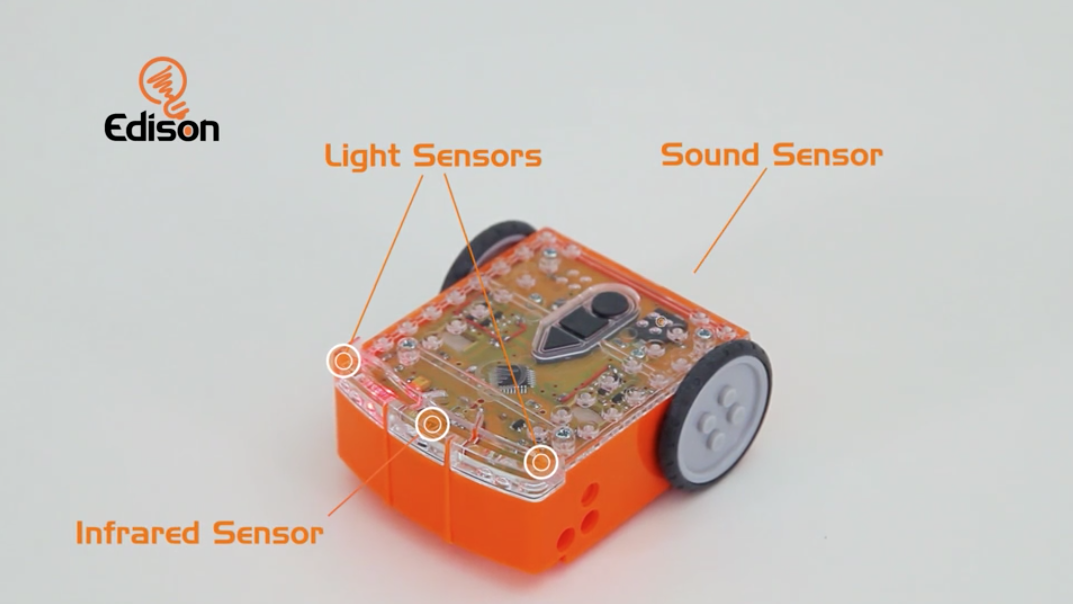
Robots in High-Tech Farming (Grades 6-8)
Students discover the four main components of robots, explore how robots are used in agriculture, and program and operate a robot to address a farming challenge.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Lynn Wallin | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- https://www.theautomationengineer.com/markets-sectors/automated-agriculture-robots-future-farming/
- https://nifa.usda.gov/topic/agriculture-technology
- http://www.handsfreehectare.com/
- https://www.sciencefriday.com/segments/the-origin-of-the-word-robot/
- https://nifa.usda.gov/announcement/usdas-national-institute-food-and-agriculture-announces-support-collaborative-robotics
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.A: identify career development, education, and entrepreneurship opportunities in the field of agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.E: identify careers in agriculture, food, and natural resources with required aptitudes in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, language arts, and social studies.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.E: describe how emerging technologies and globalization impacts agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.F: compare and contrast issues impacting agriculture, food, and natural resources such as biotechnology, employment, safety, environment, and animal welfare issues.
- Principles, of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.D: identify potential future scenarios for agriculture, food, and natural resources systems, including global impacts.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7
The student applies appropriate research methods to agriculture, food, and natural resources topics. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agricultures, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7.A: discuss major research and developments in the fields of agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.9
The student uses information technology tools to access, manage, integrate, and create information related to agriculture, food, and natural resources. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.9.C: analyze the benefits and limitations of emerging technology such as online mapping systems, drones, and robotics.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.9.D: explain the benefits of computer-based and mobile application equipment in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.b.31
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution.
- Social Studies: 8.b.31: Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 6.1.B: The student is expected to follow and give oral instructions that include multiple action steps.
- ELA: 6.1.C: The student is expected to give an organized presentation with a specific stance and position, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, natural gestures, and conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively.
- ELA: 6.1.D: The student is expected to participate in student-led discussions by eliciting and considering suggestions from other group members, taking notes, and identifying points of agreement and disagreement.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 7.1.B: The student is expected to follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems.
- ELA: 7.1.D: The student is expected to engage in meaningful discourse and provide and accept constructive feedback from others.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- ELA: 7.12.F: The student is expected to synthesize information from a variety of sources.
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 8.1.B: The student is expected to follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems.
- ELA: 8.1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively in discussions, plant agendas with clear goals and deadlines, set time limits for speakers, take notes, and vote on key issues.
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.18
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the influences of science and technology on contemporary societies. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.18.A: identify examples of scientific discoveries, technological innovations, and scientists and inventors that have shaped the world
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems; and
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.22
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.22.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.A: relate the impact of past and current research on scientific thought and society, including the process of science, cost-benefit analysis, and contributions of diverse scientists as related to the content;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.B: make informed decisions by evaluating evidence from multiple appropriate sources to assess the credibility, accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and methods used; and
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.19
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the impact of scientific discoveries and technological innovations on the political, economic, and social development of Texas. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.19.A: compare types and uses of technology, past and present
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.19.C: analyze the effects of various scientific discoveries and technological innovations on the development of Texas such as advancements in the agricultural, energy, medical, computer, and aerospace industries
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.23
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.23.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.27
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the impact of science and technology on the economic development of the United States. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.27.A: explain the effects of technological and scientific innovations such as the steamboat, the cotton gin, the telegraph, and interchangeable parts
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.31
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.31.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems; and
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.A: relate the impact of past and current research on scientific thought and society, including the process of science, cost-benefit analysis, and contributions of diverse scientists as related to the content;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.B: make informed decisions by evaluating evidence from multiple appropriate sources to assess the credibility, accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and methods used; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems; and
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.A: relate the impact of past and current research on scientific thought and society, including the process of science, cost-benefit analysis, and contributions of diverse scientists as related to the content;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.B: make informed decisions by evaluating evidence from multiple appropriate sources to assess the credibility, accuracy, cost-effectiveness, and methods used; and
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.A: decompose real-world problems into structured parts by using visual representation
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.B: analyze the patterns and sequences found in visual representations such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.D: design a plan collaboratively using visual representation to document a problem, possible solutions, and an expected timeline for the development of a coded solution
-
Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1.A: decompose real-world problems into structured parts using flowcharts