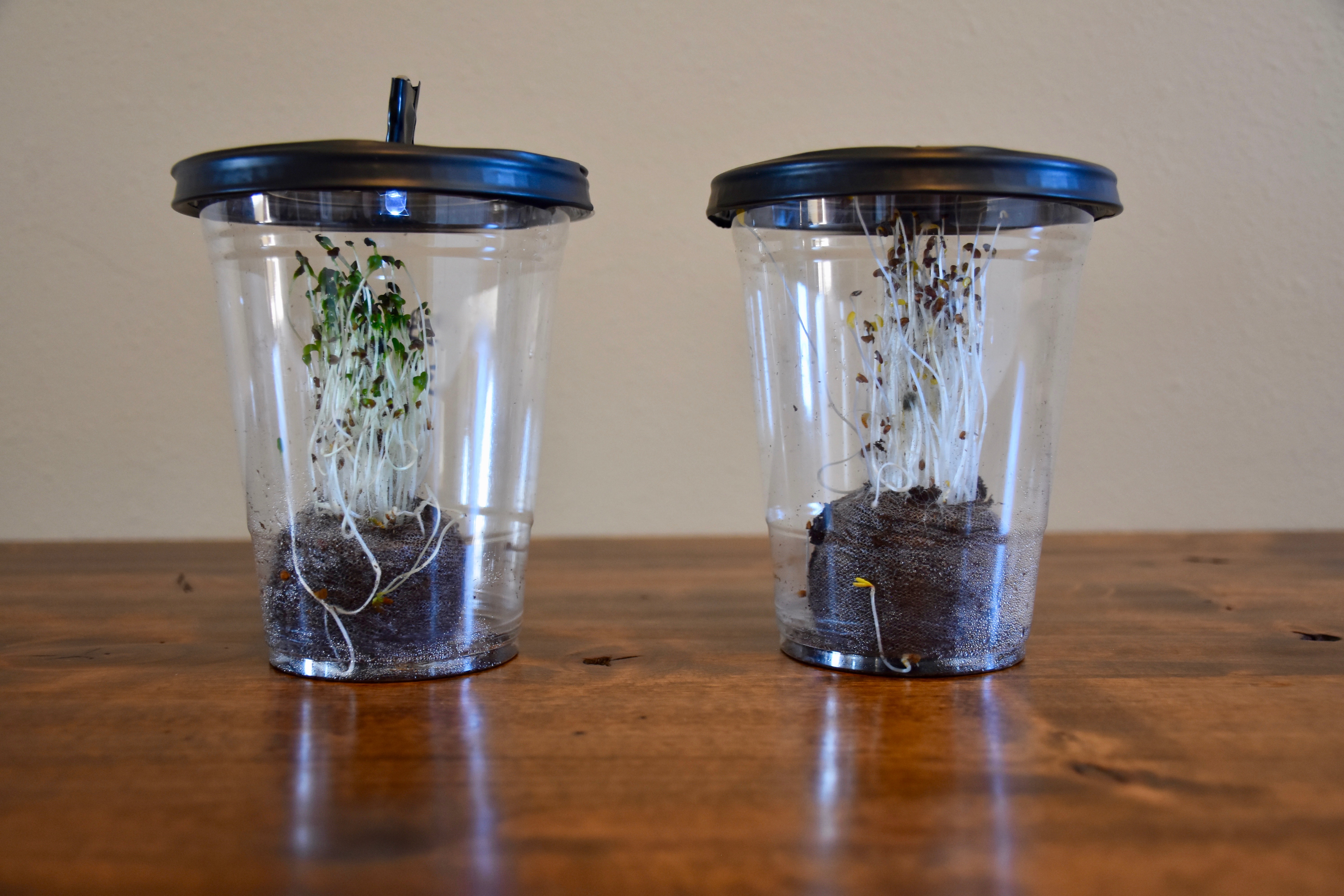
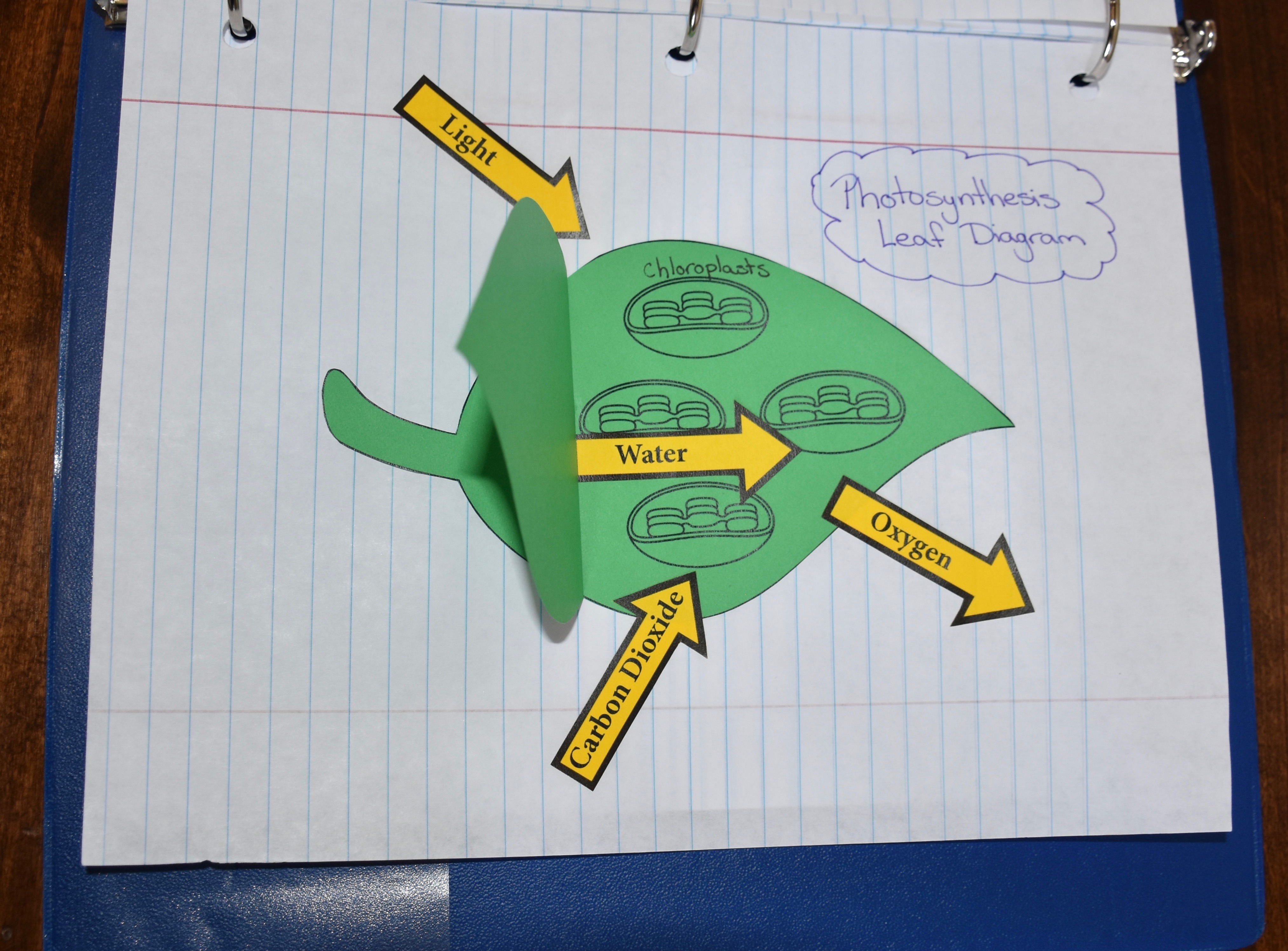
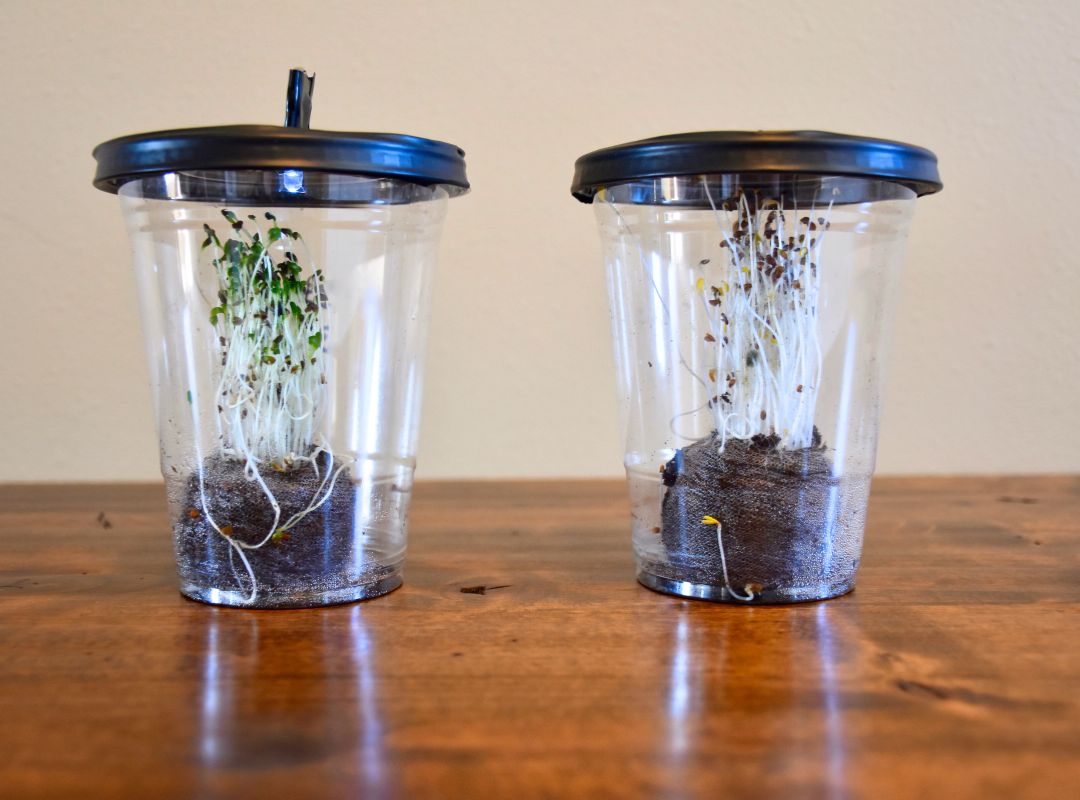
Desktop Greenhouses (Grades 3-5)
Students investigate the importance of light to plants by creating a desktop greenhouse investigation and exploring the process of photosynthesis.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Lynn Wallin | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Acknowledgements
- Storyline graphic from seedstorylines.org.
- Phenomenon chart adapted from work by Susan German.
German, S. (2017, December). Creating conceptual storylines. Science Scope, 41(4), 26-28.
German, S. (2018, January). The steps of a conceptual storyline. Science Scope, 41(5), 32-34. - Desktop Greenhouses designed by Alisha Hill, National Center for Agricultural Literacy.
Sources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Grow_light
- https://modernfarmer.com/2018/03/grow-lights-for-indoor-plants-and-indoor-gardening/
- https://www.maximumyield.com/definition/2151/indoor-farming
- https://www.gardeners.com/how-to/gardening-under-lights/5080.html
- https://medium.com/@MarkCrumpacker/4-facts-you-need-to-know-about-leds-and-vertical-farming-bb1bed18064d
- https://www.thoughtco.com/photosynthesis-facts-4169940
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 3.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 3.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 3.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
-
ELA: 3.110.5.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 3.7.F: The student is expected to respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The students develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 4.1.C: The student is expected to express an opinion supported by accurate information, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation and the conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 4.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 4.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 4.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
-
ELA: 4.110.6.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 4.7.F: The student is expected to respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.4
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
- ELA: 5.b.4: Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking- fluency. The students reads grade-level text with fluency and comprehension. The student is expected to use appropriate fluency (rate, accuracy, and prosody) when reading grade-level text.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.6
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 5.6.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- ELA: 5.6.H: The student is expected to synthesize information to create new understanding.
-
ELA: 5.110.7.b.7
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- ELA: 5.7.F: The student is expected to respond using newly acquired vocabulary as appropriate.
-
Science: 3.112.14.b.2
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses scientific practices during laboratory and outdoor investigations.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.2.A: The student is expected to plan and implement descriptive investigations, including asking and answering questions, making inferences, and selecting and using equipment or technology needed, to solve a specific problem in the natural world.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.2.B: The student is expected to collect and record data by observing and measuring using the metric system and recognize differences between observed and measured data.
- Science: 3.112.14.b.2.F: The student is expected to communicate valid conclusions supported by data in writing, by drawing pictures, and through verbal discussion.
-
Science: 4.112.15.b.2
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses scientific practices during laboratory and outdoor investigations.
- Science: 4.2.A: The student is expected to plan and implement descriptive investigations, including asking well defined questions, making inferences, and selecting and using appropriate equipment or technology to answer his/her questions.
- Science: 4.2.B: The student is expected to collect and record data by observing and measuring, using the metric system, and using descriptive words.
- Science: 4.2.F: The student is expected to communicate valid oral and written results supported by data.
-
Science: 4.112.15.b.9
Organisms and environments. The student knows and understands that living organisms within an ecosystem interact with one another and with their environment.
- Science: 4.9.A: The student is expected to investigate that most producers need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make their own food, while consumers are dependent on other organisms for food.
-
Science: 5.112.16.b.2
Scientific investigation and reasoning. The student uses scientific practices during laboratory and outdoor investigations.
- Science: 5.2.A: The student is expected to describe, plan, and implement simple experimental investigations testing one variable.
- Science: 5.2.B: The student is expected to ask well defined questions, formulate testable hypotheses, and select and use appropriate equipment and technology.
- Science: 5.2.F: The student is expected to communicate valid conclusions in both written and verbal forms.
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 3.112.5.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
-
Science: 3.112.5.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 3.112.5.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 4.112.6.b.1.E: collect observations and measurements as evidence
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Science: 4.112.6.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student describes patterns, cycles, systems, and relationships within environments. The student is expected to:
- Science: 4.112.6.b.12.A: investigate and explain how most producers can make their own food using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide through the cycling of matter
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 5.112.7.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
-
Science: 5.112.7.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 5.112.7.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats
-
Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.A: decompose story problems into smaller, manageable subproblems and identify a solution to the problems
- Technology Applications: 126.8.c.1.C: develop a plan collaboratively and document a plan that outlines specific steps taken to complete a project
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.A: decompose story problems into smaller, manageable subproblems and discuss and document various solutions to the problems
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.1.C: communicate design plans and solutions using a variety of options
-
Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6
Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question.
- Technology Applications: 126.9.c.6: Data literacy, management, and representation--organize, manage, and analyze data. The student uses data to answer questions. The student is expected to use digital tools to transform and make inferences about data to answer a question
-
Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.10.c.1.A: decompose a real-world problem into smaller, manageable subproblems using graphic organizers such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
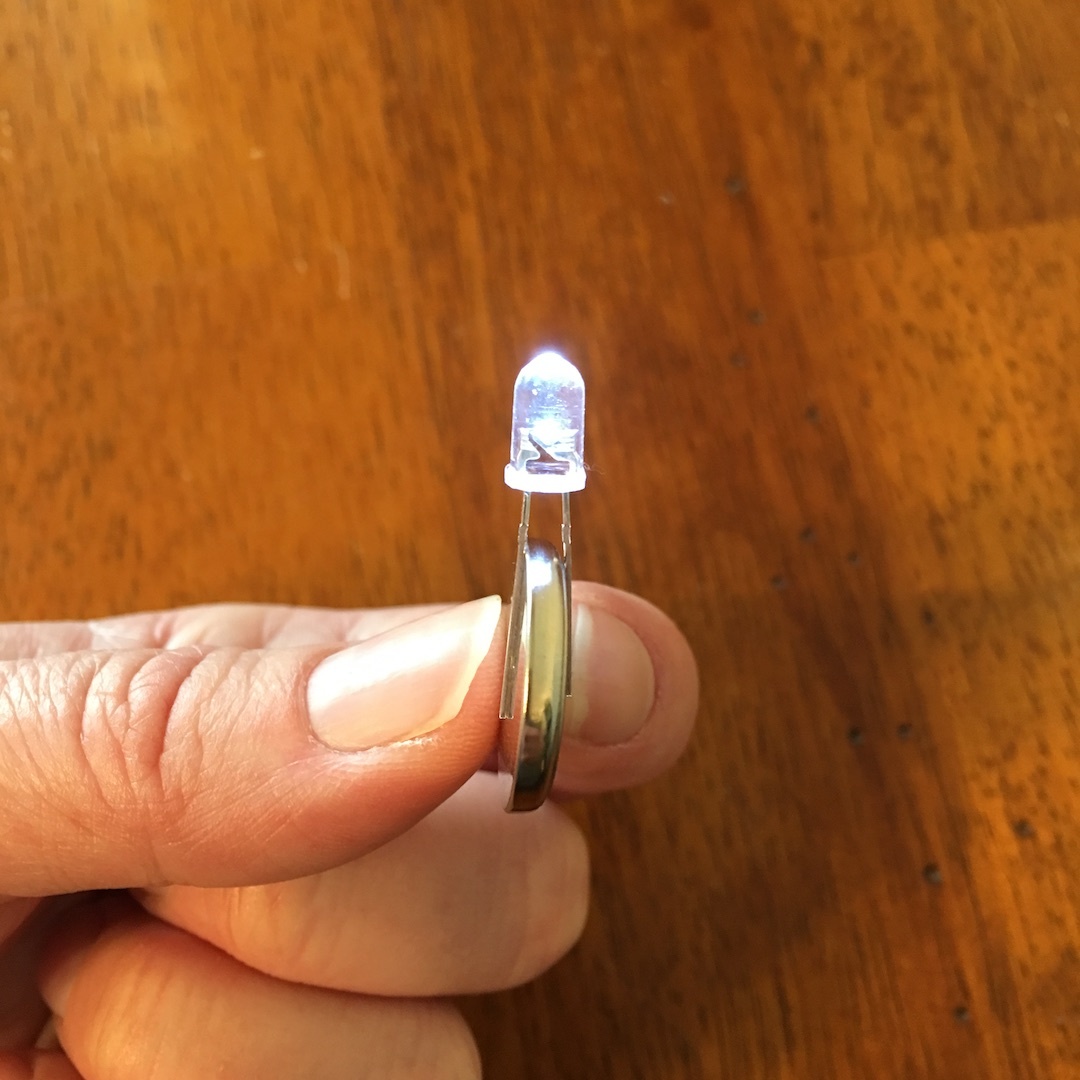


 around the battery so that the longer prong is touching the positive side of the battery. Once the light is lit, hold the prongs in place by wrapping the electrical tape around the prongs and battery.
around the battery so that the longer prong is touching the positive side of the battery. Once the light is lit, hold the prongs in place by wrapping the electrical tape around the prongs and battery.