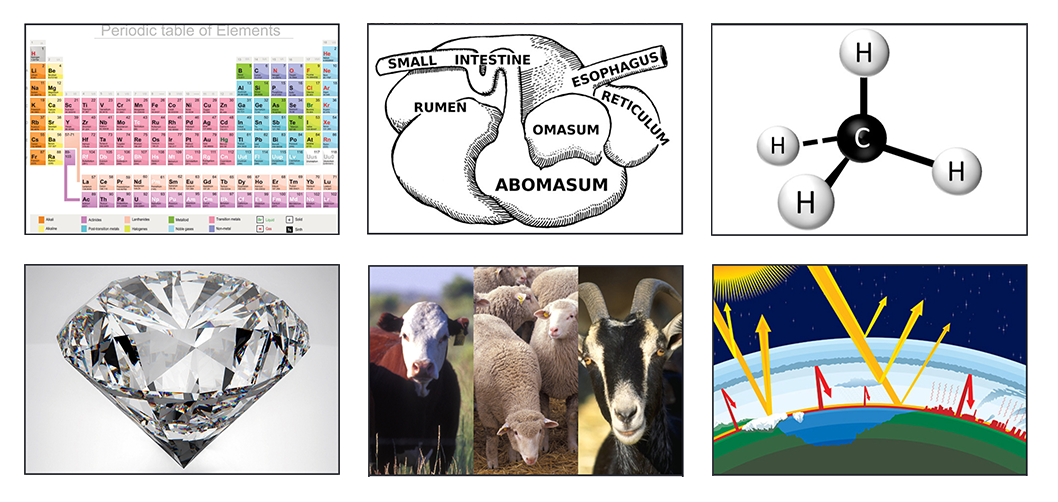
Carbon Hoofprints: Cows and Climate Change
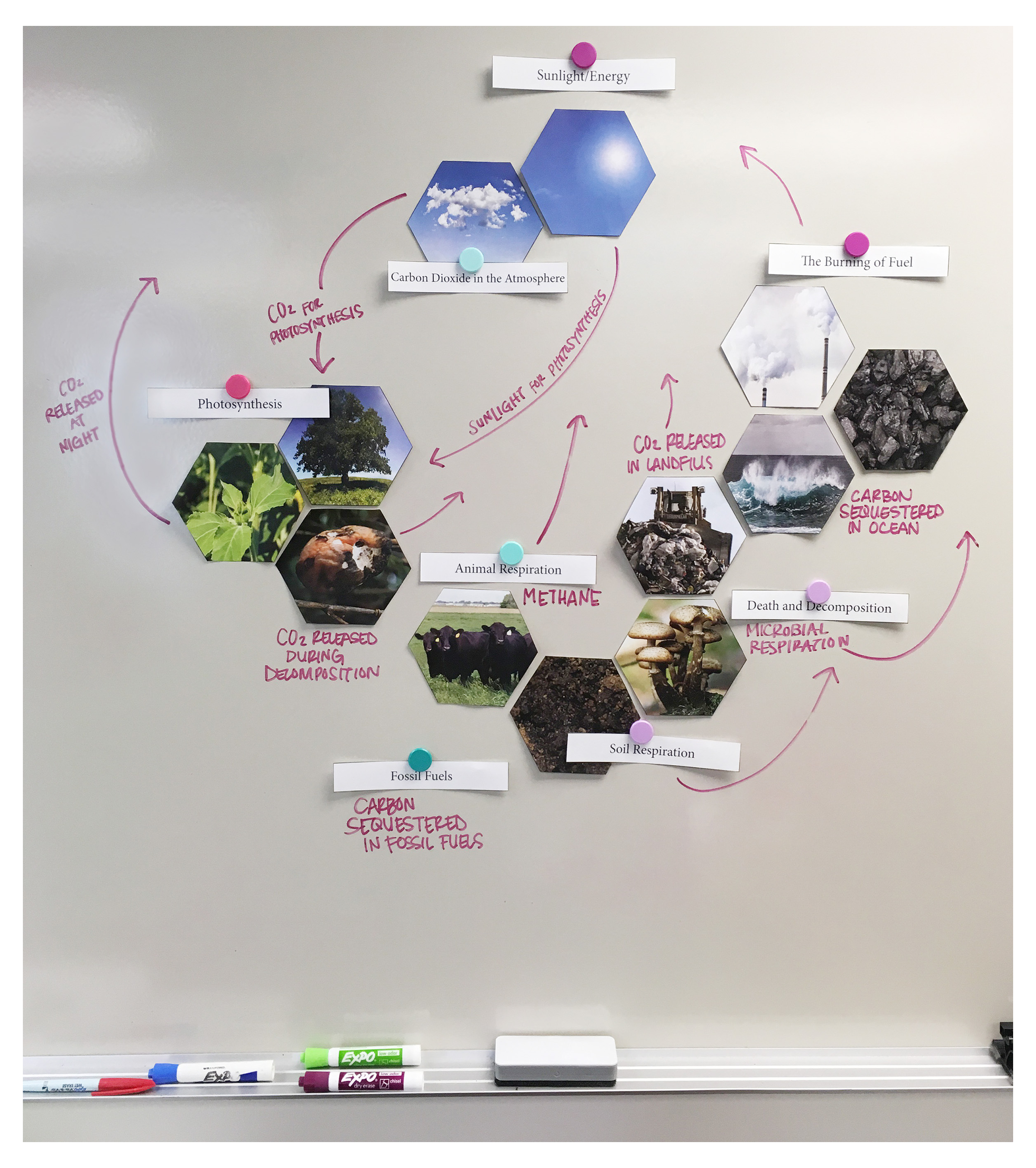
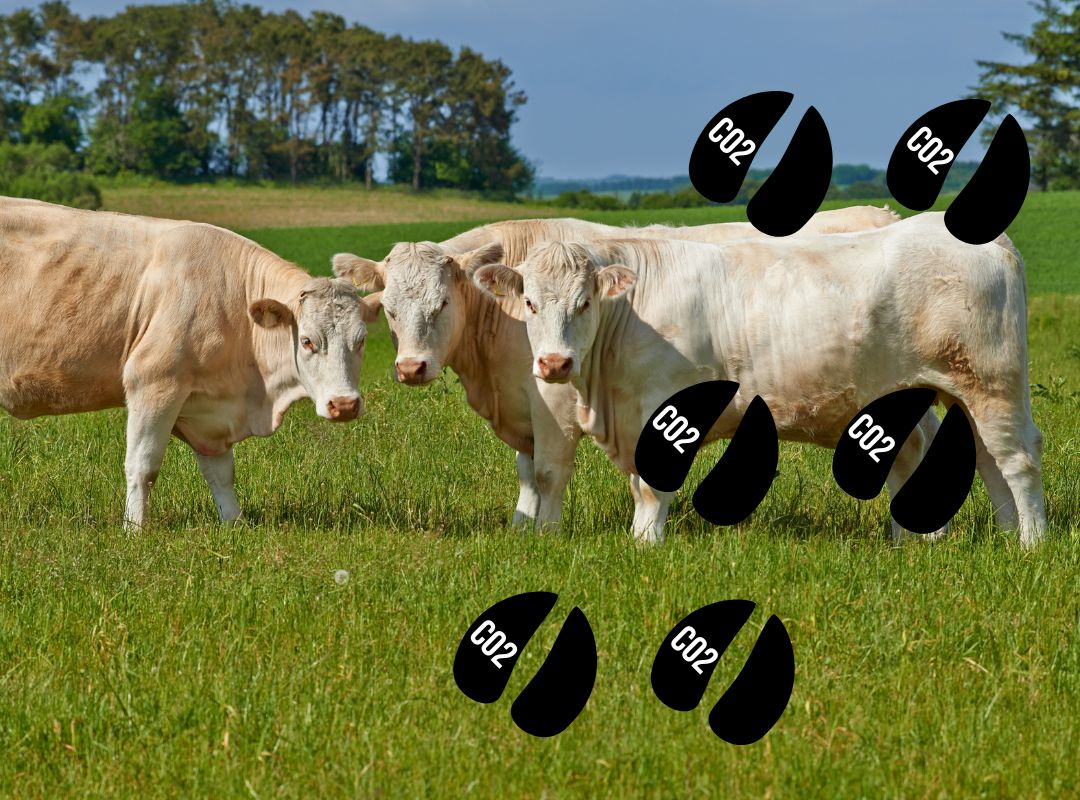
Students explore the carbon cycle and evaluate the carbon footprint of cattle. Using critical thinking skills, students will use the Claim, Evidence, and Reasoning model to determine the effect of cows’ methane production on the environment and investigate the extent cattle contribute to climate change.

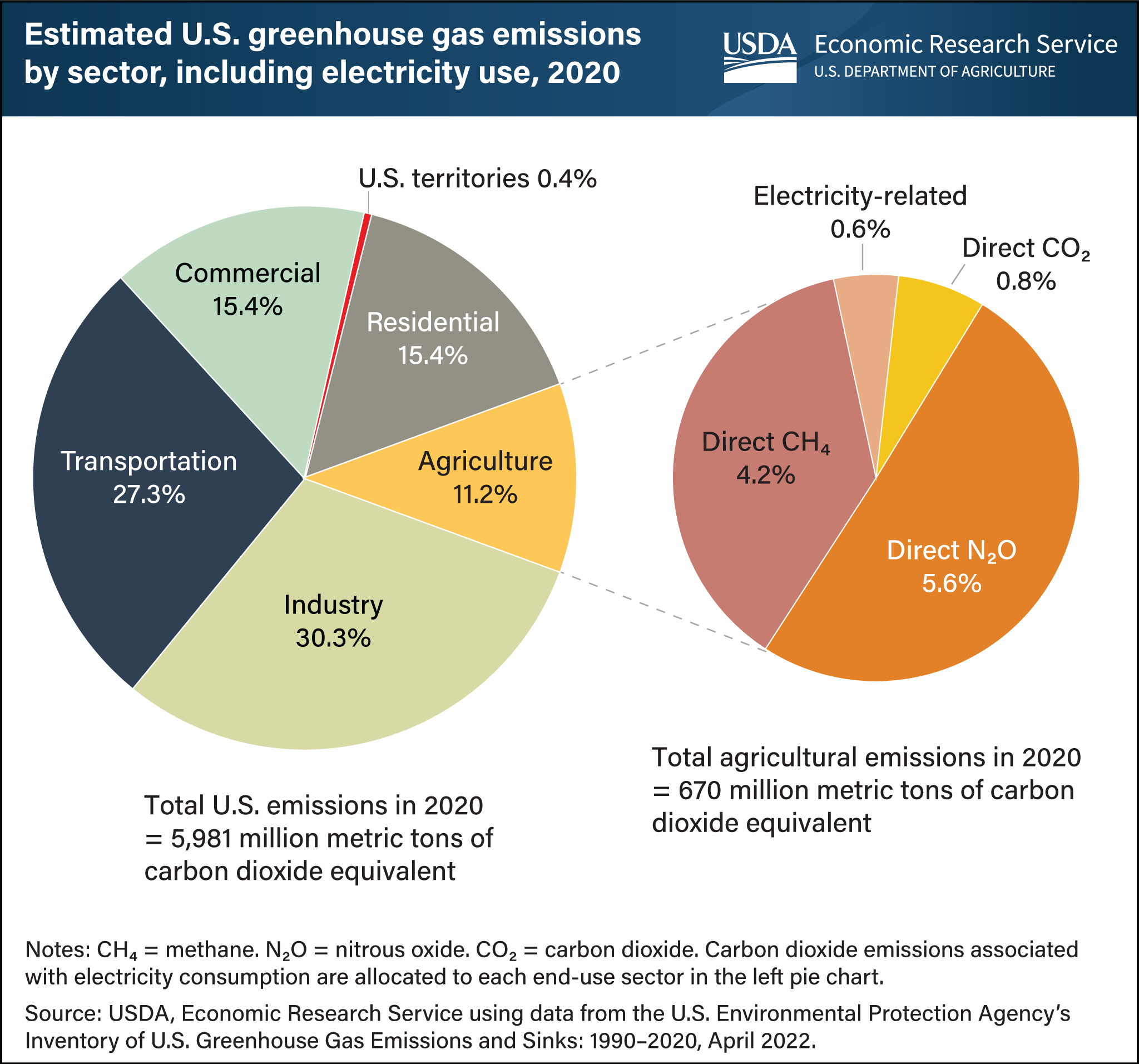
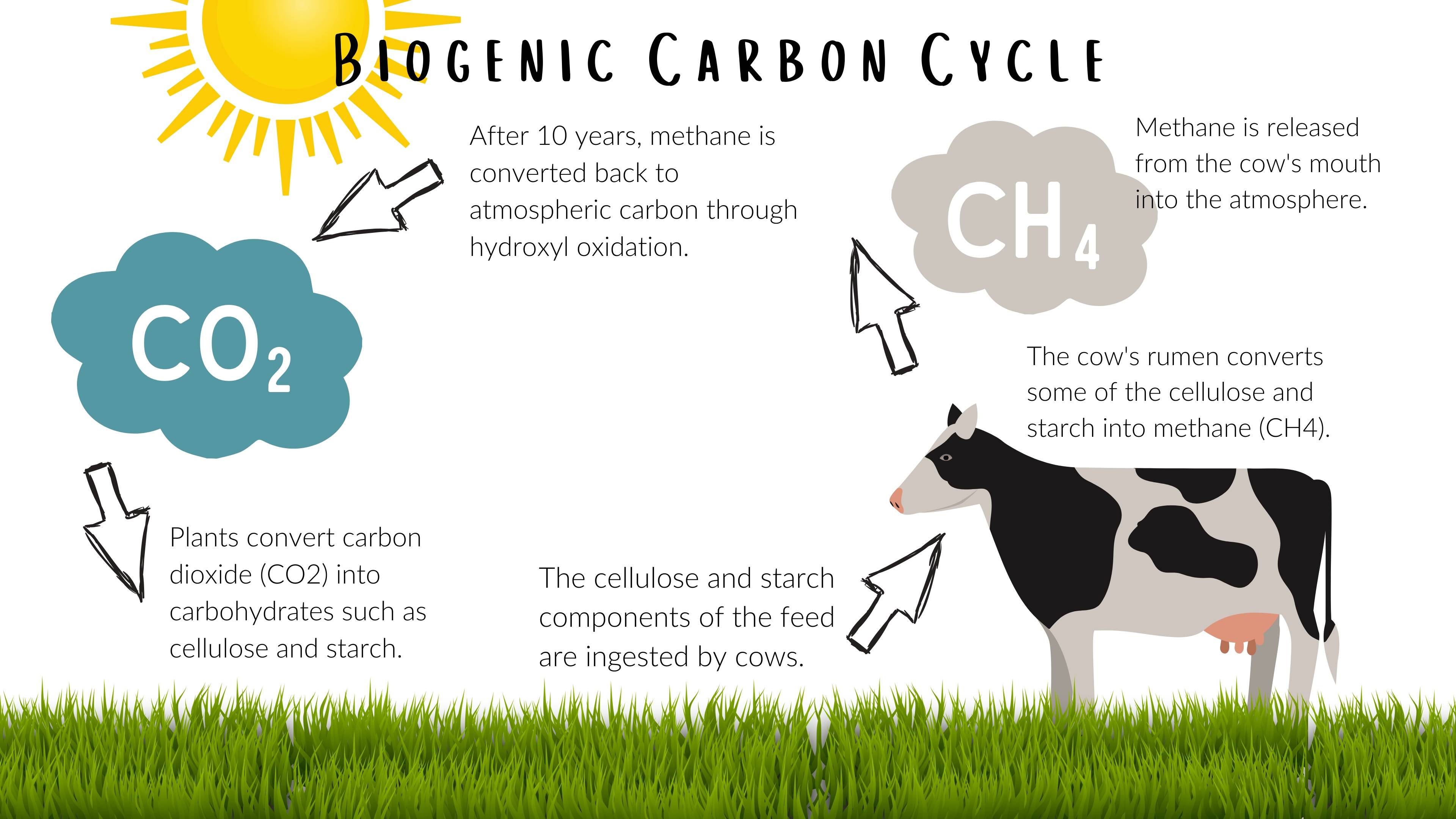
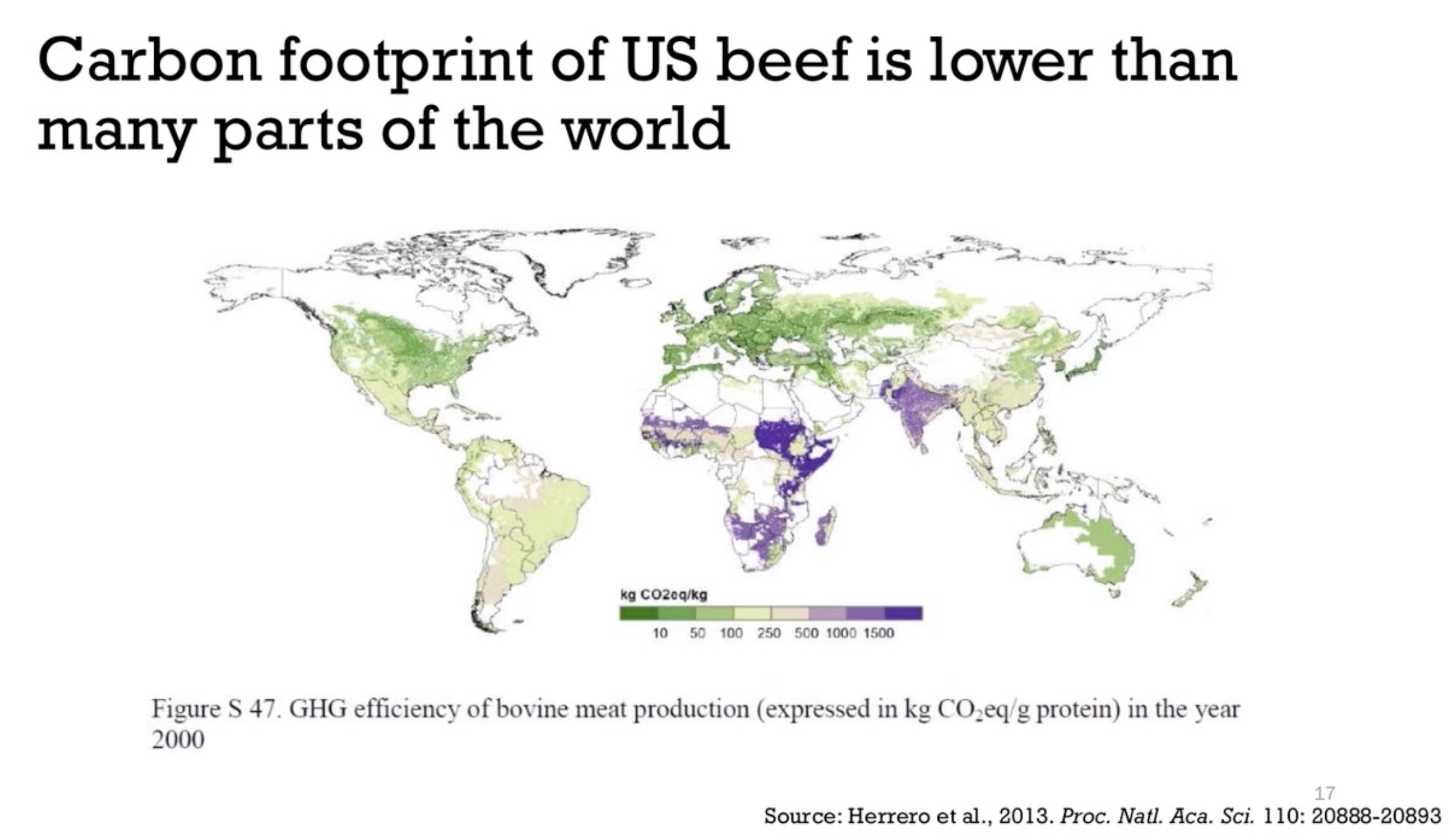
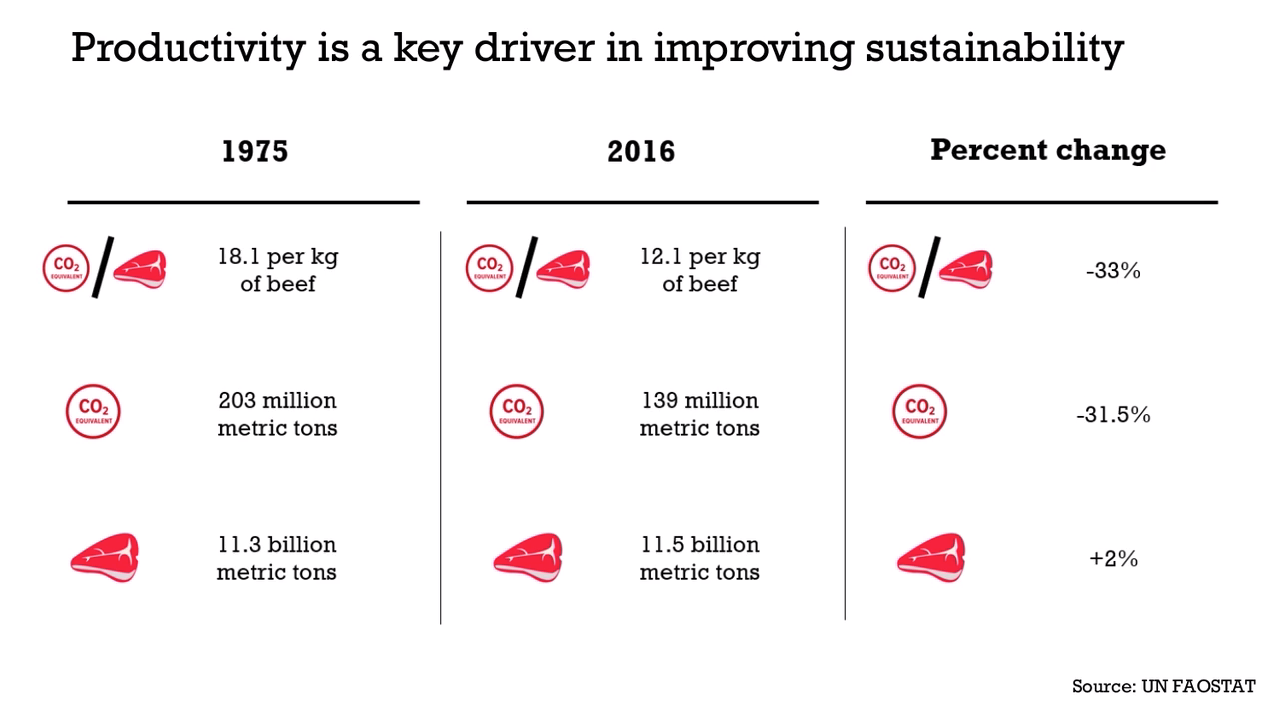
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Bekka Israelsen and Andrea Gardner | Utah Agriculture in the Classroom and National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- https://caes.ucdavis.edu/news/articles/2016/04/livestock-and-climate-change-facts-and-fiction
- https://www.animalhealthmedia.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/Addressing-the-2050-food.pdf
- https://theconversation.com/yes-eating-meat-affects-the-environment-but-cows-are-not-killing-the-climate-94968
- https://castbox.fm/episode/099%3A-Frank-Mitloehner%3A-Cattle%2C-climate-change-and-the-methane-myth-id1016351-id166145089?country=us
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tfV0XwJSLrI
- http://pods.dasnr.okstate.edu/docushare/dsweb/Get/Document-10191/ANSI-3293.pdf
- https://www.dirt-to-dinner.com/grass-or-grain-beef-is-beef/
- https://kidsgardening.org/garden-how-to-carbon-cycle-and-carbon-sequestration/?utm_source=KidsGardening+Friends&utm_campaign=83eb3dba50-EMAIL_CAMPAIGN_2019_05_01_09_25&utm_medium=email&utm_term=0_0a82c9a42d-83eb3dba50-366559713&mc_cid=83eb3dba50&mc_eid=b1977826f2
- https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2019-04/documents/us-ghg-inventory-2019-main-text.pdf
- https://extension.umn.edu/dairy-nutrition/ruminant-digestive-system#stomach-compartments-1000460
- https://learningstore.uwex.edu/Assets/pdfs/A4131-01.pdf
- https://www3.epa.gov/climatechange//kids/index.html
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PR7ATkTXSb8&list=PLJEeYejb4pU_hRlOxpkNJ1EWELOAgIIeC
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to animal systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12.B: identify animal anatomy and physiology.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.15
The student explains the relationship between agriculture, food, and natural resources and the environment. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.15.A: determine the effects of agriculture, food, and natural resources upon safety, health, and the environment.
-
English I: 110.36.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English I: 1.A: The student is expected to engage in meaningful and respectful discourse by listening actively, responding appropriately, and adjusting communication to audiences and purposes.
- English I: 1.B: The student is expected to follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems and complex processes.
- English I: 1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively, building on the ideas of others, contributing relevant information, developing a plan for consensus building, and setting ground rules for decision making.
-
Livestock Production: 130.7.c.6
The student determines nutritional requirements of ruminant and non-ruminant animals, including poultry. The student is expected to:
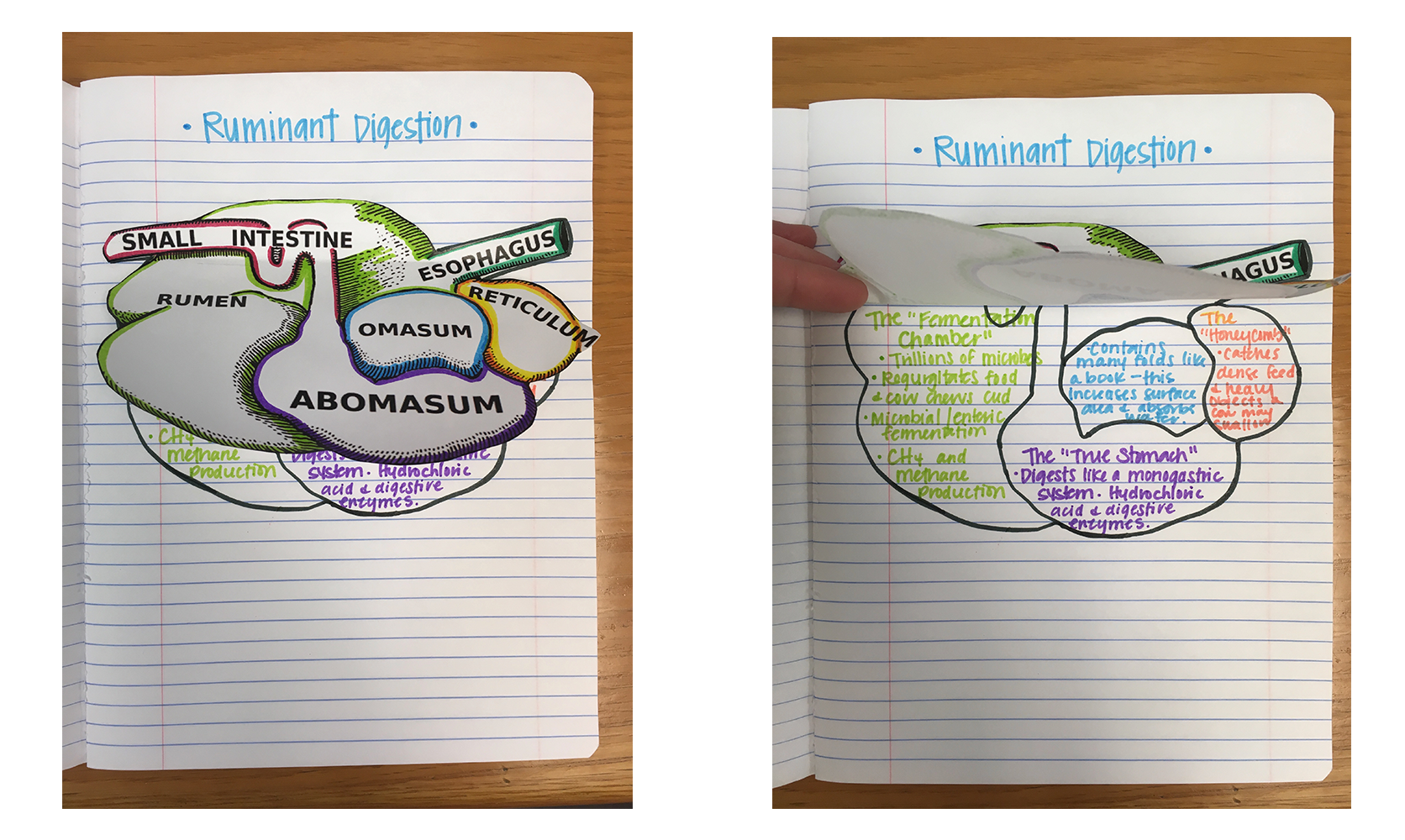
- Livestock Production: 130.7.c.6.A: describe the digestive systems of ruminant and non-ruminant animals.
-
English I: 110.36.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English I: 4.A: The student is expected to establish purpose for reading assigned and self-selected texts.
- English I: 4.F: The student is expected to make inferences and use evidence to support understanding.
- English I: 4.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- English I: 4.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as rereading, using background knowledge, asking questions, and annotating when understanding breaks down.
-
English I: 110.36.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English I: 5.B: The student is expected to write responses that demonstrate understanding of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres.
- English I: 5.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
- English I: 5.F: The student is expected to respond using acquired content and academic vocabulary as appropriate.
-
English II: 110.37.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English II: 4.A: The student is expected to establish purpose for reading assigned and self-selected texts.
- English II: 4.F: The student is expected to make inferences and use evidence to support understanding.
- English II: 4.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to determine key ideas.
- English II: 4.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as rereading, using background knowledge, asking questions, and annotating when understanding breaks down.
-
English II: 110.37.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundation language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English II: 1.A: The student is expected to engage in meaningful and respectful discourse by listening actively, responding appropriately, and adjusting communication to audiences and purposes.
- English II: 1.B: The student is expected to follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems and complex processes.
- English II: 1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively, building on the ideas of others, contributing relevant information, developing a plan for consensus building, and setting ground rules for decision making.
-
English III: 110.38.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English III: 1.A: The student is expected to engage in meaningful and respectful discourse when evaluating the clarity and coherence of a speaker's message and critiquing the impact of a speaker's use of diction and syntax.
- English III: 1.B: The student is expected to follow and give complex instructions, clarify meaning by asking pertinent questions, and respond appropriately.
- English III: 1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively, offering ideas or judgements that are purposeful in moving the team toward goals, asking relevant and insightful questions, tolerating a range of positions and ambiguity in decision making, and evaluating the work of the group based on agreed-upon criteria.
-
English III: 110.38.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English III: 4.A: The student is expected to establish purpose for reading assigned and self-selected texts.
- English III: 4.F: The student is expected to make inferences and use evidence to support understanding.
- English III: 4.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to understand key ideas.
- English III: 4.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as rereading, using background knowledge, asking questions, annotating, and using outside sources when understanding breaks down.
-
English III: 110.38.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English III: 5.B: The student is expected to write responses that demonstrate analysis of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres.
- English III: 5.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
- English III: 5.F: The student is expected to respond using acquired content and academic vocabulary as appropriate.
-
English II: 110.37.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English II: 5.B: The student is expected to write responses that demonstrate understanding of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres.
- English II: 5.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
- English II: 5.F: The student is expected to respond using acquired content and academic vocabulary as appropriate.
-
English IV: 110.39.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English IV: 1.A: The student is expected to engage in meaningful and respectful discourse when evaluating the clarity and coherence of a speaker's message and critiquing the impact of a speaker's use of diction, syntax, and rhetorical strategies.
- English IV: 1.B: The student is expected to follow and give complex instructions, clarify meaning by asking pertinent questions, and respond appropriately.
- English IV: 1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively, offering ideas or judgements that are purposeful in moving the team toward goals, asking relevant and insightful questions, tolerating a range of positions and ambiguity in decision making, and evaluating the work of the group based on agreed-upon criteria.
-
English IV: 110.39.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English IV: 4.A: The student is expected to establish purpose for reading assigned and self-selected texts.
- English IV: 4.F: The student is expected to make inferences and use evidence to support understanding.
- English IV: 4.G: The student is expected to evaluate details read to analyze key ideas.
- English IV: 4.I: The student is expected to monitor comprehension and make adjustments such as rereading, using background knowledge, asking questions, annotating, and using outside sources when understanding breaks down.
-
English IV: 110.39.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English IV: 5.B: The student is expected to write responses that demonstrate analysis of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres.
- English IV: 5.E: The student is expected to interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating.
- English IV: 5.F: The student is expected to respond using acquired content and academic vocabulary as appropriate.
-
Biology: 112.34.c.12
Science concepts. The student knows that interdependence and interactions occur within an environmental system.
- Biology: 12.D: The student is expected to describe the flow of matter through the carbon and nitrogen cycles and explain the consequences of disrupting these cycles.
-
Earth and Space Science: 112.36.c.15
Fluid Earth. The student knows that interactions among Earth's five subsystems influence climate and resource availability, which affect Earth's habitability.
- Earth and Space Science: 15.D: The student is expected to explain the global carbon cycle, including how carbon exists in different forms within the five subsystems and how these forms affect life.
-
Environmental Systems: 112.37.c.4
Science concepts. The student knows the relationships of biotic and abiotic factors within habitats, ecosystems, and biomes.
- Environmental Systems: 4.C: The student is expected to diagram abiotic cycles, including the rock, hydrologic, carbon, and nitrogen cycles.
-
Advanced Animal Science: 130.10.c.10
The student determines nutritional requirements of ruminant and non-ruminant animals. The student is expected to:
- Advanced Animal Science: 130.10.c.10.A: describe the structures and functions of the digestive system of ruminant animals, including cattle, and non-ruminant animals, including poultry.
-
Biology: 112.42.c.13
Science concepts--interdependence within environmental systems. The student knows that interactions at various levels of organization occur within an ecosystem to maintain stability. The student is expected to:
- Biology: 112.42.c.13.C: explain the significance of the carbon and nitrogen cycles to ecosystem stability and analyze the consequences of disrupting these cycles
-
Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.12
Science concepts. The student understands how Earth's systems affect and are affected by human activities, including resource use and management. The student is expected to:
- Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.12.B: analyze the impact on humans of naturally occurring extreme weather events such as flooding, hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms