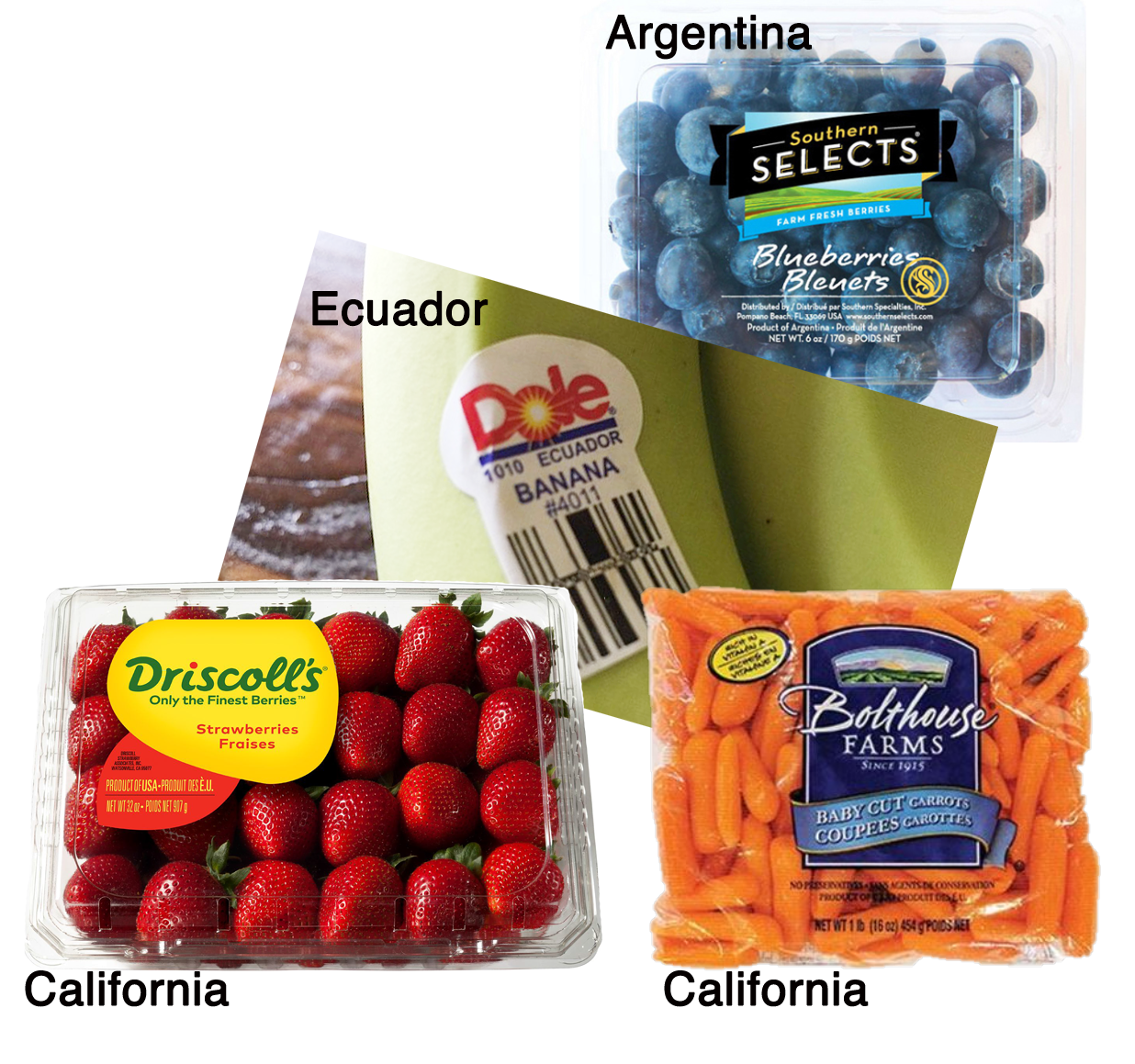
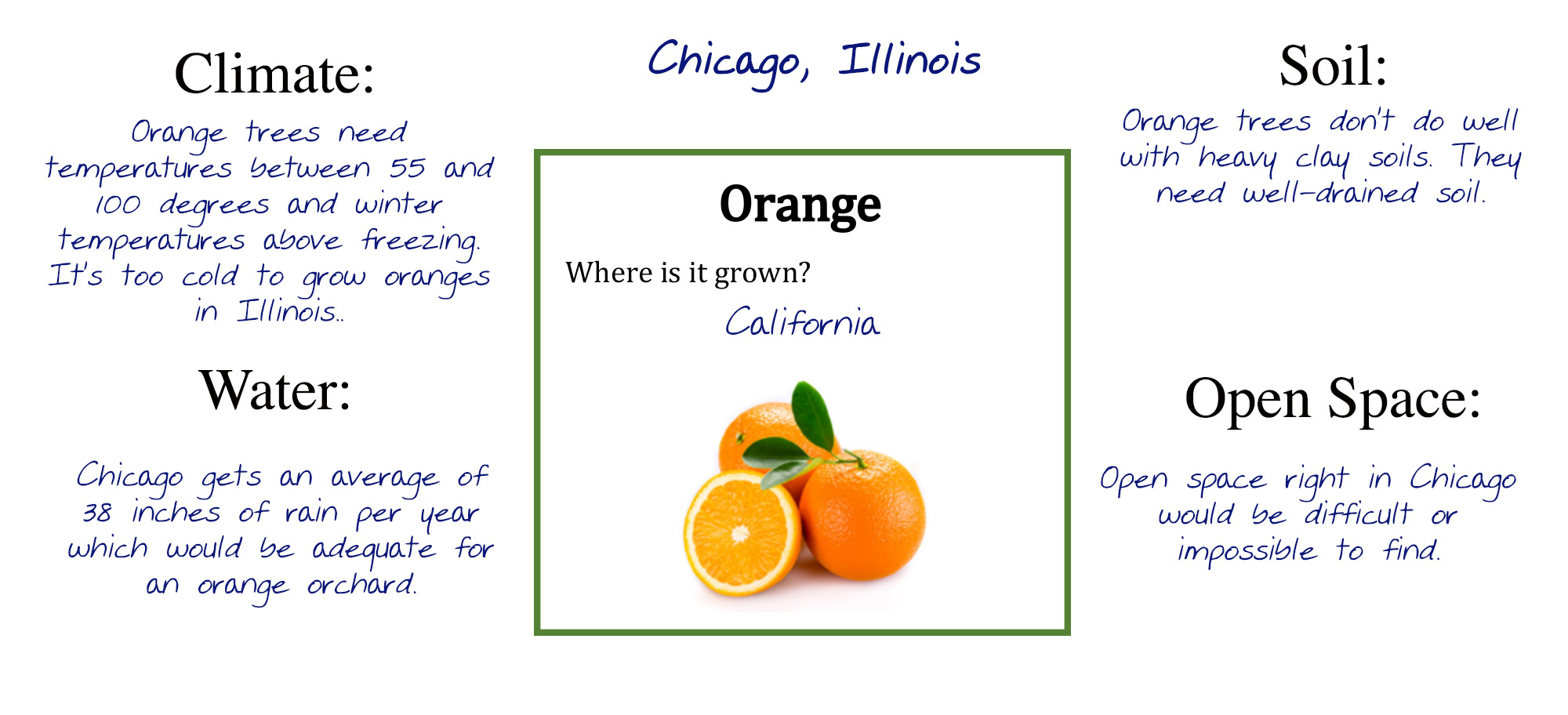
Geography and Climate for Agricultural Landscapes (Grades 6-8)
Students will discover how geography and climate influence the crops that are grown and the livestock that is raised in each state.
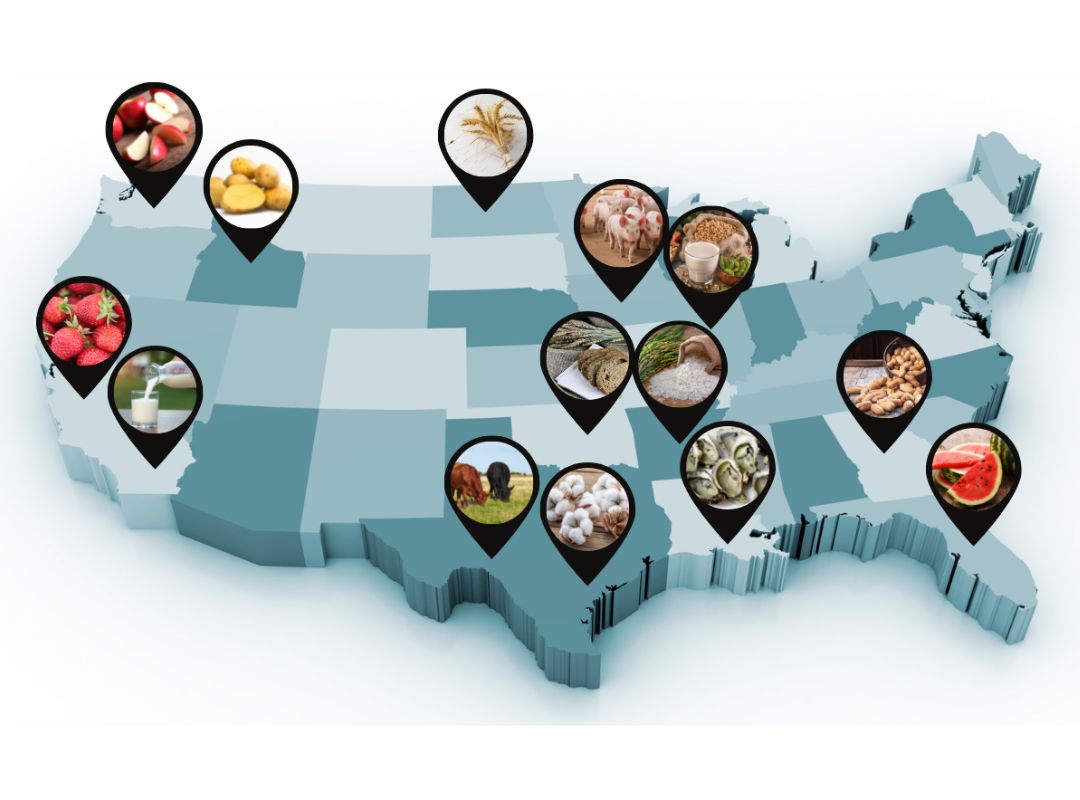
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner and Debra Spielmaker | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.b.4
Geography. The student understands how geographic factors influence the economic development and political relationships of societies.
- Social Studies: 6.4.A: The student is expected to explain the geographic factors responsible for the location of economic activities in places and regions.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.b.8
Geography. The student understands the location and characteristics of places and regions of Texas.
- Social Studies: 7.8.C: The student is expected to analyze the effects of physical and human factors such as climate, weather, landforms, irrigation, transportation, and communication on major events in Texas.
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.b.11
Geography. The student understands the physical characteristics of North America and how humans adapted to and modified the environment through the mid-19th century.
- Social Studies: 8.11.A: The student is expected to analyze how physical characteristics of the environment influenced population distribution, settlement patterns, and economic activities in the United States.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.F: compare and contrast issues impacting agriculture, food, and natural resources such as biotechnology, employment, safety, environment, and animal welfare issues.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.10
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to soil systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.10.A: identify the components and properties of soils.
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.4
Geography. The student understands how geographic factors influence the economic development and political relationships of societies. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.4.A: explain the geographic factors responsible for the location of economic activities in places and regions
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.8
Geography. The student understands the location and characteristics of places and regions of Texas. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.8.C: analyze the effects of physical and human factors such as climate, weather, landforms, irrigation, transportation, and communication on major events in Texas
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.11
Geography. The student understands the physical characteristics of North America and how humans adapted to and modified the environment through the mid-19th century. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.11.A: analyze how physical characteristics of the environment influenced population distribution, settlement patterns, and economic activities in the United States
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 6.1.B: The student is expected to follow and give oral instructions that include multiple action steps.
- ELA: 6.1.C: The student is expected to give an organized presentation with a specific stance and position, employing eye contact, speaking rate, volume, enunciation, natural gestures, and conventions of language to communicate ideas effectively.
- ELA: 6.1.D: The student is expected to participate in student-led discussions by eliciting and considering suggestions from other group members, taking notes, and identifying points of agreement and disagreement.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- ELA: 6.12.A: The student is expected to generate student-selected and teacher-guided questions for formal and informal inquiry.
- ELA: 6.12.D: The student is expected to identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources.
- ELA: 6.12.F: The student is expected to synthesize information from a variety of sources.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 7.1.D: The student is expected to engage in meaningful discourse and provide and accept constructive feedback from others.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- ELA: 7.12.A: The student is expected to generate student-selected and teacher-guided questions for formal and informal inquiry.
- ELA: 7.12.D: The student is expected to identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources.
- ELA: 7.12.F: The student is expected to synthesize information from a variety of sources.
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 8.1.D: The student is expected to participate collaboratively in discussions, plant agendas with clear goals and deadlines, set time limits for speakers, take notes, and vote on key issues.
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes.
- ELA: 8.12.A: The student is expected to generate student-selected and teacher-guided questions for formal and informal inquiry.
- ELA: 8.12.D: The student it expected to identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources.
- ELA: 8.12.F: The student is expected to synthesize information from a variety of sources.
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.20
Social studies skills. The student uses geographic tools to collect, analyze, and interpret data. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.20.A: answer geographic questions, including: Where is it located? Why is it there? What is significant about its location? How is its location related to the location of other people, places, and environments? Using latitude and longitude, where is it located?
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.20.C: compare various world regions and countries using data from maps, graphs, and charts
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.11
Earth and space. The student knows that natural events and human activity can impact global climate. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.11.A: use scientific evidence to describe how natural events, including volcanic eruptions, meteor impacts, abrupt changes in ocean currents, and the release and absorption of greenhouse gases influence climate;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.11.B: use scientific evidence to describe how human activities, including the release of greenhouse gases, deforestation, and urbanization, can influence climate; and
-
Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.B: analyze the patterns and sequences found in visual representations such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
-
Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1.B: analyze the patterns and sequences found in flowcharts