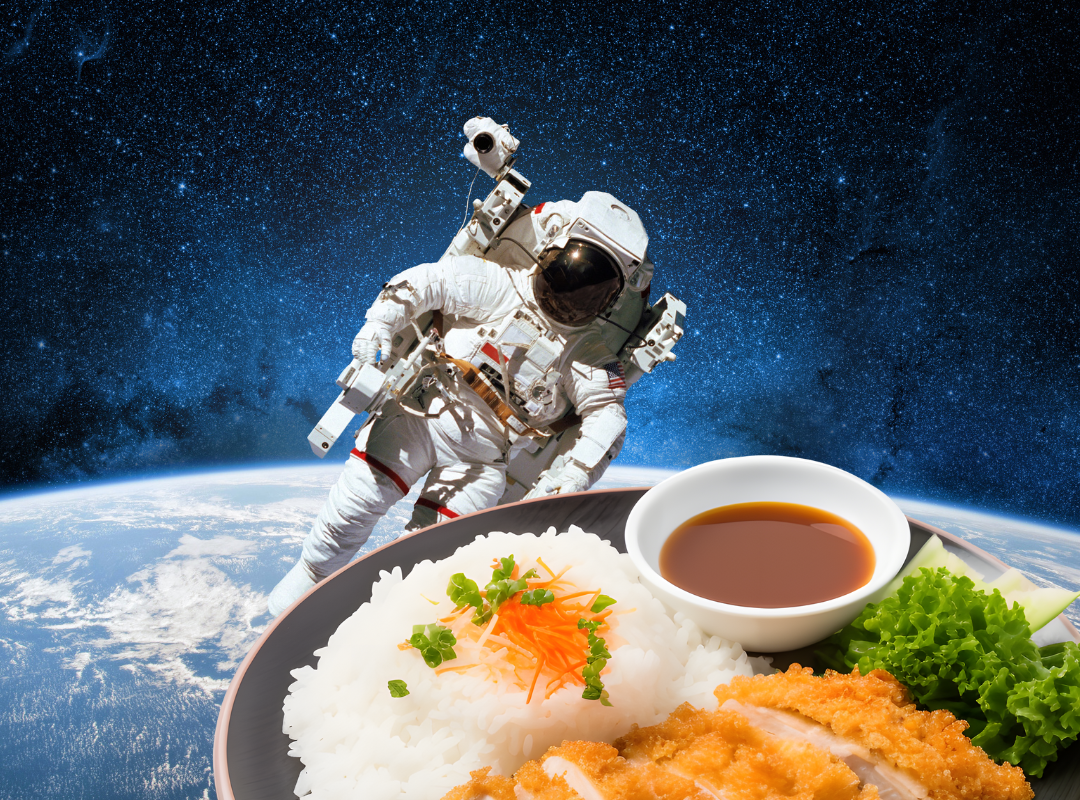
Spice-up Space Food
Through project-based learning, students work in groups to create a flavorful and nutritious meal for astronauts to eat in space. They experience careers in food and nutrition, food science, and marketing, research different ways to preserve foods, and discover how food is taken to and eaten in space.

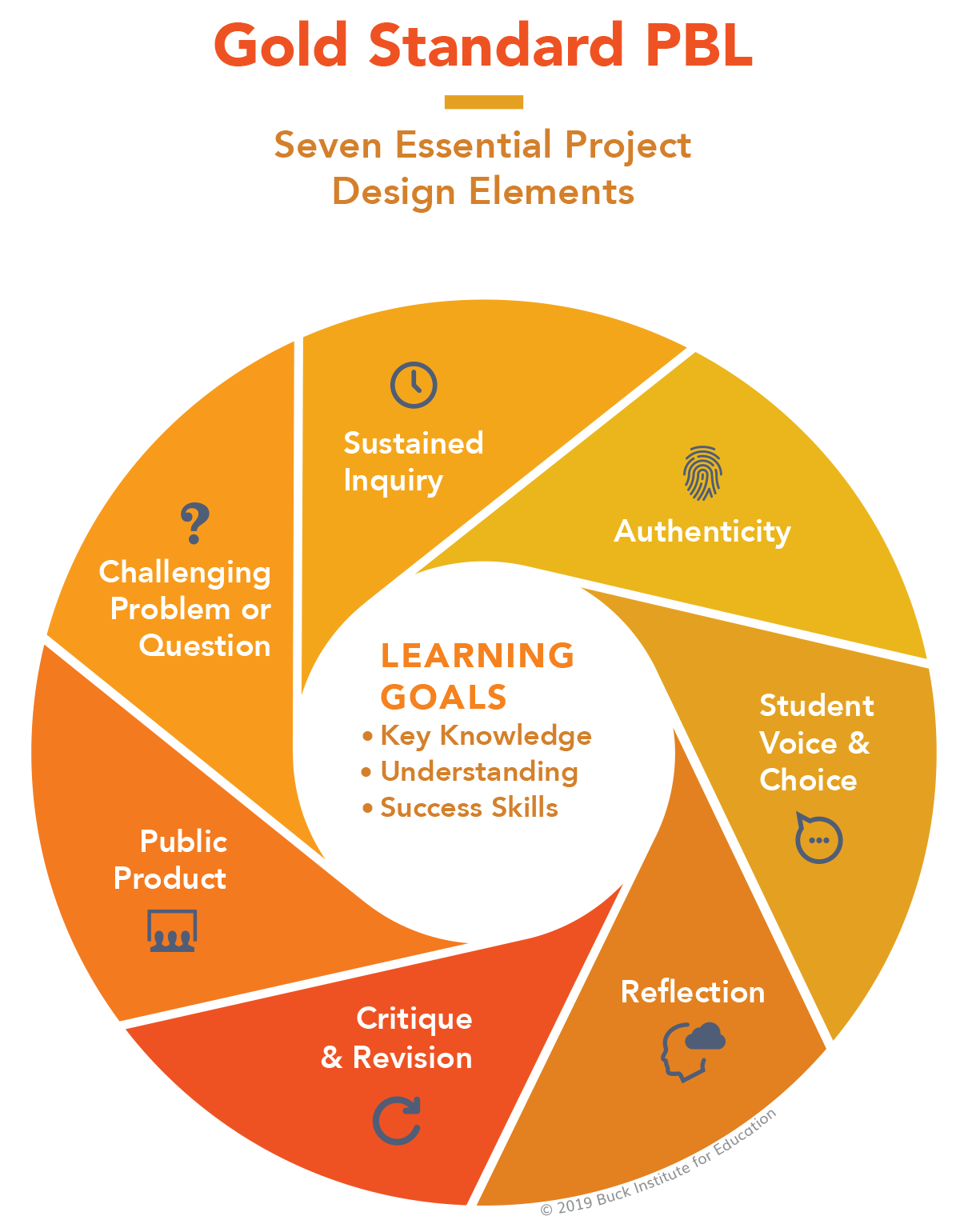
Background
Lesson Activities
Credits
Author
Jessica Clark | CCA PBL Team
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.E: identify careers in agriculture, food, and natural resources with required aptitudes in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, language arts, and social studies.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.C: evaluate significant historical and current agriculture, food, and natural resources developments.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.E: describe how emerging technologies and globalization impacts agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7
The student applies appropriate research methods to agriculture, food, and natural resources topics. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agricultures, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.7.A: discuss major research and developments in the fields of agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13
The student describes the principles of food products and processing systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.A: evaluate food products and processing systems.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.B: determine trends in world food production.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.C: discuss current issues in food production.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.D: use tools, equipment, and personal protective equipment common to food products and processing systems.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive, comparative, and experimental investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems; and
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.22
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.22.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.23
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.23.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that interdependence occurs between living systems and the environment. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.12.A: investigate how organisms and populations in an ecosystem depend on and may compete for biotic factors such as food and abiotic factors such as availability of light and water, range of temperatures, or soil composition;
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.31
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.31.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems; and
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands that ecosystems are dependent upon the cycling of matter and the flow of energy. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.A: diagram the flow of energy within trophic levels and describe how the available energy decreases in successive trophic levels in energy pyramids; and
- Science: 7.112.27.b.12.B: describe how ecosystems are sustained by the continuous flow of energy and the recycling of matter and nutrients within the biosphere.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive, comparative, and experimental investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.F: construct appropriate tables, graphs, maps, and charts using repeated trials and means to organize data;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.G: develop and use models to represent phenomena, systems, processes, or solutions to engineering problems; and
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.A: identify advantages and limitations of models such as their size, scale, properties, and materials;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.B: analyze data by identifying any significant descriptive statistical features, patterns, sources of error, or limitations;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.12.D: identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.12.F: synthesize information from a variety of sources
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.12.J: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.12.D: identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.12.F: synthesize information from a variety of sources
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.12.J: use an appropriate mode of delivery, whether written, oral, or multimodal, to present results
-
Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.A: decompose real-world problems into structured parts by using visual representation
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.B: analyze the patterns and sequences found in visual representations such as learning maps, concept maps, or other representations of data
- Technology Applications: 126.17.c.1.D: design a plan collaboratively using visual representation to document a problem, possible solutions, and an expected timeline for the development of a coded solution
-
Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1
Computational thinking--foundations. The student explores the core concepts of computational thinking, a set of problem-solving processes that involve decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithms. The student is expected to:
- Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1.A: decompose real-world problems into structured parts using flowcharts
- Technology Applications: 126.18.c.1.B: analyze the patterns and sequences found in flowcharts