Background Agricultural Connections
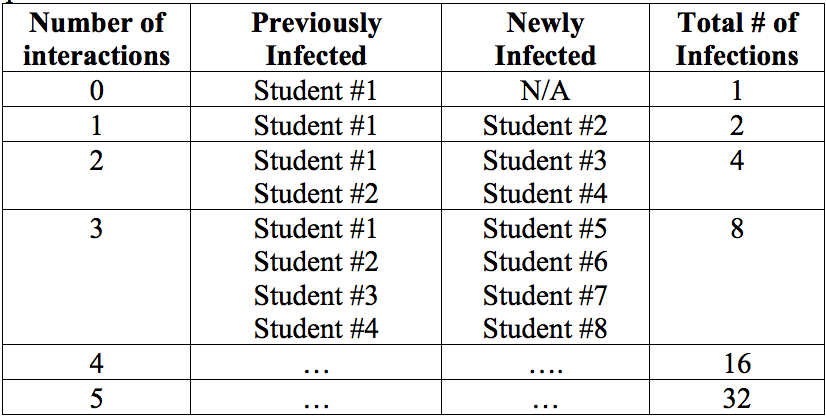
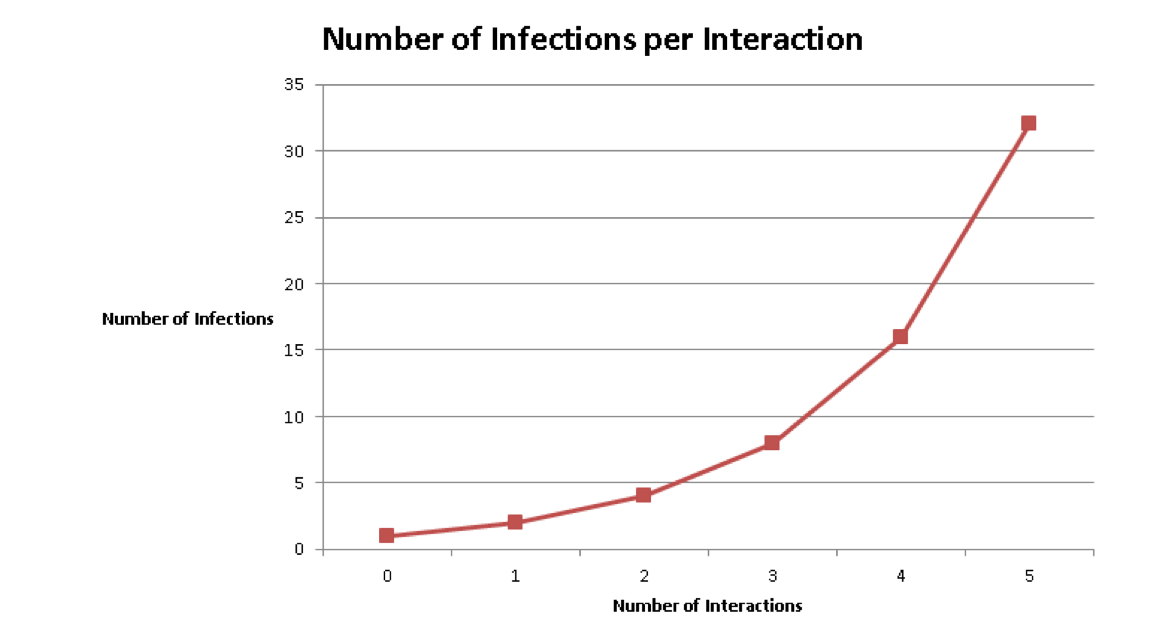
Some people are carriers of disease. Initially, these carriers may appear healthy or show only mild signs of disease. At some point they may eventually get sick, but they may not be recognized as having the disease until they've exposed and infected others. This is one reason why some pathogens can spread so quickly.
Diseases can be spread by direct contact, indirect contact, aerosols or droplets, ingestion or oral transmission, or vectors. Indirect contact transmission is the spread of pathogens through coming into contact with areas where animals live or roam, or objects or surfaces contaminated by an infected animal. Objects or surfaces that may become contaminated with pathogens are called fomites. Some examples of fomites are boots, cages, needles, bedding, clothing, vehicles, and restraint devices. Ingestion or oral transmission occurs when disease-causing agents are ingested from contaminated food or water or by licking or chewing contaminated objects in the environment. Germs can be present even when things (clothing, gloves, shoes, equipment, etc.) appear clean or when animals appear healthy.
Ways to prevent direct contact transmission:
- Isolate sick animals
- Wear gloves when working with sick animals
- Wash your hands after having contact with animals or being in animal areas even if you did not touch the animals
Ways to prevent indirect contact transmission:
- Avoid sharing equipment, or clean and disinfect equipment when sharing is necessary
- Clean and disinfect any equipment used with sick animals or animals with skin lesions
- Dispose of or wash boots and clothing after animal contact
- Wash your hands after having contact with animals or being in animal areas even if you did not touch the animals
Ways to prevent aerosol transmission:
- Increase distance between sick animals and healthy animals and people
- Wear respiratory protection when working with sick animals
- Provide fresh air to animals and people
- Decrease humidity and odor buildup in barns
- Stay away from animal barns if you are sick
Ways to prevent oral transmission:
- Wash your hands
- After contact with animals or being in animal areas even if you did not touch the animals
- After cleaning pens or contact with manure
- Before preparing or handling food
- After going to the bathroom
- Cook meat to the appropriate temperature
- Store food at the appropriate temperature
Ways to prevent vector-borne transmission:
- Use insect control products
- Work with your veterinarian to check and treat your animals for parasites
- Prevent standing water
- Check for ticks on people and pets