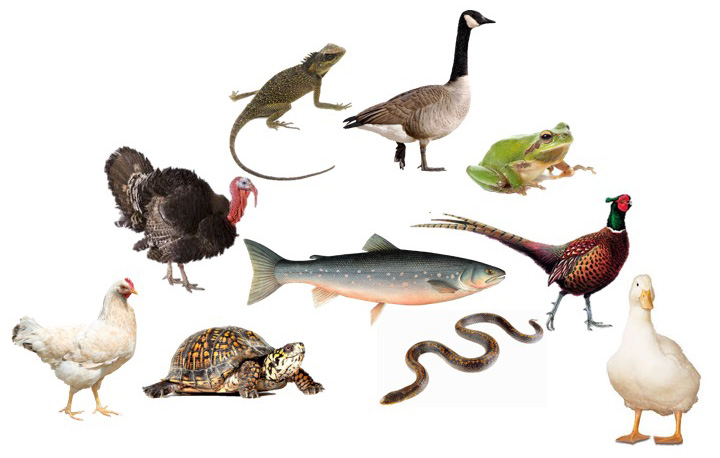
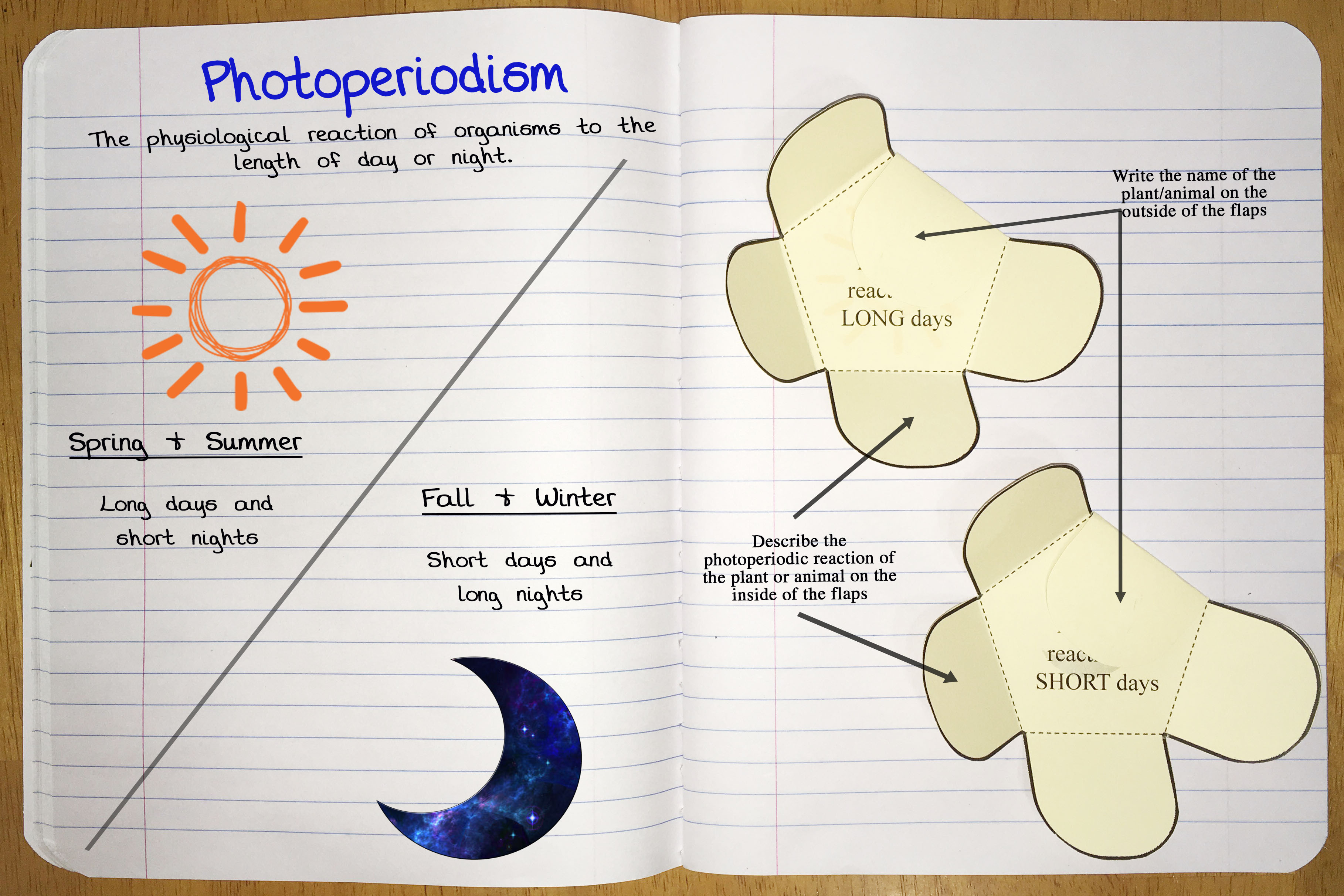
Photoperiod Phenomena (Grades 6-8)
Students will understand how photoperiodism impacts plants and animals in the environment and learn how egg farms use this science to manage the laying of eggs by their hens.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Acknowledgements
Phenomenon chart adapted from work by Susan German.
German, S. (2017, December). Creating conceptual storylines. Science Scope, 41(4), 26-28.
German, S. (2018, January). The steps of a conceptual storyline. Science Scope, 41(5), 32-34.
Sources
- https://www.incredibleegg.org/about-us/industry-data
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32796704/
- https://www.aeb.org/images/PDFs/Educators/EggProductionCycle.pdf
- https://uepcertified.com/choices-in-hen-housing/
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.C: evaluate significant historical and current agriculture, food, and natural resources developments.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to animal systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12.A: describe animal growth and development.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.12.D: explain animal selection, reproduction, breeding, and genetics.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13
The student describes the principles of food products and processing systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.A: evaluate food products and processing systems.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.B: determine trends in world food production.
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.5.E: make connections to personal experiences, ideas in other texts, and society
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking- oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.1.D: participate collaboratively in discussions, plan agendas with clear goals and deadlines, set time limits for speakers, take notes, and vote on key issues
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.D: create written and visual material such as journal entries, reports, graphic organizers, outlines, and bibliographies based on research
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to assess quantitative relationships in data; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.B: identify and investigate cause-and-effect relationships to explain scientific phenomena or analyze problems;
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.9
Earth and space. The student models the cyclical movements of the Sun, Earth, and Moon and describes their effects. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.9.A: model and illustrate how the tilted Earth revolves around the Sun, causing changes in seasons; and
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.B: explain how conservation, increased efficiency, and technology can help manage air, water, soil, and energy resources.
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to assess quantitative relationships in data; and
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats; and
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.B: identify and investigate cause-and-effect relationships to explain scientific phenomena or analyze problems;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.2
Scientific and engineering practices. The student analyzes and interprets data to derive meaning, identify features and patterns, and discover relationships or correlations to develop evidence-based arguments or evaluate designs. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.2.C: use mathematical calculations to assess quantitative relationships in data; and
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.3
Scientific and engineering practices. The student develops evidence-based explanations and communicates findings, conclusions, and proposed solutions. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.3.B: communicate explanations and solutions individually and collaboratively in a variety of settings and formats; and
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.4
Scientific and engineering practices. The student knows the contributions of scientists and recognizes the importance of scientific research and innovation on society. The student is expected to
- Science: 8.112.28.b.4.C: research and explore resources such as museums, libraries, professional organizations, private companies, online platforms, and mentors employed in a science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) field to investigate STEM careers.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.B: identify and investigate cause-and-effect relationships to explain scientific phenomena or analyze problems;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.10
Earth and space. The student knows that interactions between Earth, ocean, and weather systems impact climate. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.10.A: describe how energy from the Sun, hydrosphere, and atmosphere interact and influence weather and climate;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how human activity can impact the hydrosphere. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.11.B: describe human dependence and influence on ocean systems and explain how human activities impact these systems.
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.E: make connections to personal experiences, ideas in other texts, and society
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.A: describe personal connections to a variety of sources, including self-selected texts
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.12.D: identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.A: describe personal connections to a variety of sources, including self-selected texts
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.12.D: identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.5
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.5.E: make connections to personal experiences, ideas in other texts, and society
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.5.H: synthesize information to create new understanding
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.A: describe personal connections to a variety of sources, including self-selected texts
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.12.D: identify and gather relevant information from a variety of sources