Soil and Sustainability (Grades 6-8)
Students are introduced to the Dust Bowl and determine how to avoid another event like it in the future as they study soil texture, particle sizes, soil nutrients, and pH.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Nourish the Future
Acknowledgements
This lesson is from the Soil and Sustainability unit created by Nourish the Future.
Sources
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.C: evaluate significant historical and current agriculture, food, and natural resources developments.
- Principles, of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.D: identify potential future scenarios for agriculture, food, and natural resources systems, including global impacts.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.10
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to soil systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.10.A: identify the components and properties of soils.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.10.B: identify and describe the process of soil formation.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.10.C: conduct experiments related to soil chemistry.
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.19.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.21.C: express ideas orally based on research and experiences
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Science: 6.112.26.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive, comparative, and experimental investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems
-
Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.22
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 6.113.18.c.22.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 6.112.26.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.20.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.23
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 7.113.19.c.23.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.10
Earth and space. The student understands the rock cycle and the structure of Earth. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.10.A: differentiate between the biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere and identify components of each system;
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how resources are managed. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.A: research and describe why resource management is important in reducing global energy poverty, malnutrition, and air and water pollution; and
- Science: 6.112.26.b.11.B: explain how conservation, increased efficiency, and technology can help manage air, water, soil, and energy resources.
-
Science: 6.112.26.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student knows that interdependence occurs between living systems and the environment. The student is expected to:
- Science: 6.112.26.b.12.A: investigate how organisms and populations in an ecosystem depend on and may compete for biotic factors such as food and abiotic factors such as availability of light and water, range of temperatures, or soil composition;
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.C: organize and interpret information from outlines, reports, databases, and visuals, including graphs, charts, timelines, and maps
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.29.E: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning related to a social studies topic
-
Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.31
Social studies skills. The student uses problem-solving and decision-making skills, working independently and with others. The student is expected to:
- Social Studies: 8.113.20.c.31.B: use problem-solving and decision-making processes to identify a problem, gather information, list and consider options, consider advantages and disadvantages, choose and implement a solution, and evaluate the effectiveness of the solution
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive, comparative, and experimental investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems;
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 7.112.27.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to answer questions, explain phenomena, or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.1.B: use scientific practices to plan and conduct descriptive, comparative, and experimental investigations and use engineering practices to design solutions to problems;
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.5
Recurring themes and concepts. The student understands that recurring themes and concepts provide a framework for making connections across disciplines. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.A: identify and apply patterns to understand and connect scientific phenomena or to design solutions;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.5.G: analyze and explain how factors or conditions impact stability and change in objects, organisms, and systems.
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.6
Matter and energy. The student understands that matter can be classified according to its properties and matter is conserved in chemical changes that occur within closed systems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.6.D: compare and contrast the properties of acids and bases, including pH relative to water; and
-
Science: 8.112.28.b.12
Organisms and environments. The student understands stability and change in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to:
- Science: 8.112.28.b.12.A: explain how disruptions such as population changes, natural disasters, and human intervention impact the transfer of energy in food webs in ecosystems;
- Science: 8.112.28.b.12.B: describe how primary and secondary ecological succession affect populations and species diversity after ecosystems are disrupted by natural events or human activity; and
- Science: 8.112.28.b.12.C: describe how biodiversity contributes to the stability and sustainability of an ecosystem and the health of the organisms within the ecosystem.
-
Science: 7.112.27.b.11
Earth and space. The student understands how human activity can impact the hydrosphere. The student is expected to:
- Science: 7.112.27.b.11.A: analyze the beneficial and harmful influences of human activity on groundwater and surface water in a watershed; and
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.C: use text evidence to support an appropriate response
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.6.H: respond orally or in writing with appropriate register, vocabulary, tone, and voice
-
ELA: 6.110.22.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 6.110.22.b.12.A: generate student-selected and teacher-guided questions for formal and informal inquiry
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.C: use text evidence to support an appropriate response
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.6.H: respond orally or in writing with appropriate register, vocabulary, tone, and voice
-
ELA: 7.110.23.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 7.110.23.b.12.A: generate student-selected and teacher-guided questions for formal and informal inquiry
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.6
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.C: use text evidence to support an appropriate response
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.6.H: respond orally or in writing with appropriate register, vocabulary, tone, and voice
-
ELA: 8.110.24.b.12
Inquiry and research: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student engages in both short-term and sustained recursive inquiry processes for a variety of purposes. The student is expected to:
- ELA: 8.110.24.b.12.A: generate student-selected and teacher-guided questions for formal and informal inquiry
-
Math: 6.111.26.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 6.111.26.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
-
Math: 6.111.26.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division while solving problems and justifying solutions. The student is expected to:
- Math: 6.111.26.b.3.D: add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers fluently
- Math: 6.111.26.b.3.E: multiply and divide positive rational numbers fluently
-
Math: 6.111.26.b.4
Proportionality. The student applies mathematical process standards to develop an understanding of proportional relationships in problem situations. The student is expected to:
- Math: 6.111.26.b.4.H: convert units within a measurement system, including the use of proportions and unit rates
-
Math: 7.111.27.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 7.111.27.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
-
Math: 7.111.27.b.3
Number and operations. The student applies mathematical process standards to add, subtract, multiply, and divide while solving problems and justifying solutions. The student is expected to:
- Math: 7.111.27.b.3.A: add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers fluently
- Math: 7.111.27.b.3.B: apply and extend previous understandings of operations to solve problems using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of rational numbers
-
Math: 7.111.27.b.4
Proportionality. The student applies mathematical process standards to represent and solve problems involving proportional relationships. The student is expected to:
- Math: 7.111.27.b.4.E: convert between measurement systems, including the use of proportions and the use of unit rates
-
Math: 8.111.28.b.1
Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to:
- Math: 8.111.28.b.1.A: apply mathematics to problems arising in everyday life, society, and the workplace
 Soil is made up of three different particle sizes in varying amounts: sand, silt, and clay. Clay are the smallest particles, yet they hold the most water and nutrients. Clay particles are charged particles and can hold onto the ions in nutrient compounds, allowing roots to easily absorb and use them. The disadvantage of clay soil is that it can become water-logged and when it dries, the soil surface may become hard as rock. Clay soils also may become easily compacted, since the spaces between the particles are so small. Water does not easily move through clay soils, so it is said to be less permeable than other soils.
Soil is made up of three different particle sizes in varying amounts: sand, silt, and clay. Clay are the smallest particles, yet they hold the most water and nutrients. Clay particles are charged particles and can hold onto the ions in nutrient compounds, allowing roots to easily absorb and use them. The disadvantage of clay soil is that it can become water-logged and when it dries, the soil surface may become hard as rock. Clay soils also may become easily compacted, since the spaces between the particles are so small. Water does not easily move through clay soils, so it is said to be less permeable than other soils.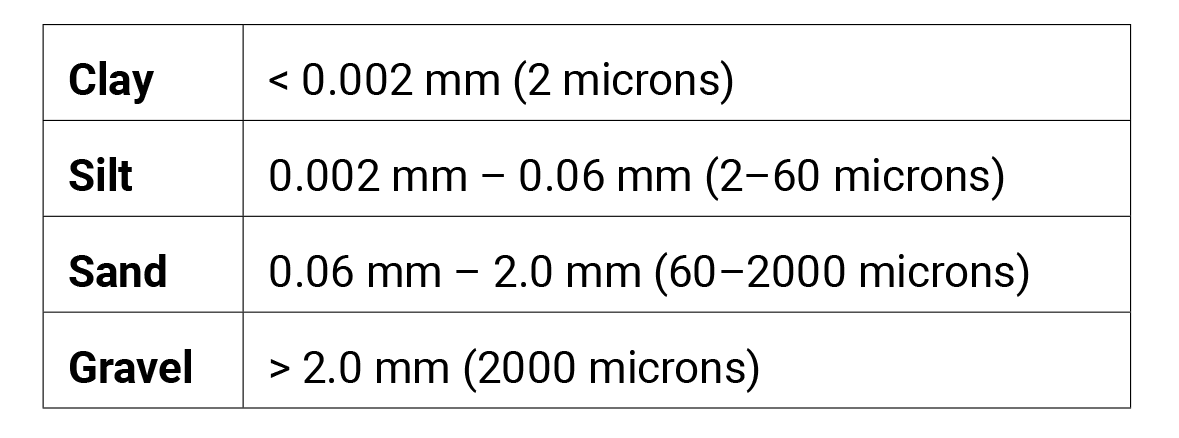 The sediment sizes and percentages of each in a sample are determined by the history of geologic and climatic events in an area.
The sediment sizes and percentages of each in a sample are determined by the history of geologic and climatic events in an area.