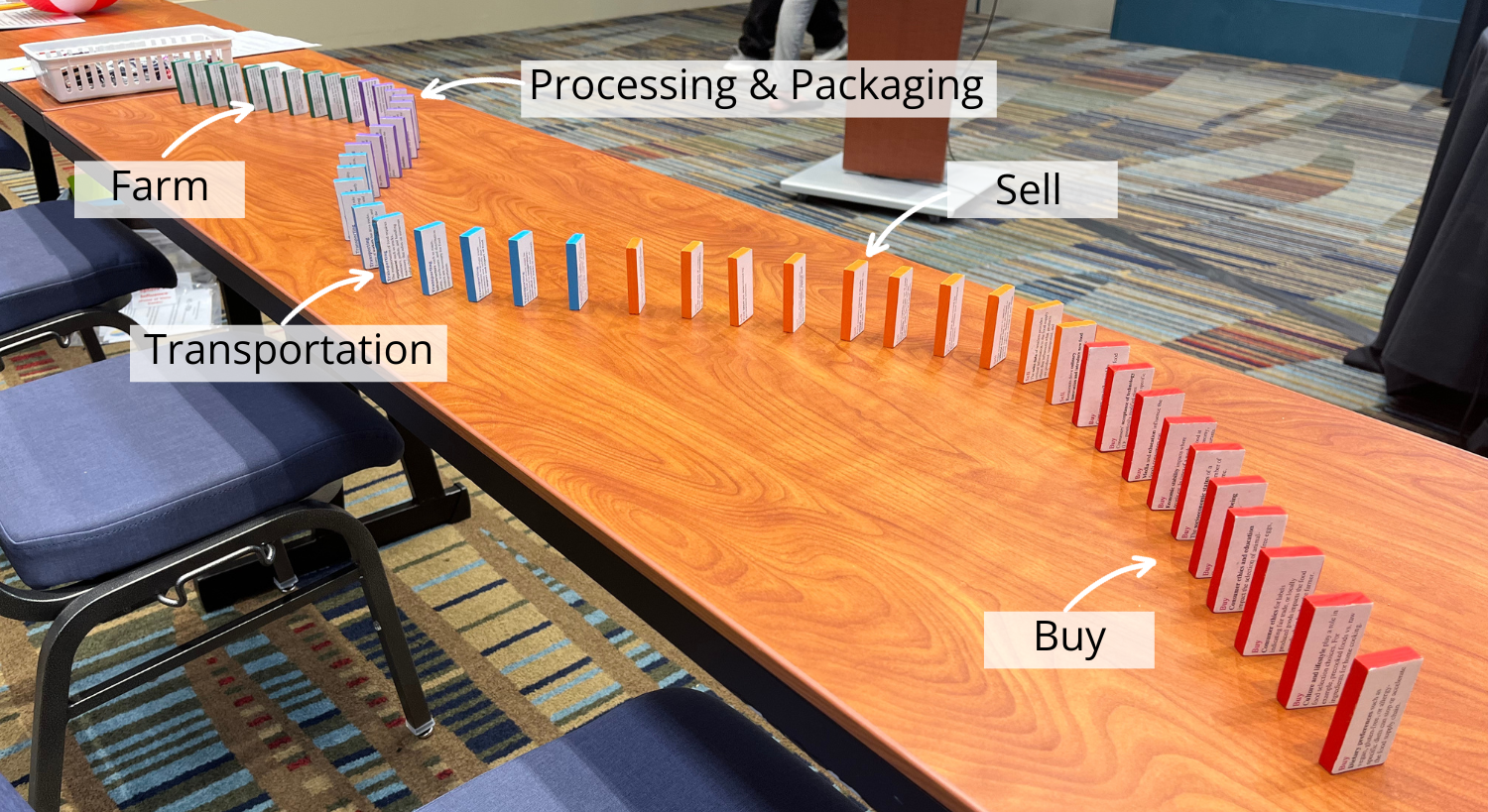
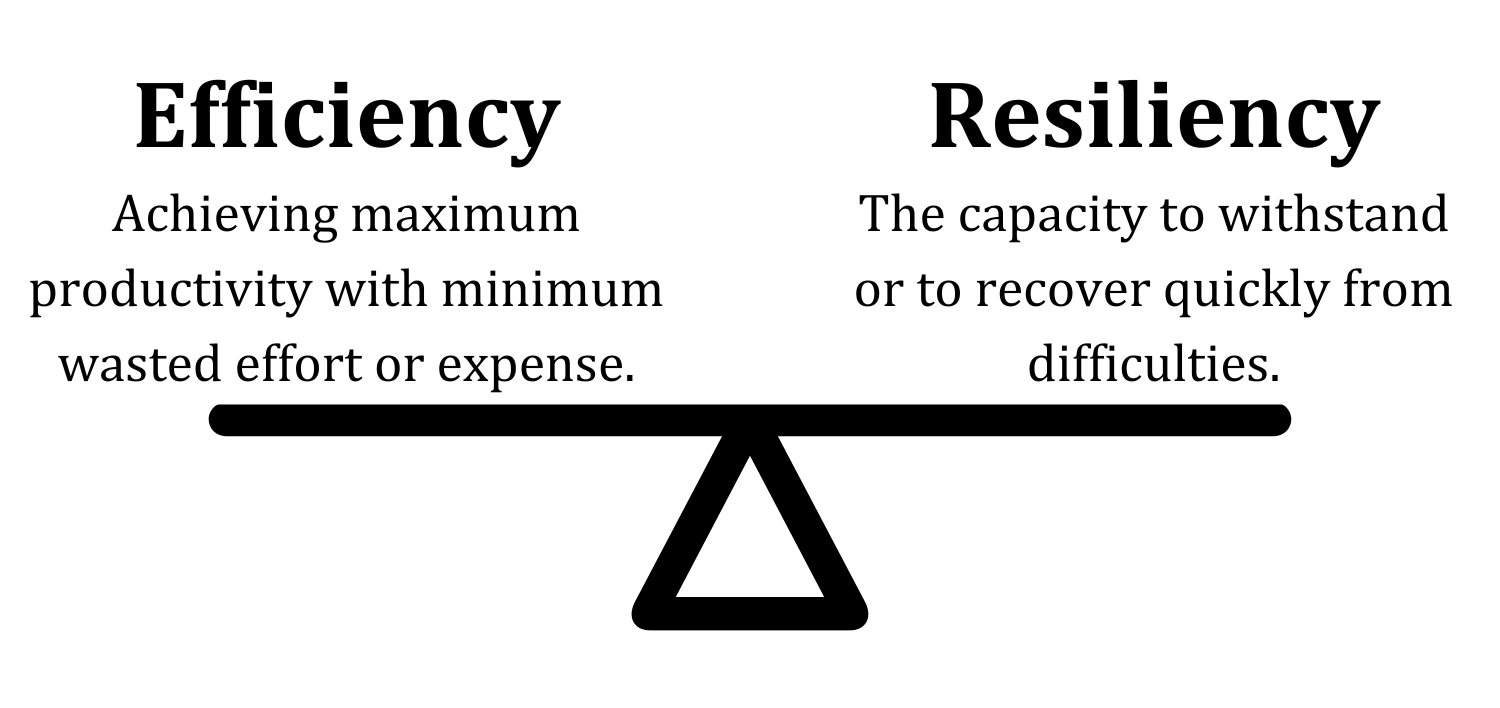
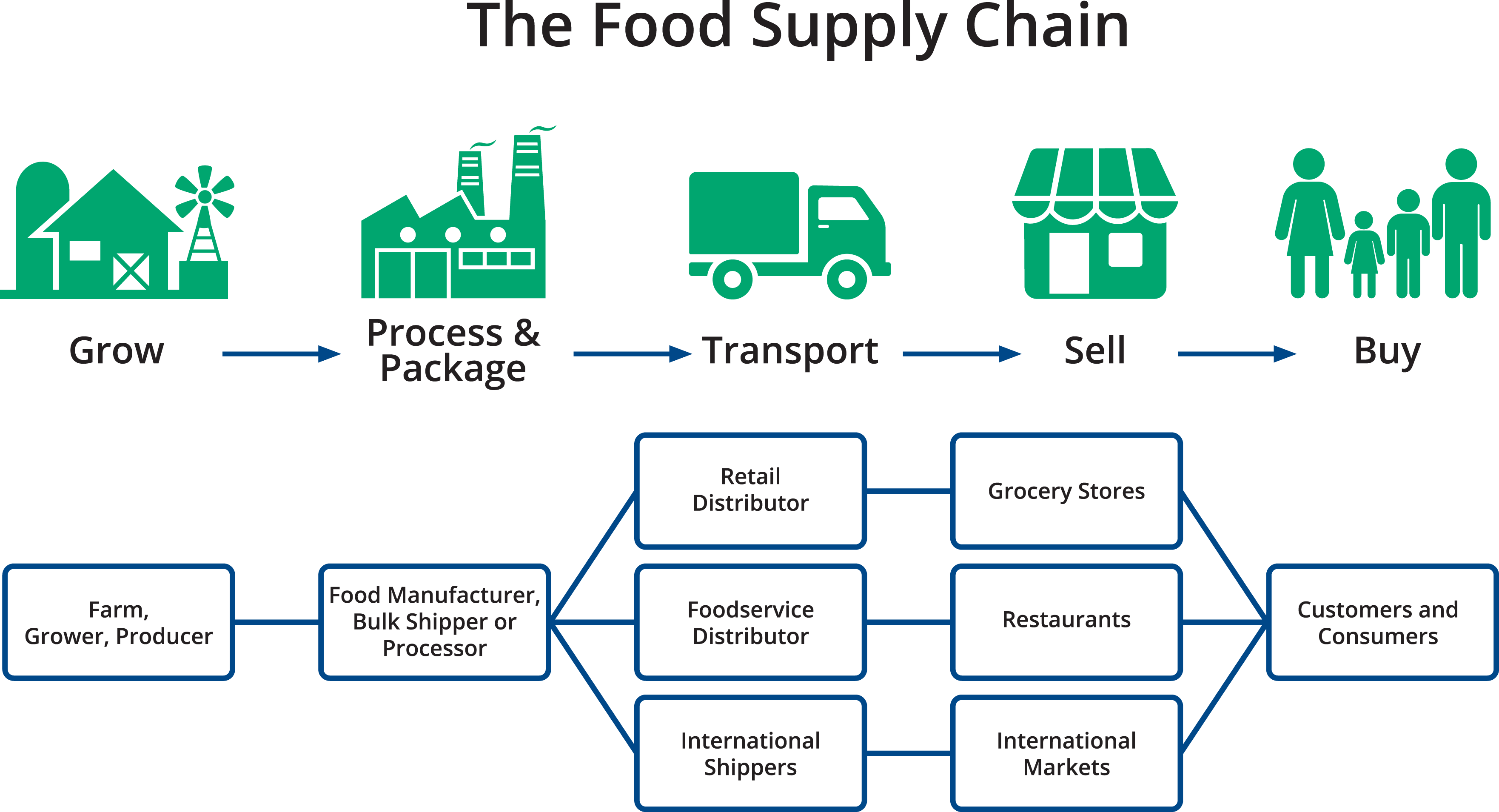
Tracing the Agricultural Supply Chain
Explore the complexity of global commodity chains that link the production and consumption of agricultural products. Discover how economics, politics, infrastructure, and other conditions affect the distribution of food throughout the world.

Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Andrea Gardner | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Acknowledgements
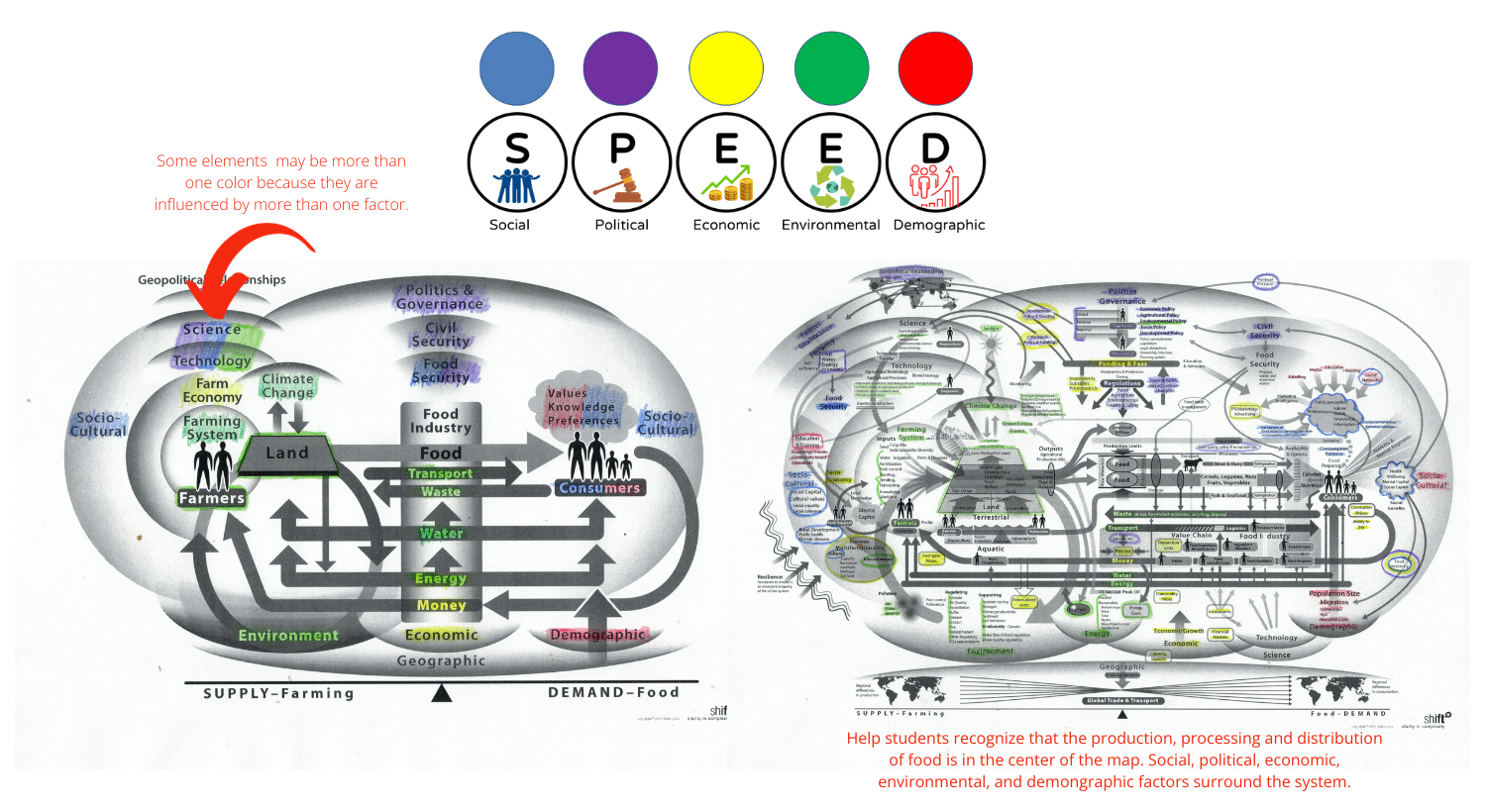
The Food System Maps used in Activity 2 were created by Rene Michalak and Brenda Schroeder. The images are courtesy of ShiftN.
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.A: identify career development, education, and entrepreneurship opportunities in the field of agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.3
The student analyzes concepts related to global diversity. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.3.B: evaluate marketing factors and practices that impact the global markets.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.A: define the scope of agriculture.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.C: evaluate significant historical and current agriculture, food, and natural resources developments.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.E: describe how emerging technologies and globalization impacts agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.F: compare and contrast issues impacting agriculture, food, and natural resources such as biotechnology, employment, safety, environment, and animal welfare issues.
- Principles, of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.D: identify potential future scenarios for agriculture, food, and natural resources systems, including global impacts.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13
The student describes the principles of food products and processing systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.A: evaluate food products and processing systems.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.B: determine trends in world food production.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.C: discuss current issues in food production.
-
Agribusiness Management and Marketing: 130.4.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Agribusiness Management and Marketing: 130.4.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, and systems of operation in agribusiness systems.
-
Agribusiness Management and Marketing: 130.4.c.3
The student recognizes roles within teams, work units, departments, organizations, inter-organizational systems, and the larger environment. The student is expected to:
- Agribusiness Management and Marketing: 130.4.c.3.A: identify how key organizational systems affect organizational performance and the quality of products and services related to agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Agribusiness Management and Marketing: 130.4.c.3.B: demonstrate an understanding of the global context of agricultural industries and careers.
-
World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.22
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.22.C: use social studies terminology correctly
-
Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and Its Benefits: 113.31.d.22
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and Its Benefits: 113.31.d.22.A: use social studies terminology correctly
-
English I: 110.36.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English I: 110.36.c.1.A: engage in meaningful and respectful discourse by listening actively, responding appropriately, and adjusting communication to audiences and purposes;
- English I: 110.36.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, building on the ideas of others, contributing relevant information, developing a plan for consensus building, and setting ground rules for decision making
-
English I: 110.36.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English I: 110.36.c.5.B: write responses that demonstrate understanding of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres
- English I: 110.36.c.5.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
English II: 110.37.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundation language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English II: 110.37.c.1.A: engage in meaningful and respectful discourse when evaluating the clarity and coherence of a speaker's message and critiquing the impact of a speaker's use of diction and syntax
- English II: 110.37.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, building on the ideas of others, contributing relevant information, developing a plan for consensus building, and setting ground rules for decision making
-
English III: 110.38.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English III: 110.38.c.1.A: engage in meaningful and respectful discourse when evaluating the clarity and coherence of a speaker's message and critiquing the impact of a speaker's use of diction and syntax
- English III: 110.38.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, offering ideas or judgments that are purposeful in moving the team toward goals, asking relevant and insightful questions, tolerating a range of positions and ambiguity in decision making, and evaluating the work of the group based on agreed-upon criteria
-
English III: 110.38.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English III: 110.38.c.5.B: write responses that demonstrate analysis of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres
- English III: 110.38.c.5.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
English II: 110.37.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English II: 110.37.c.5.B: write responses that demonstrate understanding of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres
- English II: 110.37.c.5.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
English IV: 110.39.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English IV: 110.39.c.1.A: engage in meaningful and respectful discourse when evaluating the clarity and coherence of a speaker's message and critiquing the impact of a speaker's use of diction, syntax, and rhetorical strategies
- English IV: 110.39.c.1.D: participate collaboratively, offering ideas or judgments that are purposeful in moving the team toward goals, asking relevant and insightful questions, tolerating a range of positions and ambiguity in decision making, and evaluating the work of the group based on agreed-upon criteria
-
English IV: 110.39.c.5
Response skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student responds to an increasingly challenging variety of sources that are read, heard, or viewed.
- English IV: 110.39.c.5.B: write responses that demonstrate analysis of texts, including comparing texts within and across genres
- English IV: 110.39.c.5.E: interact with sources in meaningful ways such as notetaking, annotating, freewriting, or illustrating
-
Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, and systems of operation in food processing.
-
Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.3
The student explains the impact of food science systems. The student is expected to:
- Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.3.A: explain the significance of food science systems.
- Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.3.B: define trends in food production, world population, and supply and demand for food products.
-
Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.7
The student demonstrates an understanding of the trends and issues important to careers in the food science industry by comparing and contrasting issues affecting the food science industry, including biotechnology, employment, safety, environmental, and animal welfare issues. The student is expected to:
- Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.7.B: identify issues affecting food science.
- Food Technology and Safety: 130.15.c.7.E: apply economic principles such as supply, demand, and profit to food science systems.
-
Food Processing: 130.16.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Food Processing: 130.16.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, and systems of operation in the food processing industry, including the value-added products industry.
-
Food Processing: 130.16.c.3
The student knows the relationship of the food processing industry to the free enterprise system. The student is expected to:
- Food Processing: 130.16.c.3.A: explain the importance of the food processing industry in the free enterprise system.
- Food Processing: 130.16.c.3.B: explain trends in the consumption of food products.
-
United States History Studies Since 1877: 113.41.d.26
Science, technology, and society. The student understands the impact of science, technology, and the free enterprise system on the economic development of the United States. The student is expected to:
- United States History Studies Since 1877: 113.41.d.26.C: describe the effect of technological innovations in the workplace such as assembly line manufacturing and robotics
-
United States History Studies Since 1877: 113.41.d.29
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- United States History Studies Since 1877: 113.41.d.29.B: use social studies terminology correctly
-
World History Studies: 113.42.d.27
Science, technology, and society. The student understands how major scientific and mathematical discoveries and technological innovations have affected societies from 1750 to the present. The student is expected to:
- World History Studies: 113.42.d.27.D: explain the role of telecommunication technology, computer technology, transportation technology, and medical advancements in developing the modern global economy and society
-
World History Studies: 113.42.d.30
Social studies skills. The student communicates in written, oral, and visual forms. The student is expected to:
- World History Studies: 113.42.d.30.A: use social studies terminology correctly
-
Environmental Systems: 112.50.c.12
Science concepts. The student understands how ethics and economic priorities influence environmental decisions. The student is expected to:
- Environmental Systems: 112.50.c.12.A: evaluate cost-benefit trade-offs of commercial activities such as municipal development, food production, deforestation, over-harvesting, mining, and use of renewable and non-renewable energy sources;
- Environmental Systems: 112.50.c.12.B: evaluate the economic impacts of individual actions on the environment such as overbuilding, habitat destruction, poaching, and improper waste disposal
- Environmental Systems: 112.50.c.12.C: analyze how ethical beliefs influence environmental scientific and engineering practices such as methods for food production, water distribution, energy production, and the extraction of minerals

.png)