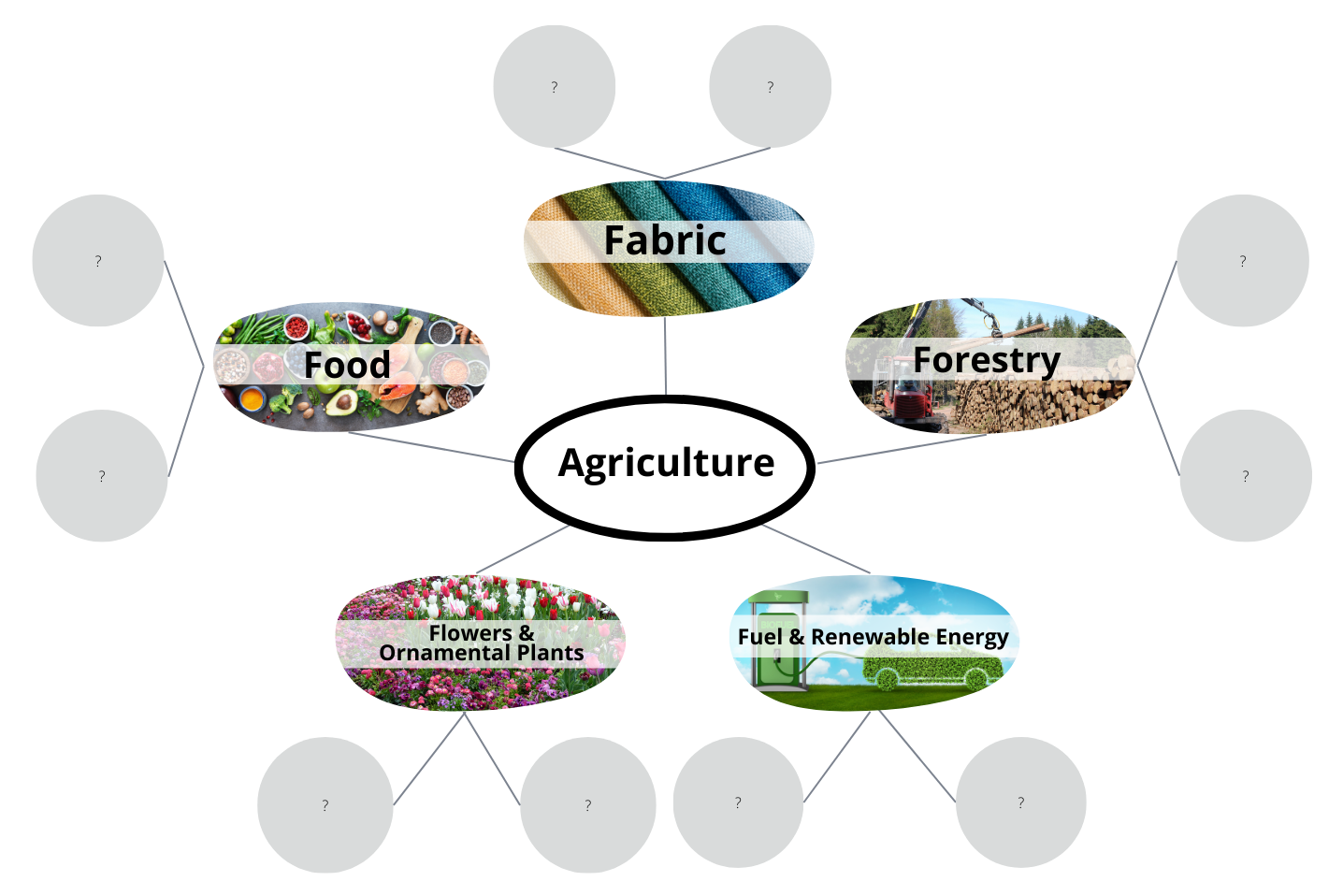
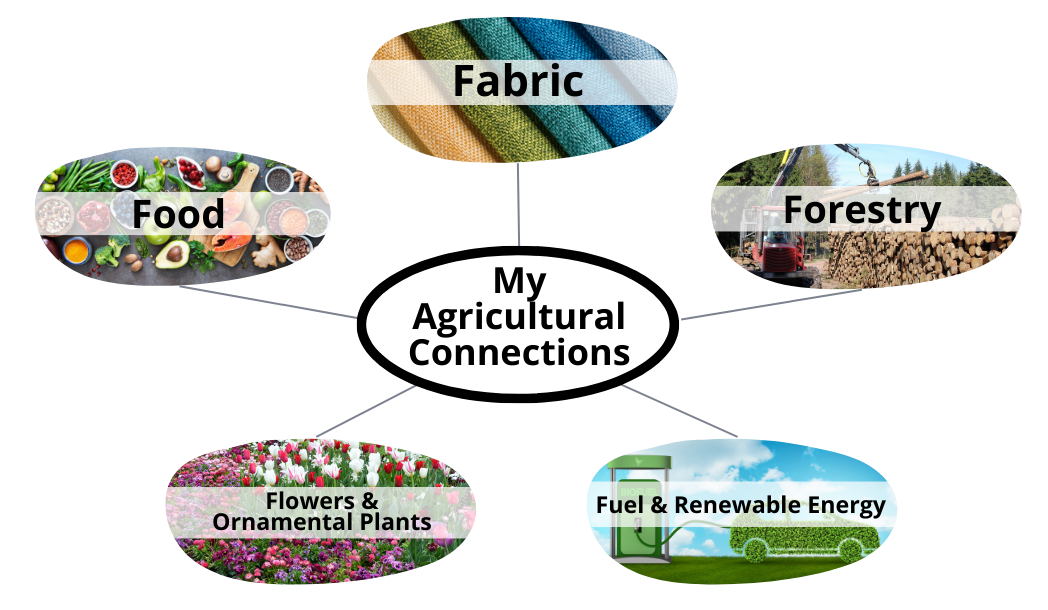
My Agricultural Connections (Grades 9-12)
Explore how we are each connected to agriculture through our food, clothing, shelter, fuel, and more. Students will be introduced to agriculture and begin to recognize the depth and complexities of agricultural systems locally and globally.
Background
Lesson Activities
Recommended Companion Resources
Credits
Author
Amelia Miller and Andrea Gardner | National Center for Agricultural Literacy (NCAL)
Sources
- https://www.northernag.net/how-much-popcorn-does-the-average-american-eat-each-year/
- https://msu.edu/~sindijul/Fruits%20and%20Vegetables/BANANAS.htm
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/to-your-health/wp/2015/01/20/we-eat-100-acres-of-pizza-a-day-in-the-u-s/?noredirect=on&utm_term=.7a6ae1e2d003
- https://columbustelegram.com/banner-press/news/fun-facts-about-the-food-we-eat/article_6cf8be89-0a8e-53f4-9a81-f9f2bfe1921b.html
Standards
Texas Content Area Standards
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1
The student demonstrates professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.B: apply competencies related to resources, information, interpersonal skills, problem solving, critical thinking, and systems of operation in agriculture, food, and natural resources.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.1.E: identify careers in agriculture, food, and natural resources with required aptitudes in science, technology, engineering, mathematics, language arts, and social studies.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4
The student explains the historical, current, and future significance of the agriculture, food, and natural resources industry. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.A: define the scope of agriculture.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.4.B: analyze the scope of agriculture, food, and natural resources and its effect upon society.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6
The student demonstrates appropriate personal and communication skills. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.A: demonstrate written and oral communication skills appropriate for formal and informal situations such as prepared and extemporaneous presentations.
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.6.B: demonstrate effective listening skills appropriate for formal and informal situations.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11
The student develops technical knowledge and skills related to plant systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.11.D: identify plants of importance to agriculture, food, and natural resources
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13
The student describes the principles of food products and processing systems. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.13.A: evaluate food products and processing systems.
-
Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.15
The student explains the relationship between agriculture, food, and natural resources and the environment. The student is expected to:
- Principles of Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resources: 130.2.c.15.D: research and analyze alternative energy sources that stem from or impact agriculture, food, and natural resources.
-
World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.12
Economics. The student understands the economic importance of, and issues related to, the location and management of resources. The student is expected to:
- World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.12.A: analyze how the creation, distribution, and management of key natural resources affects the location and patterns of movement of products, money, and people
-
World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.21
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- World Geography Studies: 113.43.d.21.F: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning for an intended audience and purpose
-
Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and Its Benefits: 113.31.d.21
Social studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- Economics with Emphasis on the Free Enterprise System and Its Benefits: 113.31.d.21.F: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning for an intended audience and purpose
-
English I: 110.36.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English I: 110.36.c.1.A: engage in meaningful and respectful discourse by listening actively, responding appropriately, and adjusting communication to audiences and purposes;
- English I: 110.36.c.1.B: follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems and complex processes;
-
English I: 110.36.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English I: 110.36.c.4.G: evaluate details read to determine key ideas
-
English II: 110.37.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English II: 110.37.c.4.G: evaluate details read to determine key ideas
-
English II: 110.37.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundation language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English II: 110.37.c.1.A: engage in meaningful and respectful discourse when evaluating the clarity and coherence of a speaker's message and critiquing the impact of a speaker's use of diction and syntax
- English II: 110.37.c.1.B: follow and give complex oral instructions to perform specific tasks, answer questions, or solve problems and complex processes
-
English III: 110.38.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English III: 110.38.c.1.B: follow and give complex instructions, clarify meaning by asking pertinent questions, and respond appropriately
-
English III: 110.38.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English III: 110.38.c.4.G: evaluate details read to understand key ideas
-
English IV: 110.39.c.1
Developing and sustaining foundational language skills: listening, speaking, discussion, and thinking--oral language. The student develops oral language through listening, speaking, and discussion.
- English IV: 110.39.c.1.B: follow and give complex instructions, clarify meaning by asking pertinent questions, and respond appropriately
-
English IV: 110.39.c.4
Comprehension skills: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts. The student uses metacognitive skills to both develop and deepen comprehension of increasingly complex texts.
- English IV: 110.39.c.4.G: evaluate details read to analyze key ideas
-
English I: 110.36.c.9
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and use appropriate conventions.
- English I: 110.36.c.9.B.i: develop drafts into a focused, structured, and coherent piece of writing in timed and open-ended situations by using an organizing structure appropriate to purpose, audience, topic, and context
-
English II: 110.37.c.9
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and use appropriate conventions.
- English II: 110.37.c.9.B.i: develop drafts into a focused, structured, and coherent piece of writing in timed and open-ended situations by using an organizing structure appropriate to purpose, audience, topic, and context
-
English III: 110.38.c.9
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and use appropriate conventions.
- English III: 110.38.c.9.B.i: develop drafts into a focused, structured, and coherent piece of writing in timed and open-ended situations by using strategic organizational structures appropriate to purpose, audience, topic, and context
-
English IV: 110.39.c.9
Composition: listening, speaking, reading, writing, and thinking using multiple texts--writing process. The student uses the writing process recursively to compose multiple texts that are legible and use appropriate conventions.
- English IV: 110.39.c.9.B.i: develop drafts into a focused, structured, and coherent piece of writing in timed and open-ended situations by using strategic organizational structures appropriate to purpose, audience, topic, and context
-
World History Studies: 113.42.d.28
Social studies skills. The student understands how historians use historiography to interpret the past and applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired from a variety of valid sources, including technology. The student is expected to:
- World History Studies: 113.42.d.28.F: formulate and communicate visually, orally, or in writing a claim supported by evidence and reasoning for an intended audience and purpose
-
Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.1
Scientific and engineering practices. The student, for at least 40% of instructional time, asks questions, identifies problems, and plans and safely conducts classroom, laboratory, and field investigations to explain phenomena or design solutions using appropriate tools and models. The student is expected to:
- Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.1.A: ask questions and define problems based on observations or information from text, phenomena, models, or investigations
- Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.1.E: collect quantitative data using the International System of Units (SI) and qualitative data as evidence
- Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.1.F: organize quantitative and qualitative data using scatter plots, line graphs, bar graphs, charts, data tables, digital tools, diagrams, scientific drawings, and student-prepared models
-
Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.12
Science concepts. The student understands how Earth's systems affect and are affected by human activities, including resource use and management. The student is expected to:
- Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.12.A: evaluate the impact on humans of natural changes in Earth's systems such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions
- Earth Systems Science: 112.49.c.12.C: analyze the natural and anthropogenic factors that affect the severity and frequency of extreme weather events and the hazards associated with these events